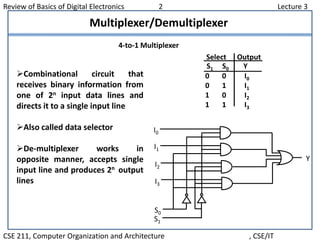
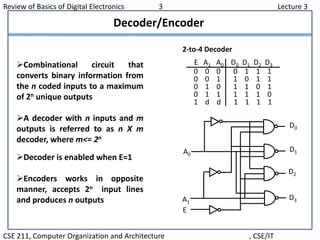
This document summarizes key concepts from Lecture 3 of a digital electronics course, including logic gates, flip flops, registers, counters, multiplexers, demultiplexers, decoders, and encoders. It provides examples and explanations of 4-to-1 multiplexers and 2-to-4 decoders. It also describes octal to binary encoders and how decoders can be expanded.