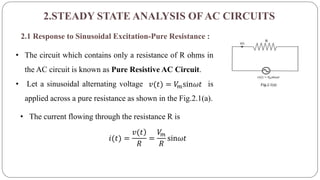
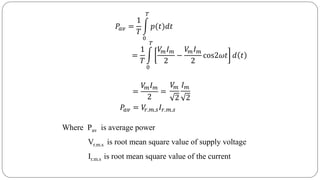
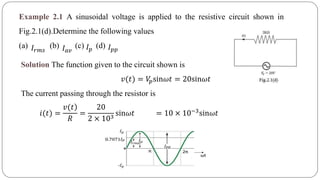
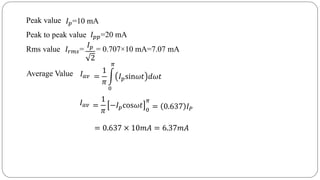
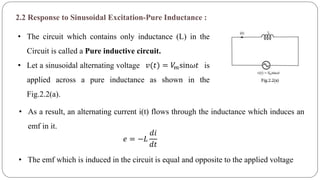
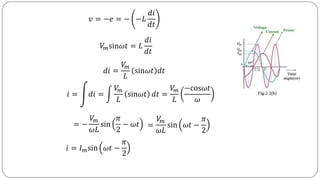
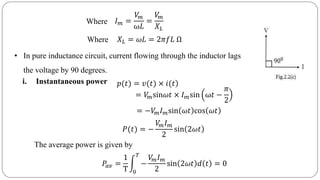
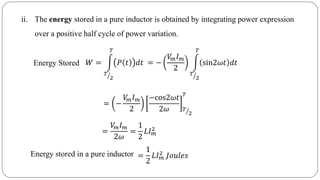
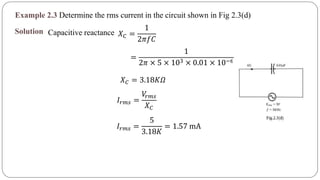
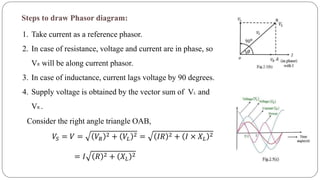
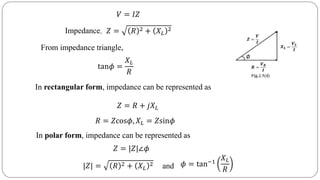
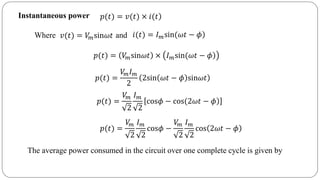
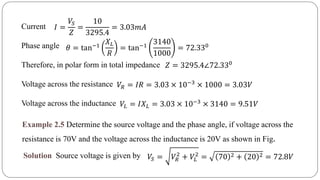
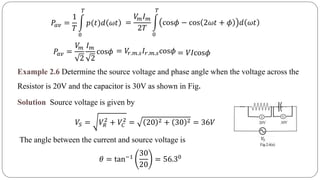
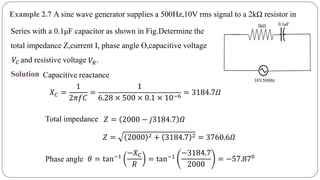
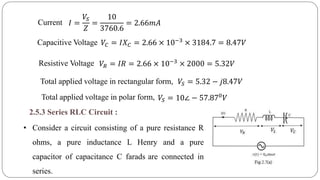
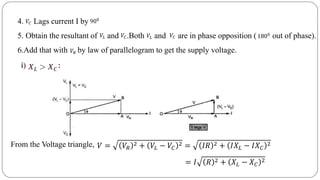
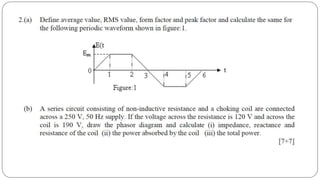
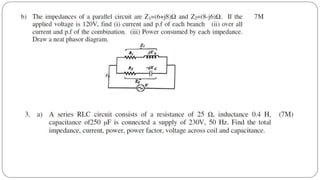
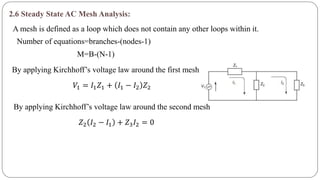
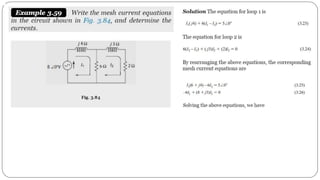
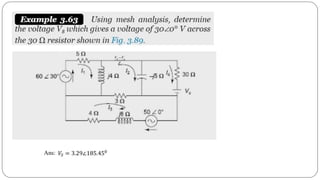
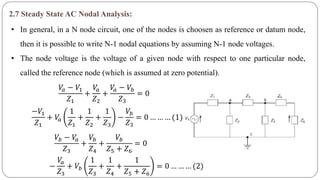
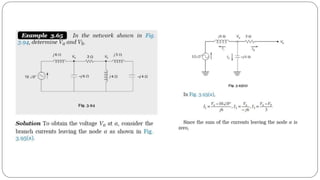
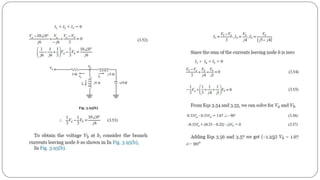
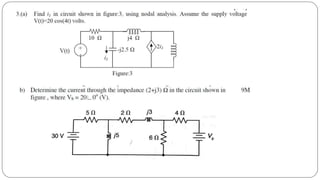
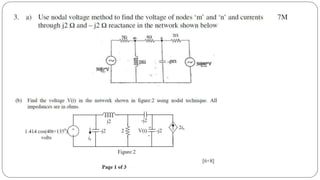
