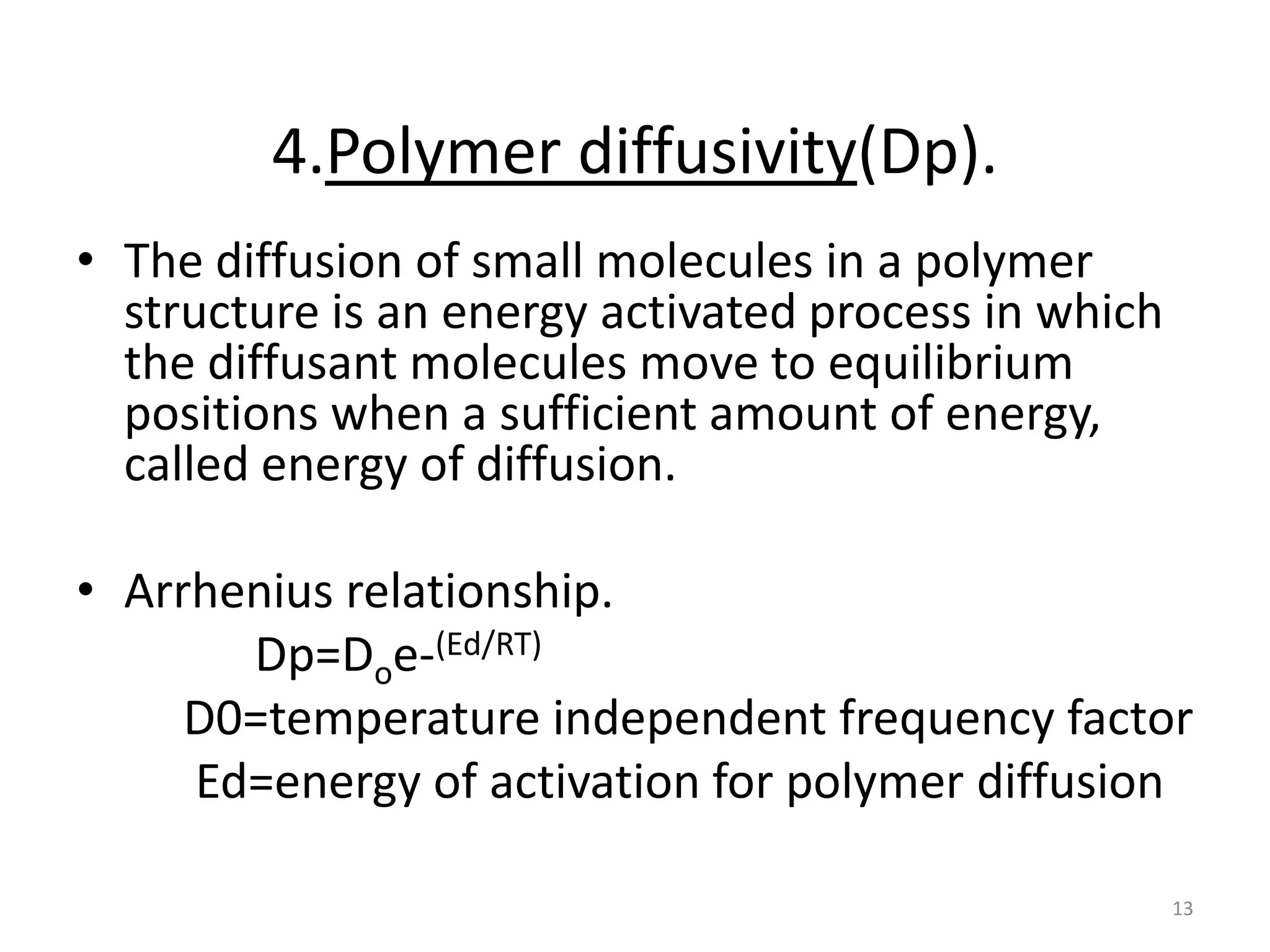
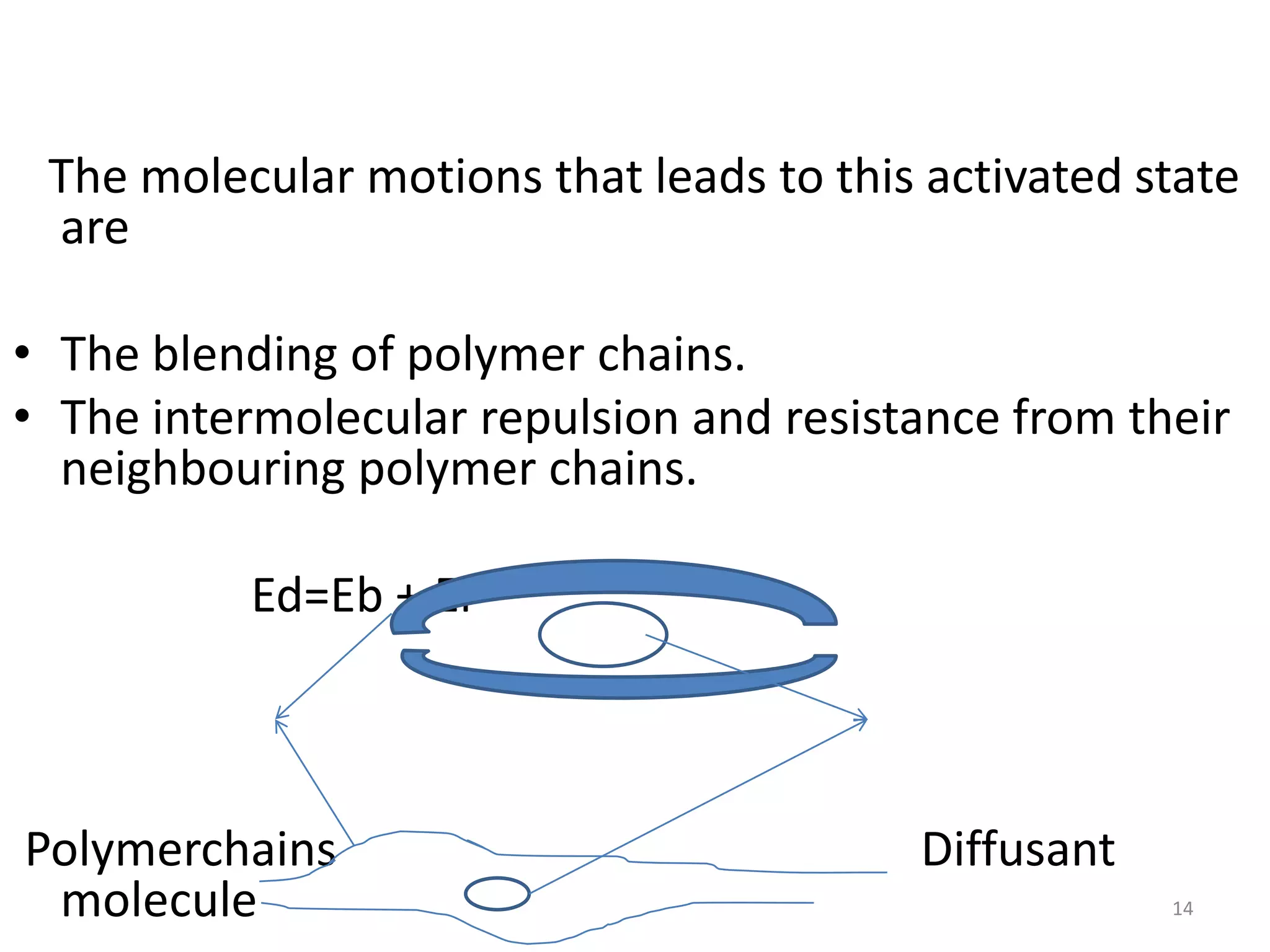
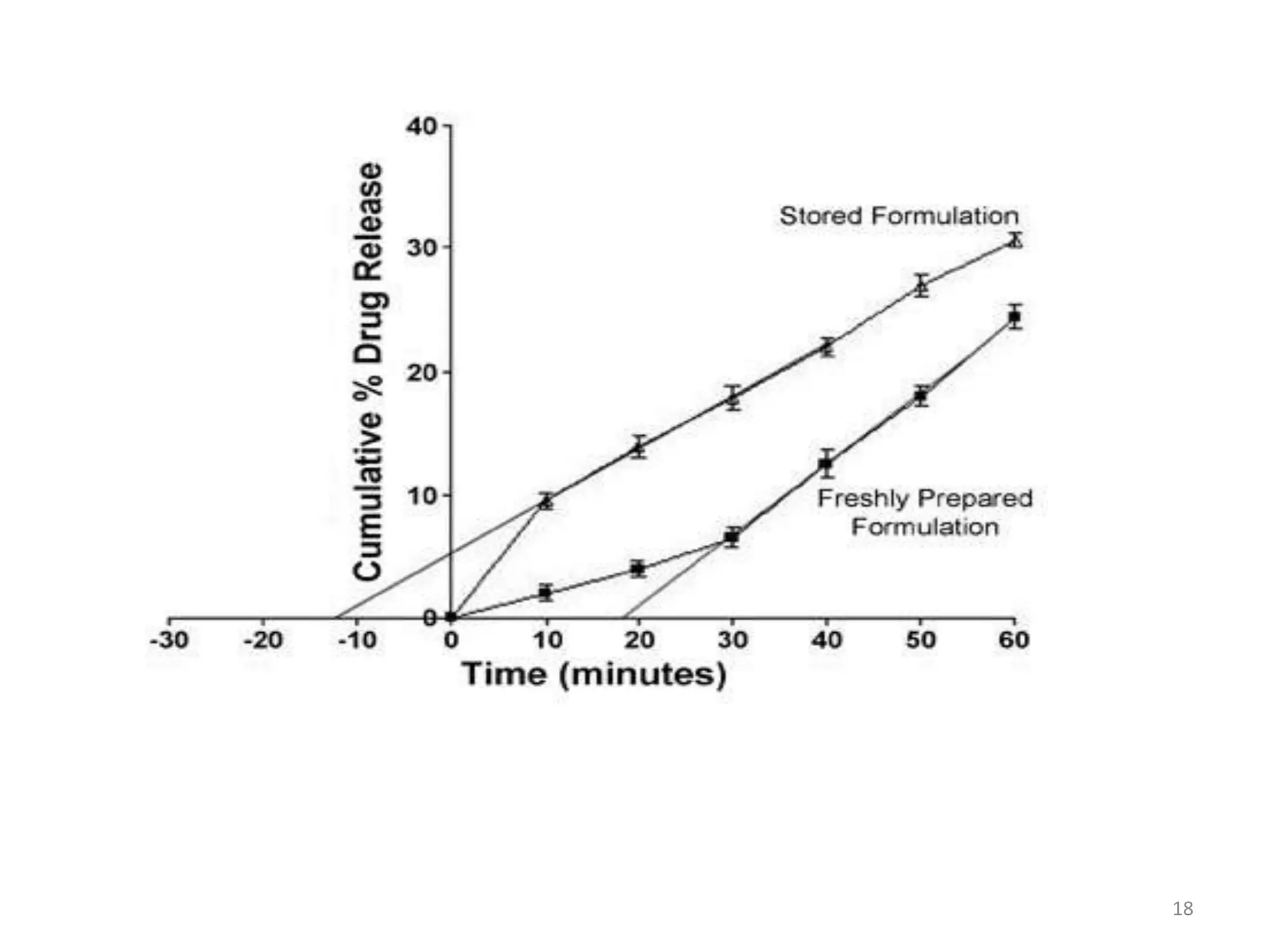
1. The key system parameters that affect controlled drug delivery include polymer solubility, solution solubility, partition coefficient, polymer diffusivity, thickness of diffusion layers, and drug loading dose.
