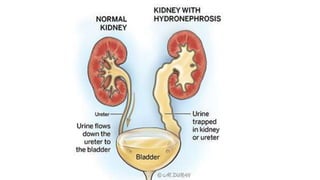
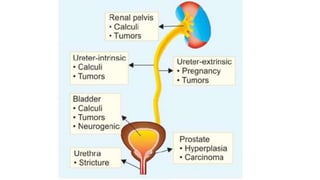
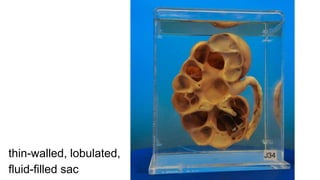
Hydronephrosis is defined as the aseptic dilation of the kidney's collecting system due to urinary outflow obstruction, which can lead to kidney atrophy and hydroureter. Causes include structural issues like urinary calculi, tumors, benign prostatic hyperplasia, and congenital abnormalities, as well as neurogenic factors. Treatment varies based on the underlying cause and severity, with potential complications including urinary tract infections and pyelonephritis.