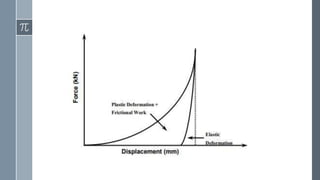
Compaction profiles are hysteresis curves that illustrate the relationship between axial and radial pressures during the compaction cycle of powders, including phases of compression, elastic deformation, and decompression. They are analyzed using compaction simulators to assess compression behavior, determine force and displacement characteristics, and understand die wall friction. Applications of compaction profiles include monitoring compaction cycles, assessing powder elasticity, and calculating ejection force requirements.


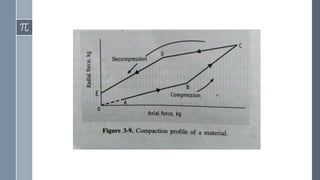



![(a). Compression phase [horizontal and vertical punch movement]
(b). Dwell time [plane punch head area is under compression roller]
(c). Decompression phase [both punches move away from upper & lower
surfaces]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/compactionprofiles-181111104544/85/Compaction-profiles-7-320.jpg)