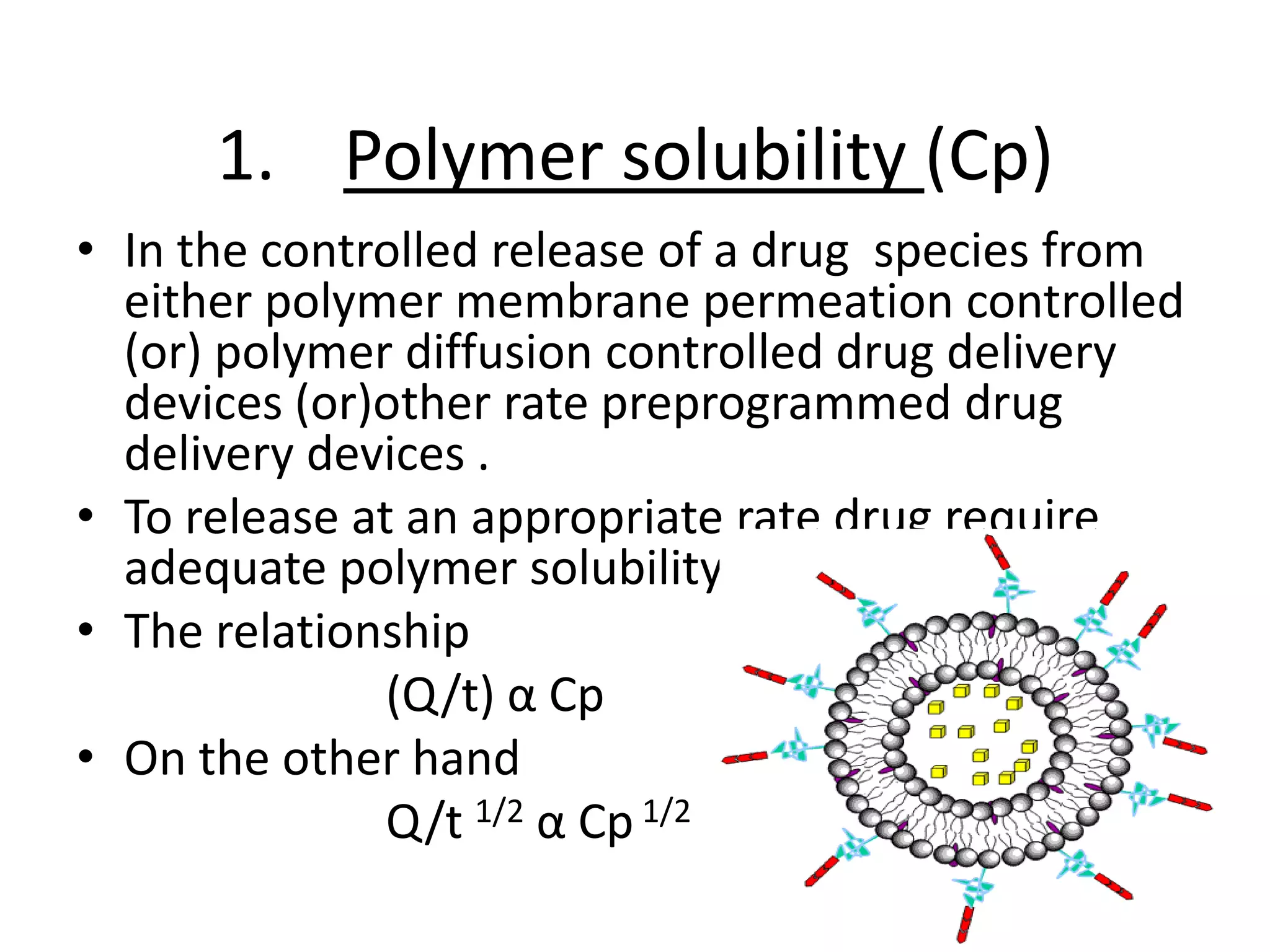
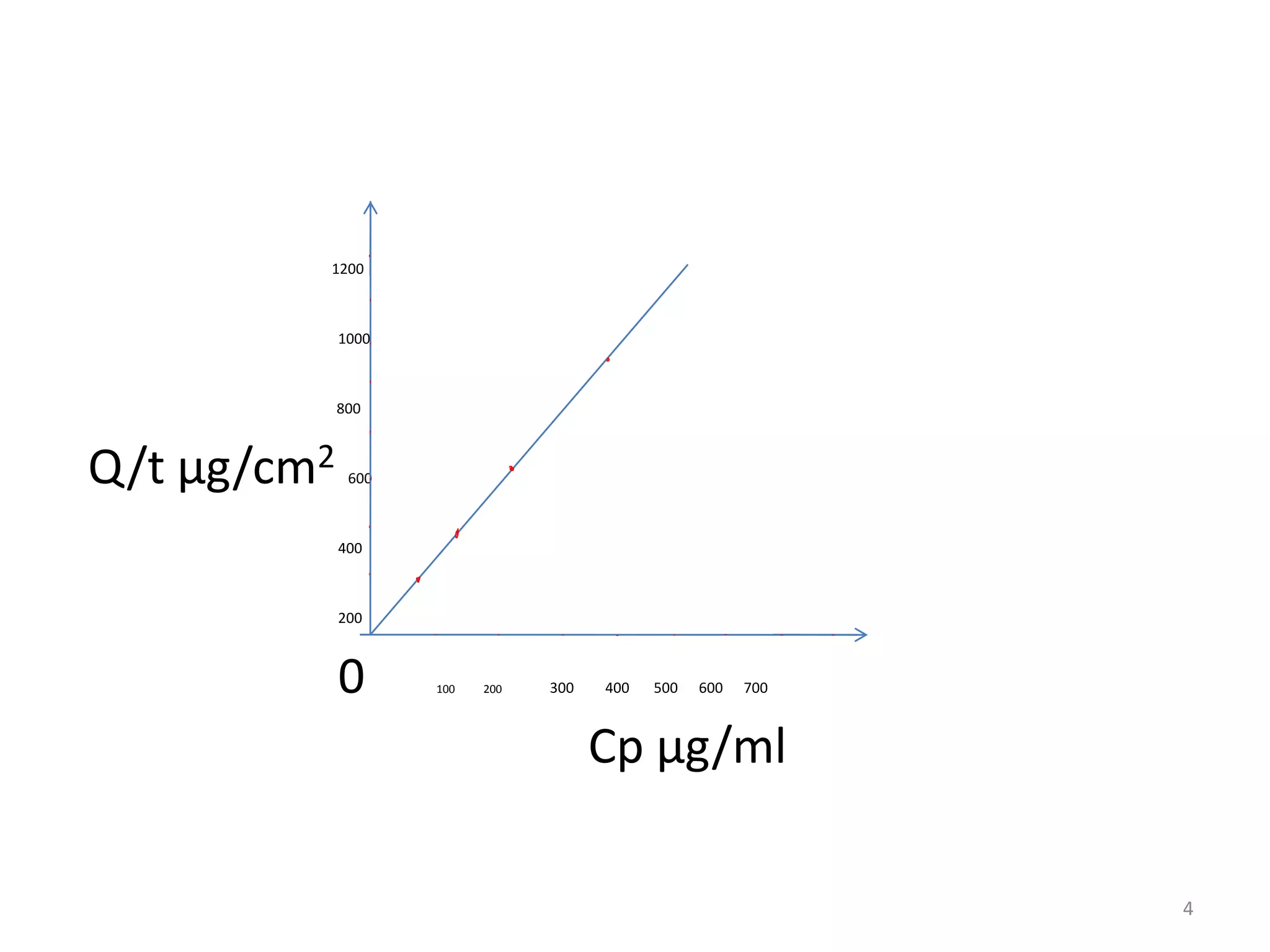