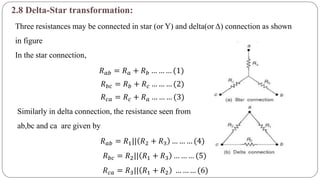
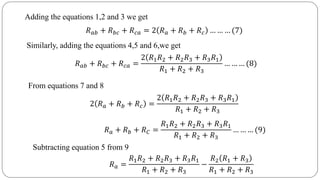
The document discusses steady state analysis of AC circuits. It covers the response of pure resistance, inductance and capacitance circuits to sinusoidal excitation. The key points are:
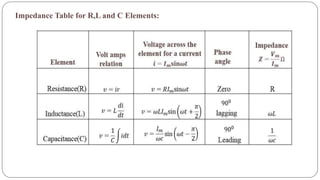
- In a pure resistance circuit, current and voltage are in phase. In pure inductance, current lags voltage by 90 degrees. In pure capacitance, current leads voltage by 90 degrees.
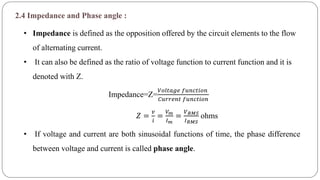
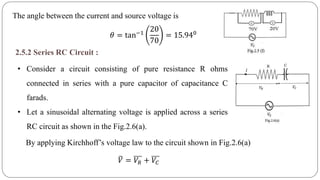
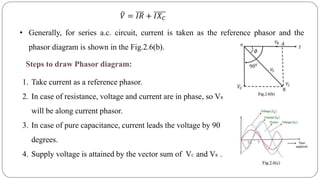
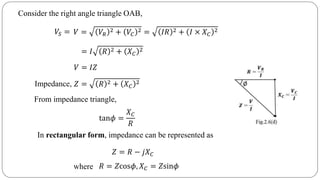
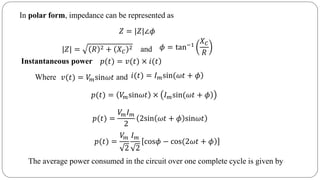
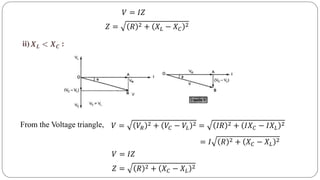
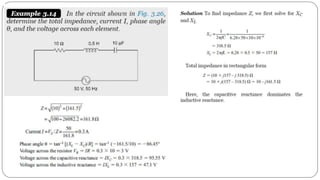
- Impedance is defined as the ratio of voltage to current. It has both magnitude and phase angle. Impedance of series R, L, and C circuits can be calculated using phasor diagrams.
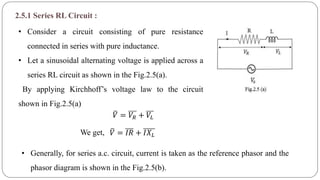
- For series RL circuits, the total impedance is the square root of the sum of the squares of resistance and reactance.