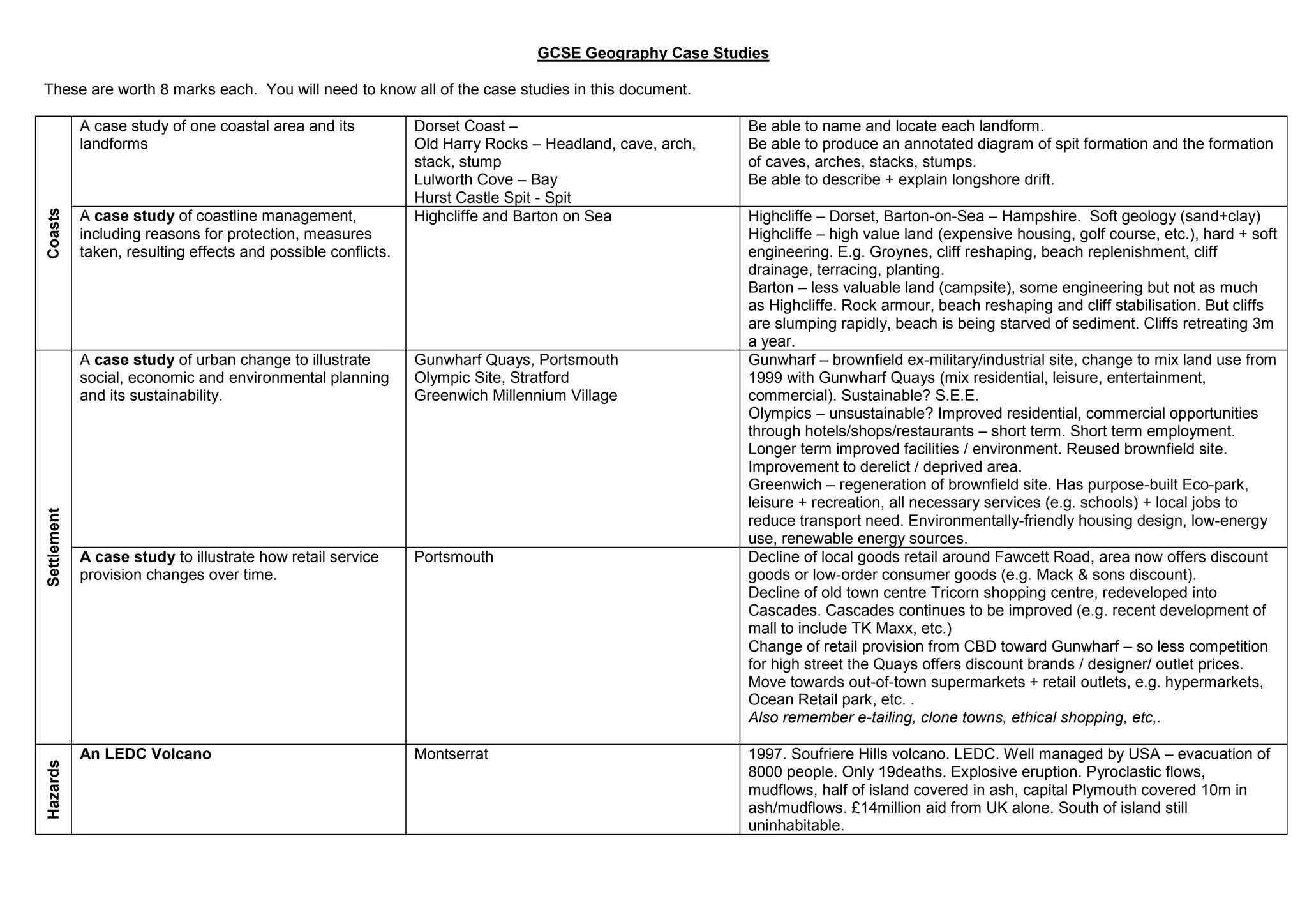
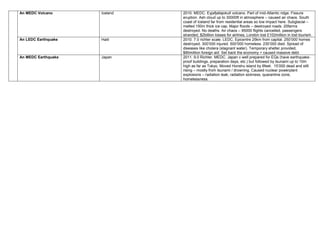
This document provides case studies on various topics in GCSE Geography including coastal landforms in Dorset, coastline management techniques in Hampshire, urban change examples in Portsmouth and London, retail changes over time in Portsmouth, and natural hazards including volcanic eruptions and earthquakes in locations around the world. Specific landforms, management strategies, urban development projects, and hazard events are described along with their impacts and management approaches.