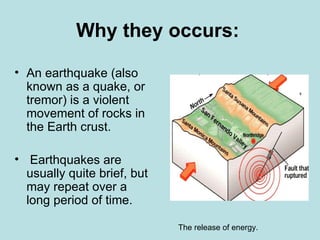
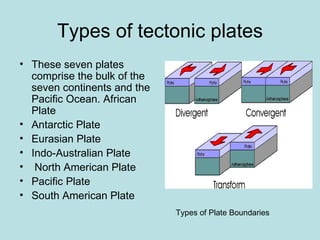
Earthquakes are caused by the release of energy in the Earth's crust due to movements of tectonic plates. The main types of fault that cause earthquakes are normal, reverse thrust, and strike-slip. Earthquakes produce seismic waves that damage buildings and infrastructure, endangering human life. They can also trigger tsunamis, which are large ocean waves that inundate coastal areas. Scientists are still working on predicting earthquakes, but earthquake-proofing of buildings has helped reduce risks in places like Japan and California that experience frequent seismic activity.