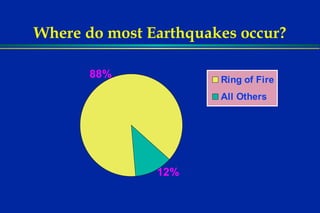
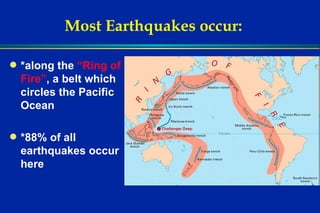
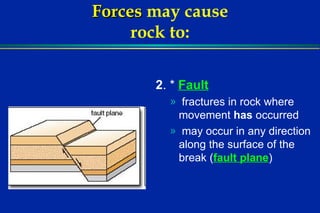
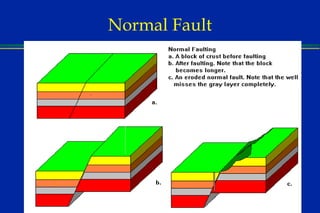
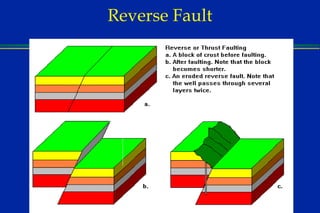
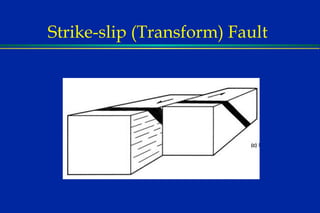
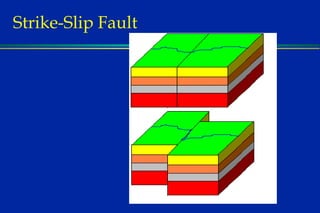
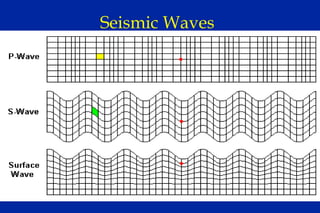
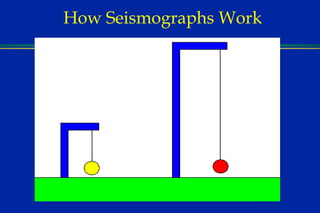
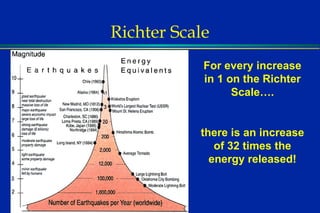
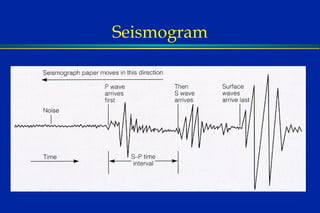
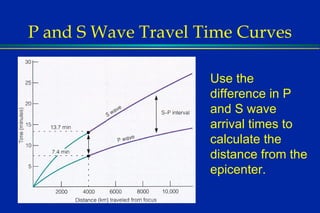
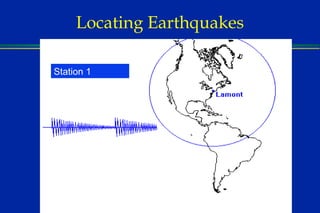
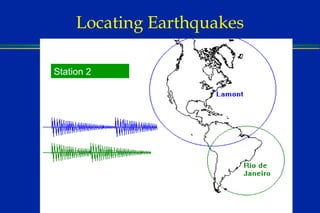
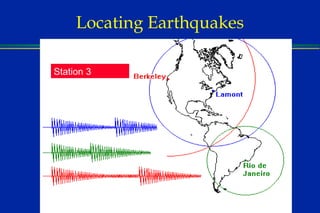
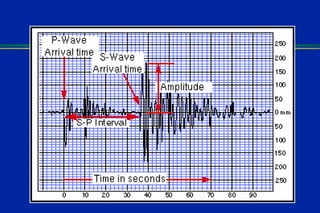
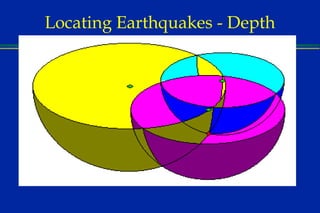
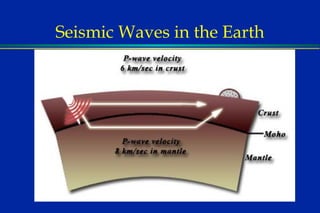
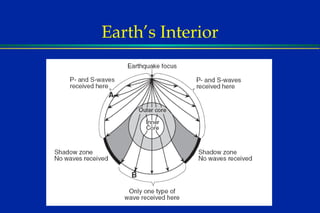
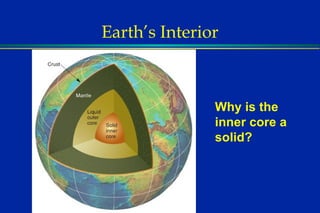
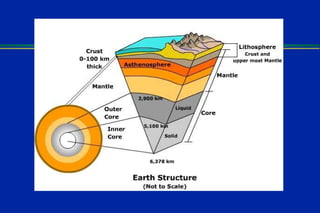
Earthquakes are caused by sudden movements within Earth's crust that cause rocks to bend, break or fracture. Most earthquakes occur along the Ring of Fire, a belt circling the Pacific Ocean where 88% of all quakes take place, and also along other belts where tectonic plates meet. Forces like tension, compression and shearing cause three types of rock fractures - normal faults where the rock moves apart, reverse faults where it moves together, and strike-slip faults where it slides horizontally past another part of the crust.