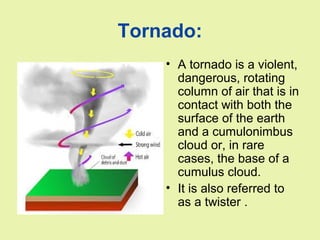
This document discusses different types of natural disasters. It categorizes natural disasters into geological, hydrological, meteorological, wildfires, health, and space disasters. For each category, it provides examples and descriptions of specific disaster types. Geological disasters include avalanches, landslides, earthquakes, sinkholes, and volcanic eruptions. Hydrological disasters include floods, limnic eruptions, and tsunamis. Meteorological disasters include blizzards, cyclonic storms, droughts, thunderstorms, hailstorms, heat waves, and tornadoes. Health disasters refer to epidemics and pandemics. Space disasters include airbursts and solar flares. In summary, the document provides a