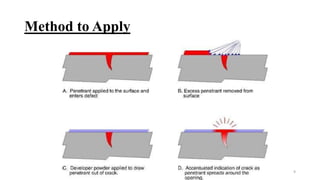
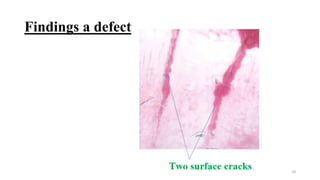
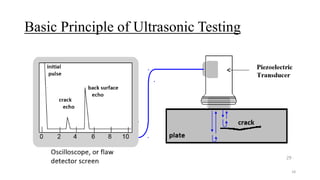
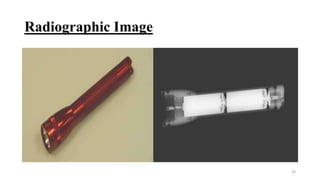
Non-destructive testing (NDT) allows inspection of materials without damaging them. Common NDT methods include visual testing, dye penetrant testing, magnetic particle testing, ultrasonic testing, eddy current testing, and radiography testing. Each method has advantages and limitations for detecting different types of surface or internal flaws in various materials. NDT increases safety and quality while reducing costs compared to destructive testing.