EE Study Notes provides information on various electrical engineering concepts:
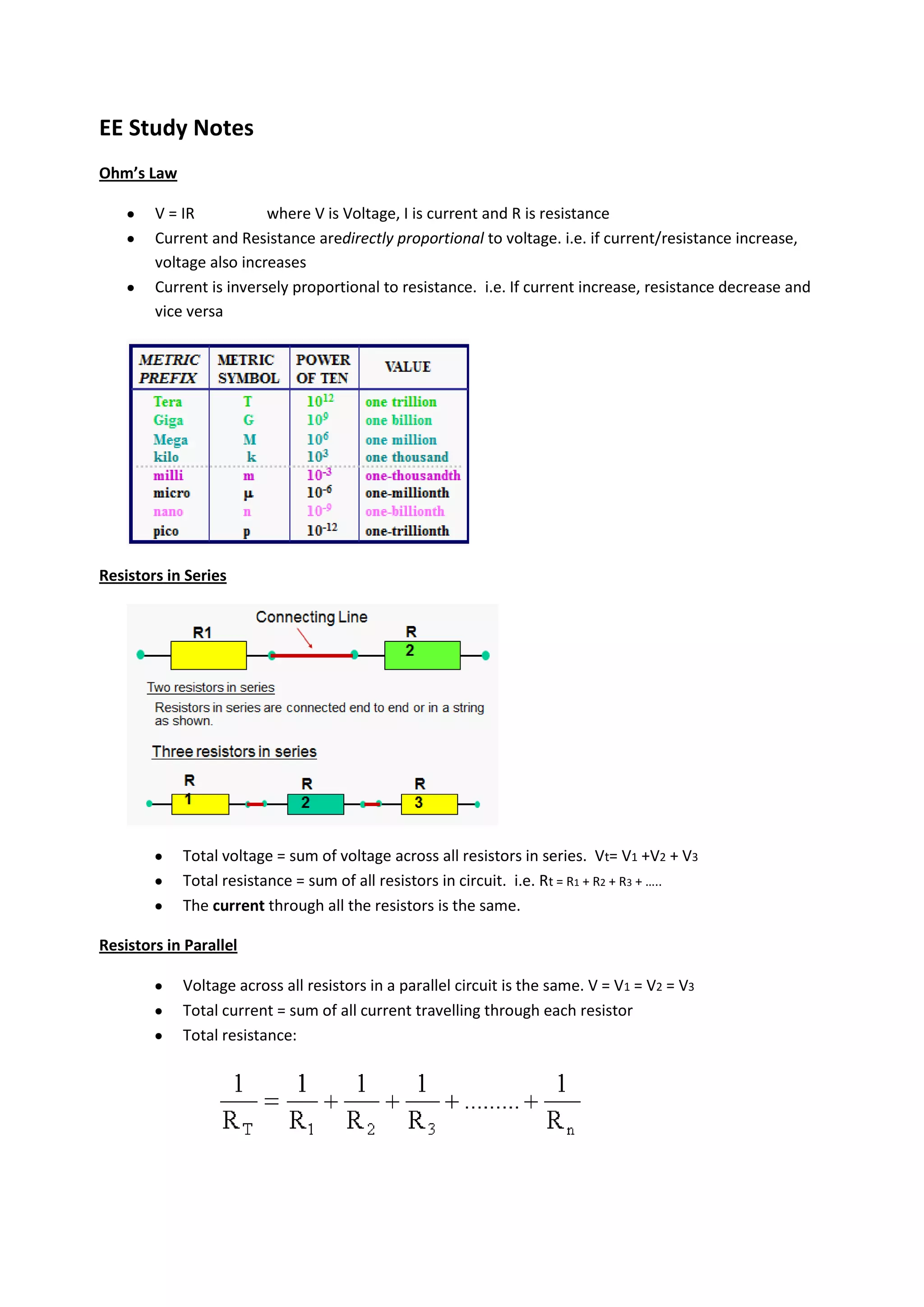
1. Ohm's Law defines the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit. Resistors in series have a total voltage equal to the sum of individual voltages and a single current. Resistors in parallel have the same voltage but total current equals the sum of individual currents.
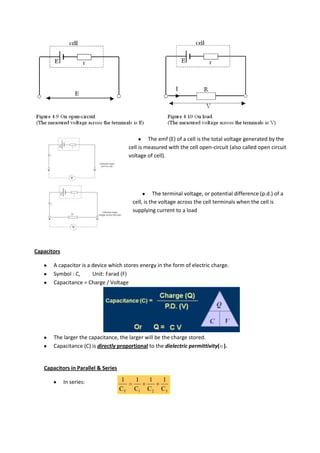
2. Capacitors store energy in the form of electric charge, with capacitance determining how much charge is stored for a given voltage. Capacitors combine in series and parallel like resistors.
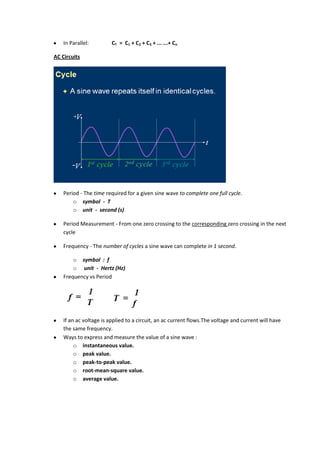
3. AC circuits have voltage and current that vary sinusoidally over time. Phase relationships describe whether voltage and current are in phase, or if