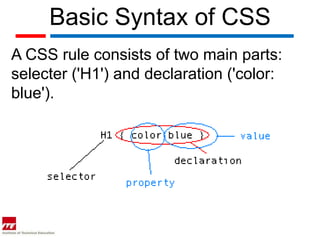
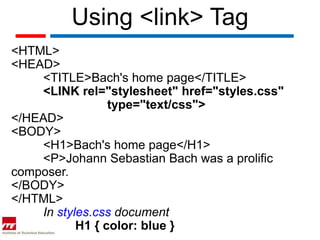
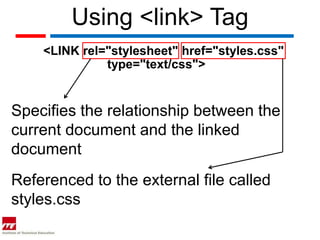
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) allow complete control over webpage layout and content appearance. CSS rules specify selectors and declarations to format HTML elements, and can be applied to entire sites from a single external style sheet. CSS optimizes websites for different devices, speeds up loading, and reduces file sizes. CSS rules contain selectors, declarations with properties and values, and follow a specific syntax.