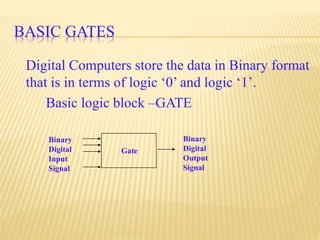
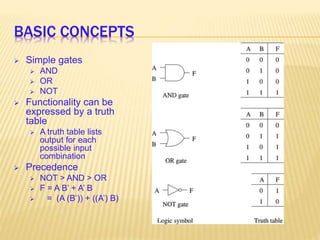
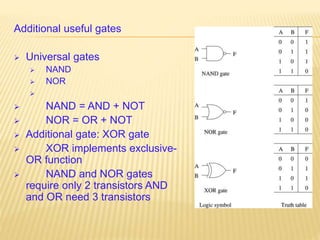
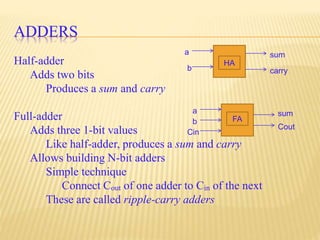
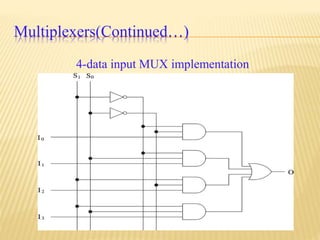
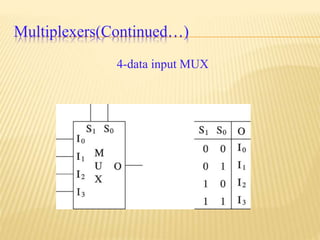
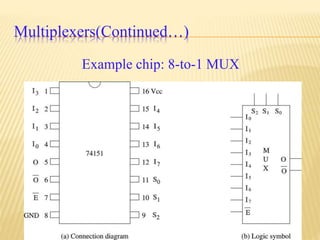
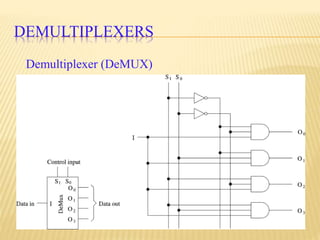
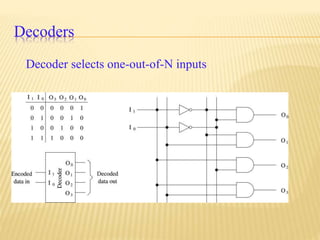
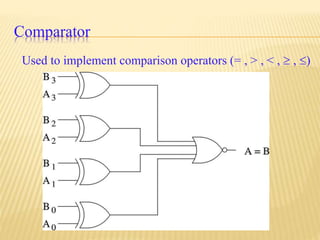
This document provides an overview of digital electronics and basic digital logic gates. It discusses how digital computers store data in binary format using logic 0 and 1. There are two main types of logic blocks: combinational logic blocks whose output depends only on the current inputs, and sequential logic blocks whose output depends on the current inputs and previous state. Common basic logic gates like AND, OR, and NOT are described along with more useful gates like NAND and NOR. Combinational circuits like half adders, full adders, multiplexers, decoders, and comparators are explained at a high level.