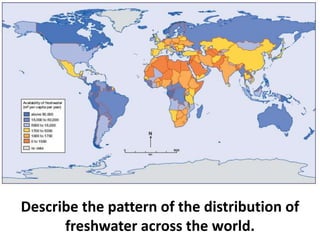
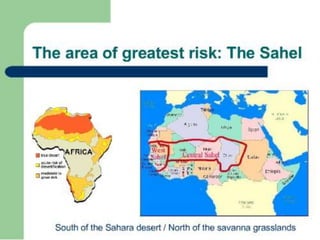
Droughts occur when there is not enough rainfall to support people or crops and can have severe consequences. Drought is caused by both natural factors like changes in weather patterns as well as human factors such as deforestation, overpopulation, and overextraction of water. The vast majority of deaths from drought have occurred in three countries: Ethiopia, Sudan, and Mozambique. Case studies of drought in Ethiopia and Australia show how drought can impact populations through famine, disease, loss of livestock, and economic hardship. Responses to drought involve aid efforts, management of water resources, and strategies to prevent desertification.




















![Exam Qs
• Describe & explain the causes of drought.
[4marks]
• What are the patterns associated with
droughts? [2marks]
• With reference to a case study, describe the
effects of and responses to drought. [6marks]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/droughtslideshare-110524093848-phpapp01/85/Drought-23-320.jpg)