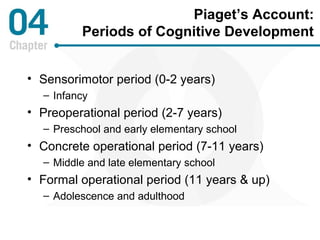
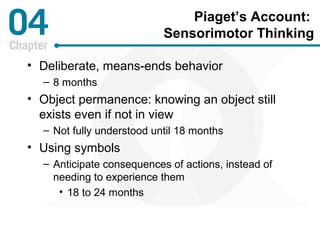
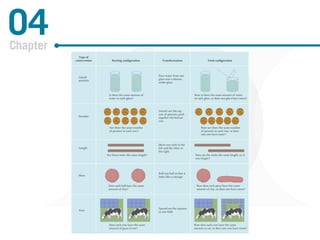
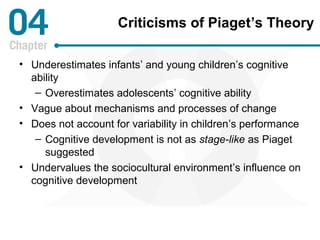
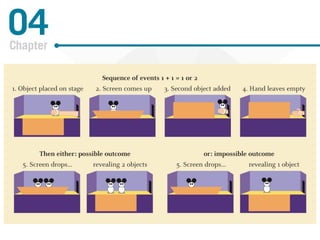
Piaget's theory of cognitive development posits that children progress through distinct stages as they develop more advanced cognitive abilities. According to Piaget, infants progress from sensorimotor thinking to preoperational thinking as they develop object permanence and the ability to use symbols. Children then progress to concrete operational thinking where they can conserve and understand perspectives other than their own. The information processing approach views cognitive development through a computer model of mental hardware and software that allows for attention, learning, memory, and number skills to develop from infancy through early childhood. Vygotsky emphasized the role of social interaction and the zone of proximal development in cognitive development. Language develops rapidly as children gain the insight that words are symbols and use fast mapping