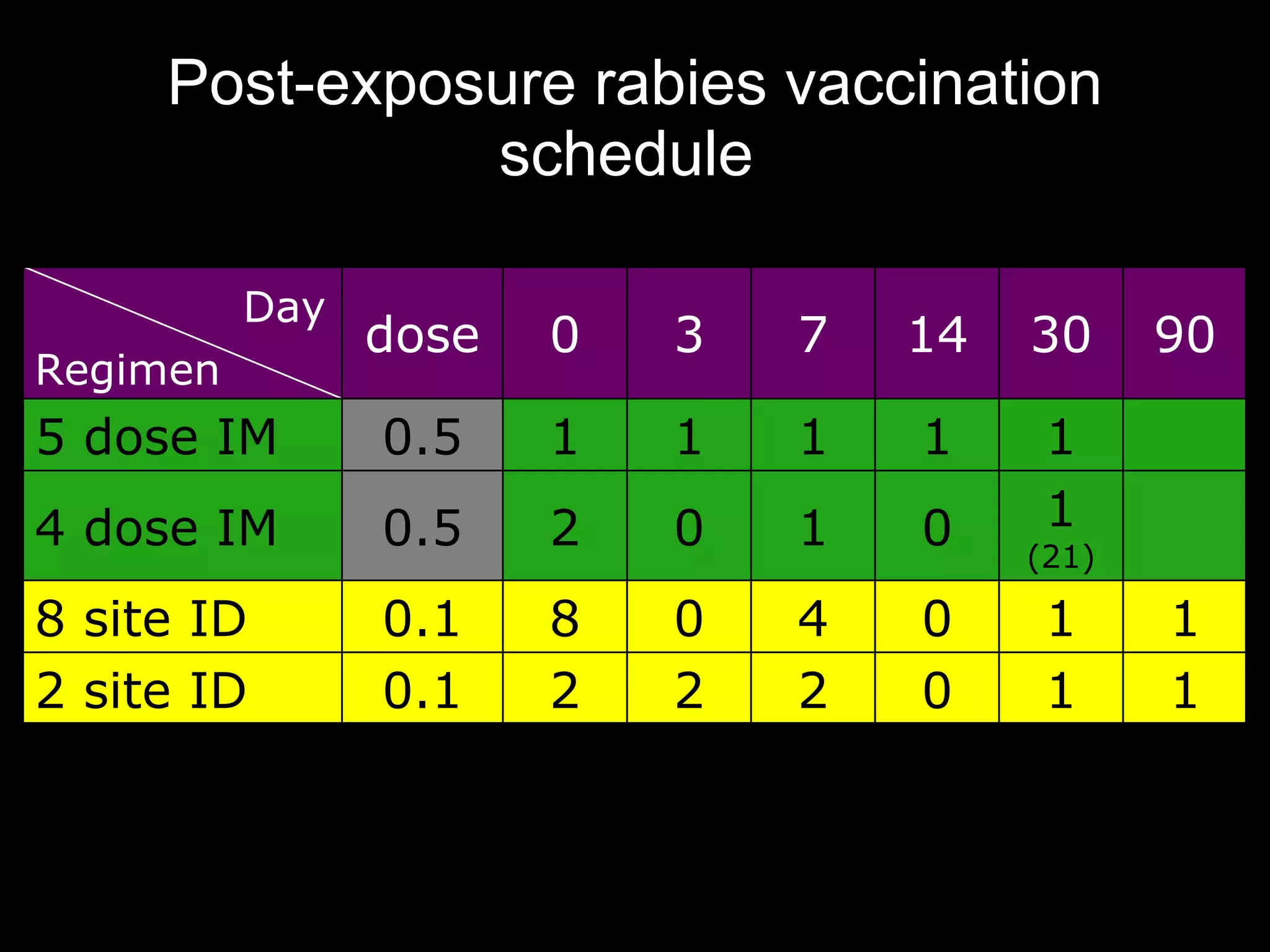
