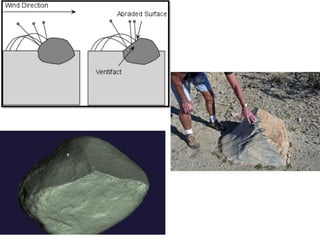
Wind is a major geological agent that causes erosion, transportation, and deposition. The three types of erosive work by wind are deflation, abrasion, and attrition. Deflation involves the removal of sand and dust particles, creating depressions called oases or desert pavement surfaces called hammadas. Abrasion occurs when wind carries sand and dust, grinding and polishing rock surfaces to form landforms like yardangs, pedestal rocks, and ventifacts. Transportation by wind moves loose materials through suspension, saltation, or rolling. Depositional features formed by wind include migrating dunes and loess deposits of wind-blown silt. Engineering in dune and loess areas requires stabilizing structures and treating