1) Earthquakes are caused by vibrations induced in the earth's crust due to internal or external forces that shake parts of the crust and structures on it.
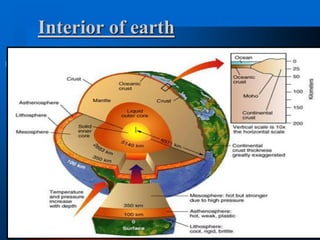
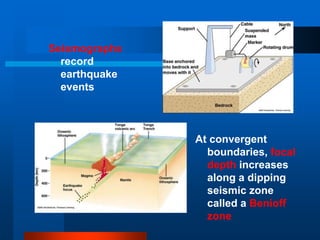
2) Seismographs are instruments used to measure earthquake vibrations and locate the focus or epicenter. The focus is the point where faulting begins inside the earth, and the epicenter is the point directly above the focus on the surface.
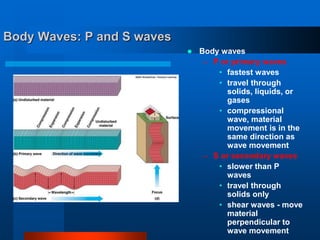
3) There are two main types of seismic waves produced by earthquakes: body waves that travel through the earth's interior, and surface waves that travel along the surface.