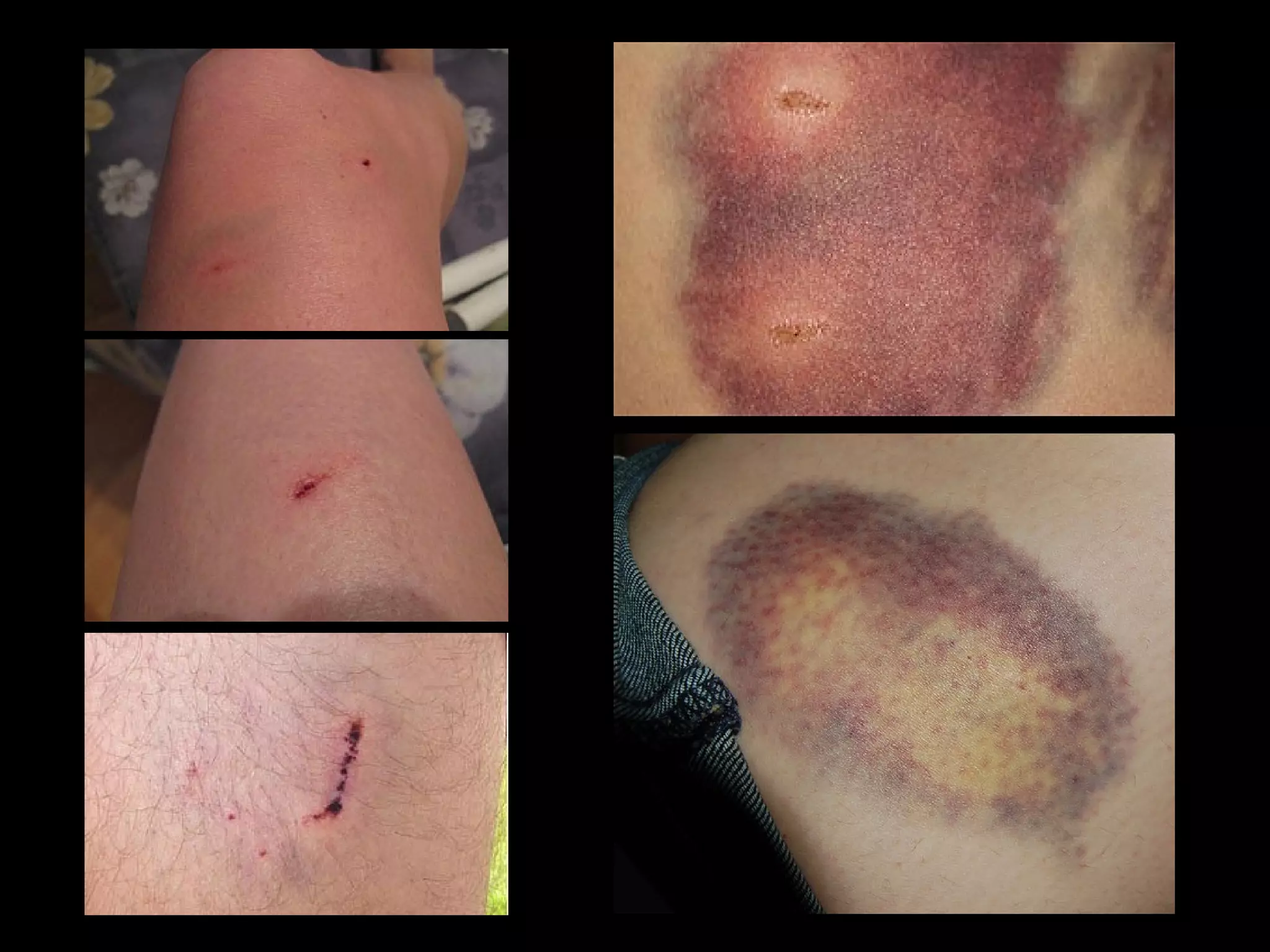