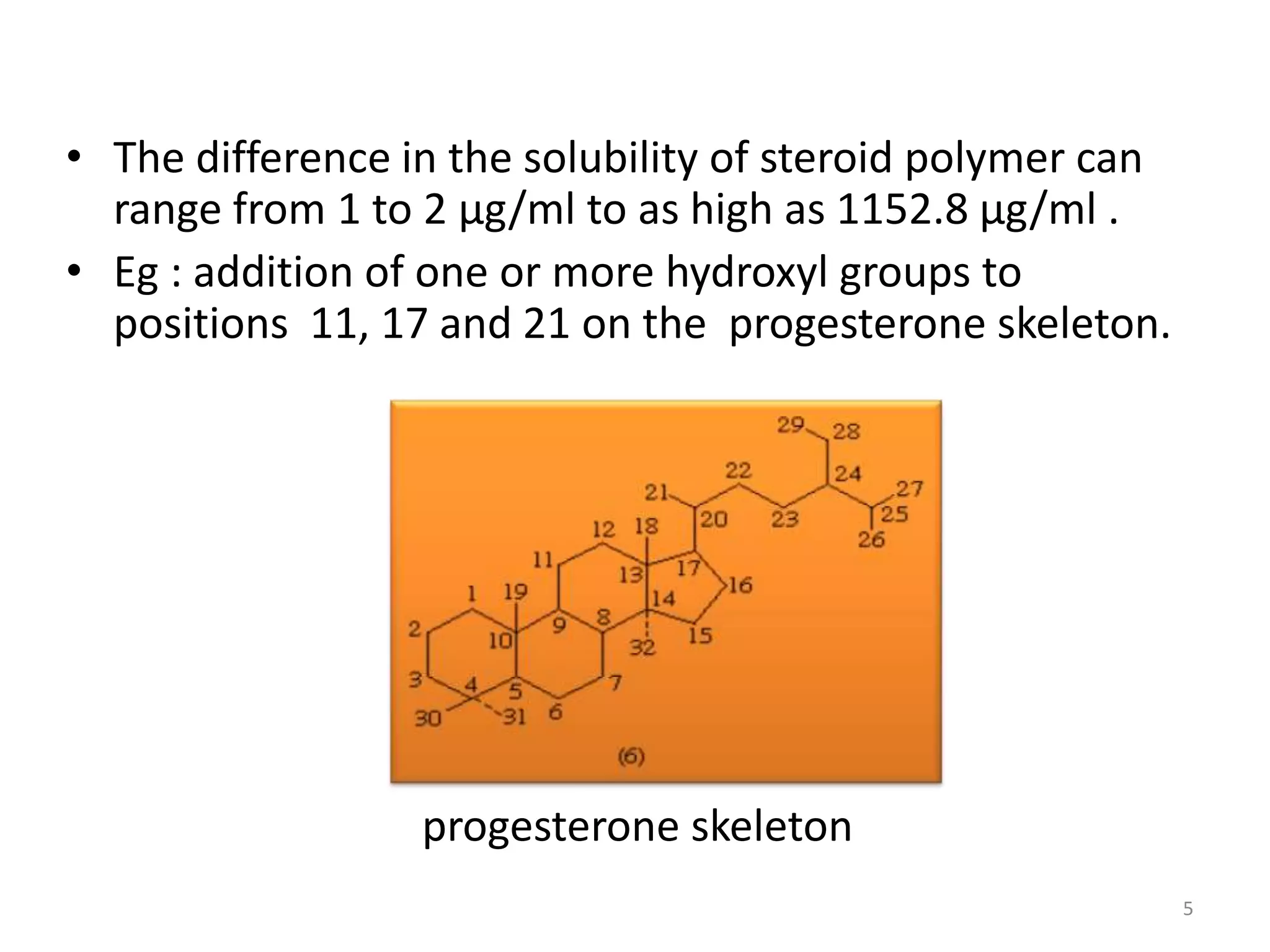
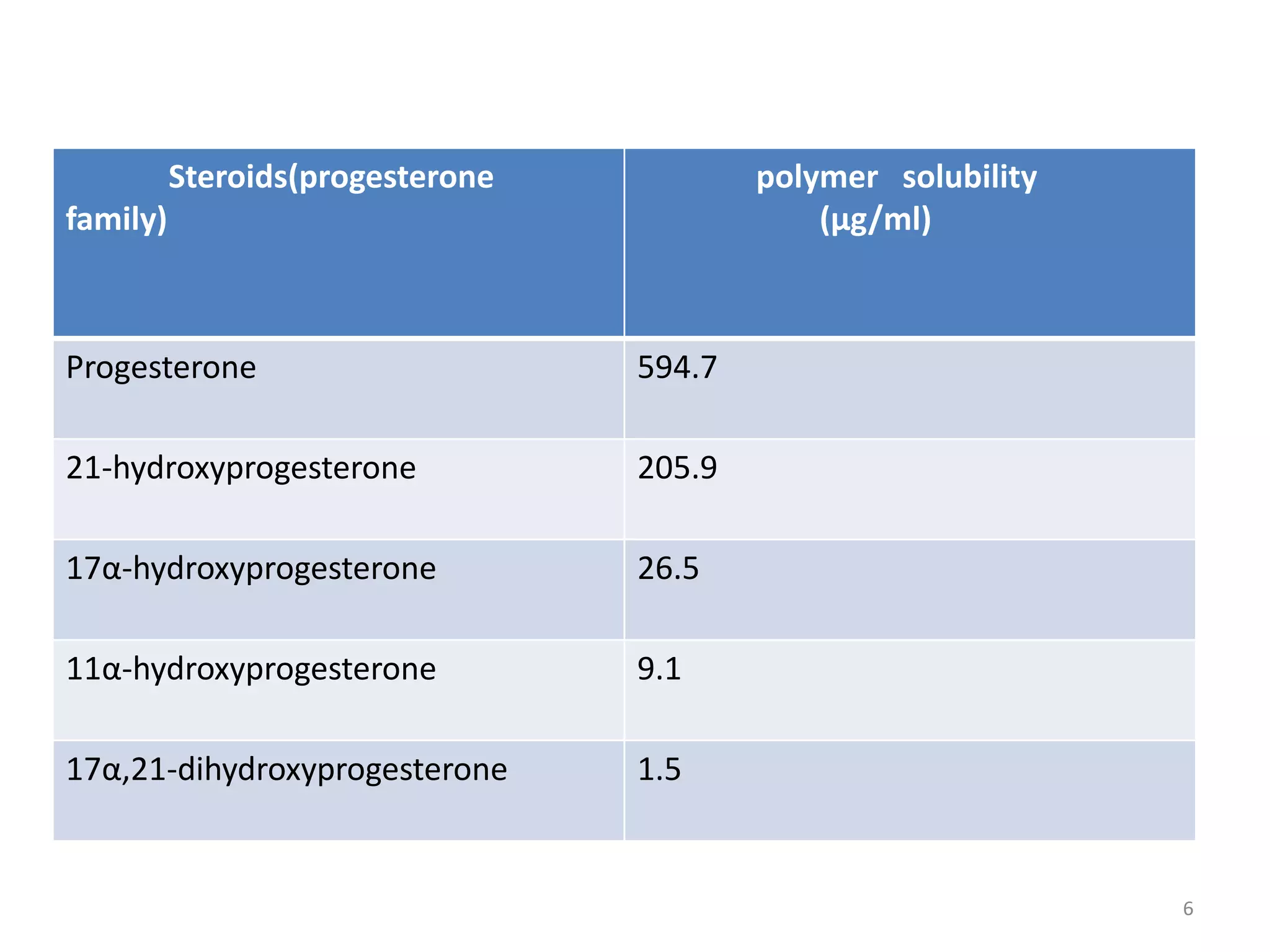
2. Higher polymer solubility generally leads to a higher drug release rate, while maintaining an appropriate sink condition by ensuring the solution concentration is much higher than the bulk concentration is important.
