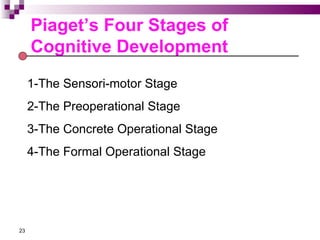
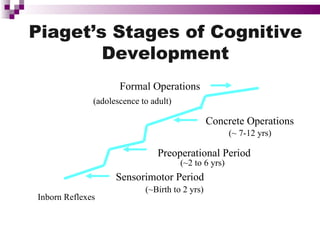
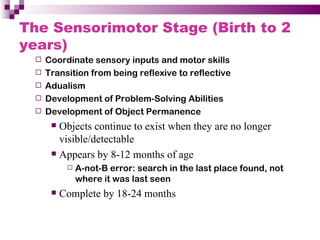
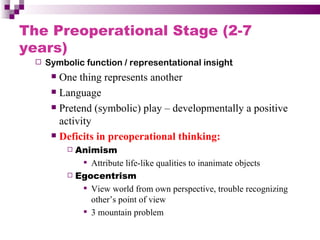
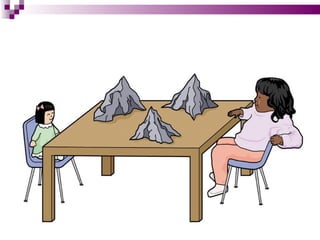
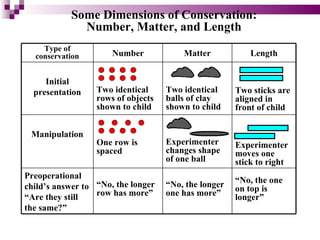
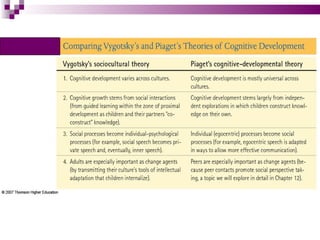
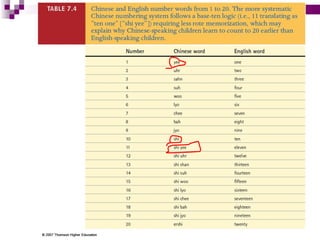
Child development occurs through physical, cognitive, and social/emotional domains. There are several theories that describe child development, including psychoanalytic theories like Freud's psychosexual stages and Erikson's psychosocial stages. Behavioral theories like Watson's classical conditioning and Skinner's operant conditioning emphasize the environment's role. Piaget's stages of cognitive development describe how children construct understanding. Kohlberg outlined stages of moral development from obedience to internalized principles. Overall, development involves biological and environmental influences in a progressive, stage-like process.