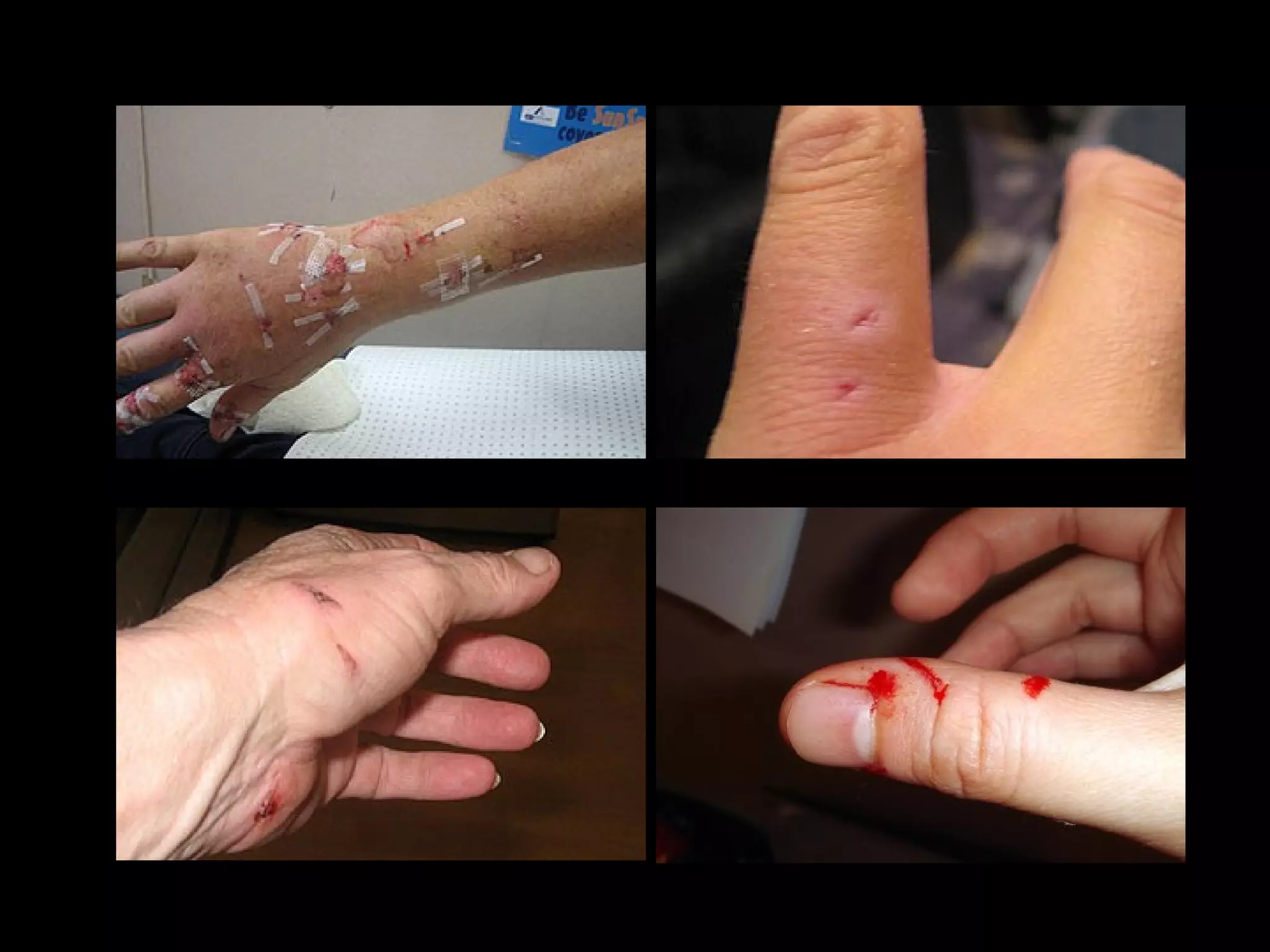
