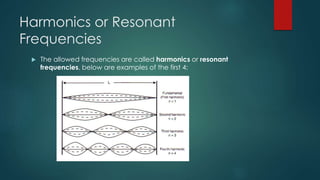
This document discusses standing waves on strings. It explains that when a string with fixed ends is plucked, waves travel back and forth along the string creating standing waves. The allowed wavelengths are λ=2L/m, where L is the string length and m is a positive integer. These standing waves are called the normal modes of vibration, and their frequencies are given by fm=mf1, where f1 is the fundamental frequency. The document provides an example problem involving calculating the wave speed, number of reflections, wavelengths, frequencies, and node spacing for the first two normal modes of a plucked guitar string.