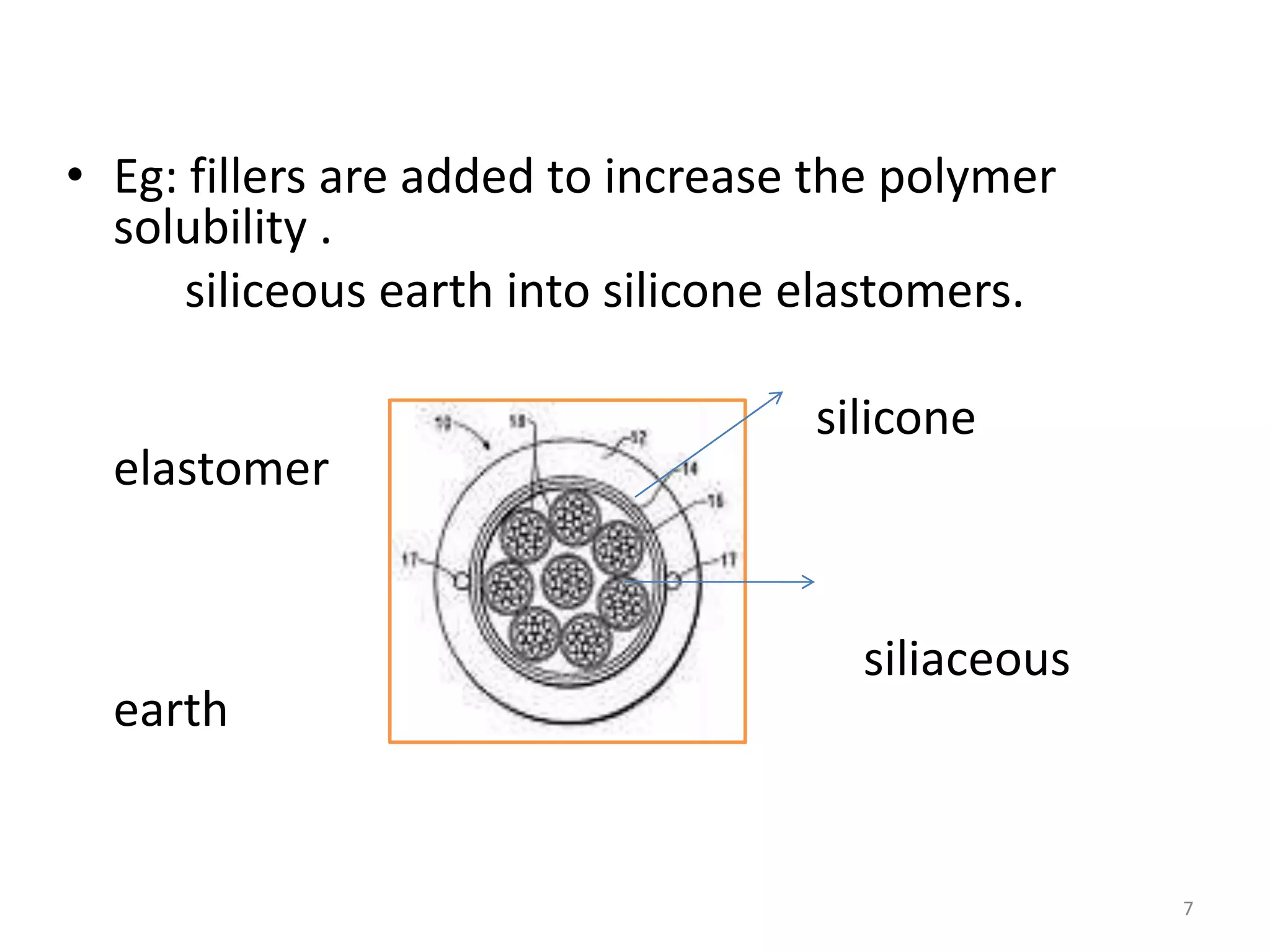
3. Parameters like polymer crystallinity, cross-linking, and filler content can impact the polymer diffusivity, with higher crystallinity, cross-linking, or filler content typically lowering the diffusivity.