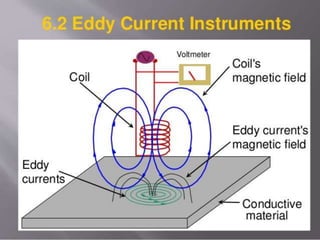
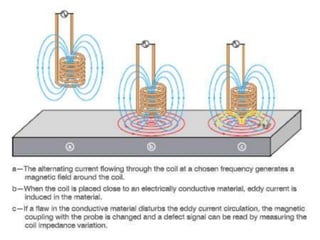
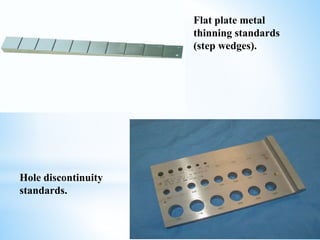
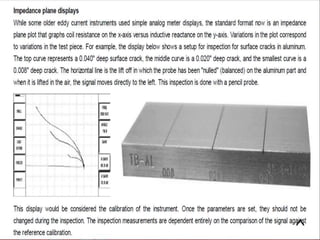
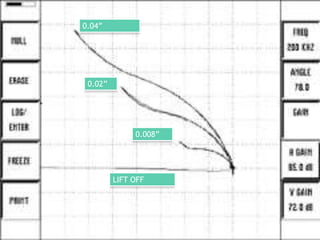
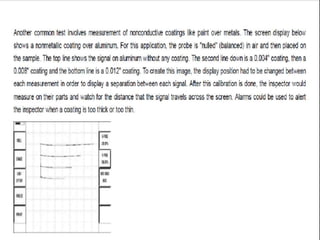
This document provides an overview of eddy current testing. It discusses the history of eddy current theory dating back to Faraday's discovery of electromagnetic induction in 1832. It defines eddy currents as oscillating electrical currents induced in a conductive material by an alternating magnetic field. The document describes the equipment used for eddy current testing, including portable flaw detectors, probes, and reference samples of known materials and defects used for calibration. It explains that calibration is important to ensure consistent, accurate, and reliable readings from eddy current instruments.