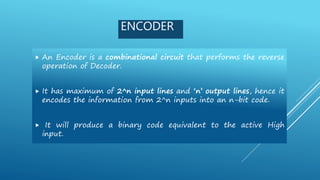
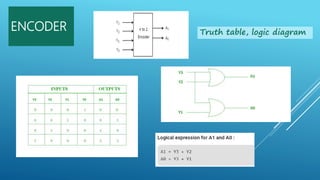
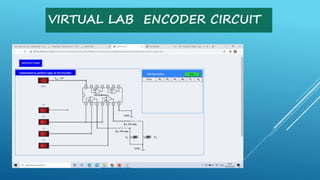
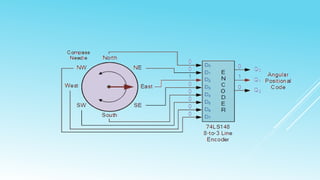
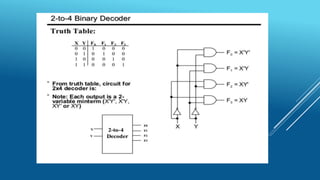
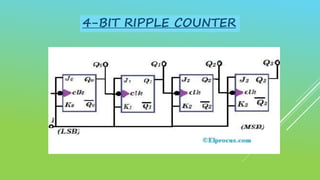
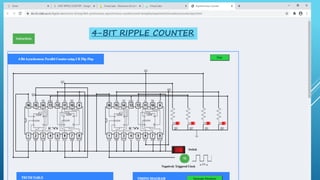
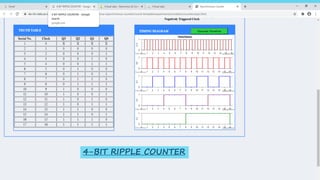
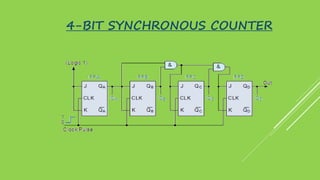
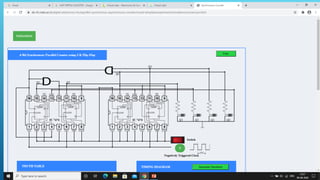
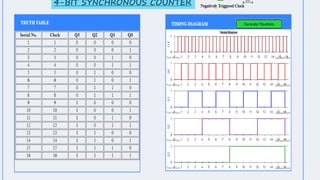
This document summarizes several digital circuit experiments to be conducted in a digital circuits lab session. It includes experiments on code converters, binary addition/subtraction, multiplexers, encoders, decoders, and various counter circuits. Encoders and decoders are explained in more detail. Encoders translate information from multiple inputs into a binary code on fewer outputs, while decoders perform the reverse operation. Both are used for applications involving motion monitoring and control by translating between rotary/linear positions and digital signals. The lab session will provide hands-on experience designing and building these basic digital components and circuits.