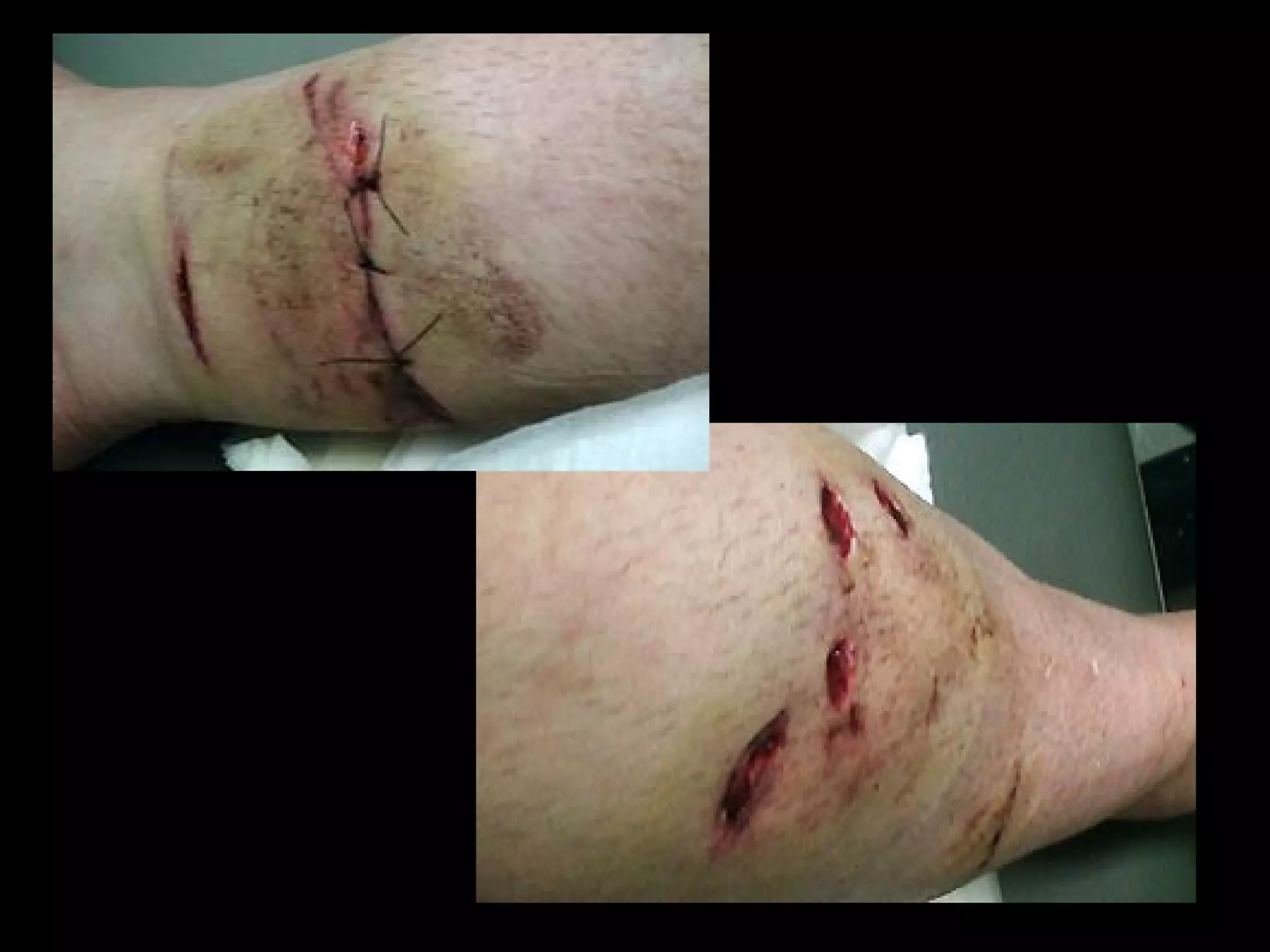
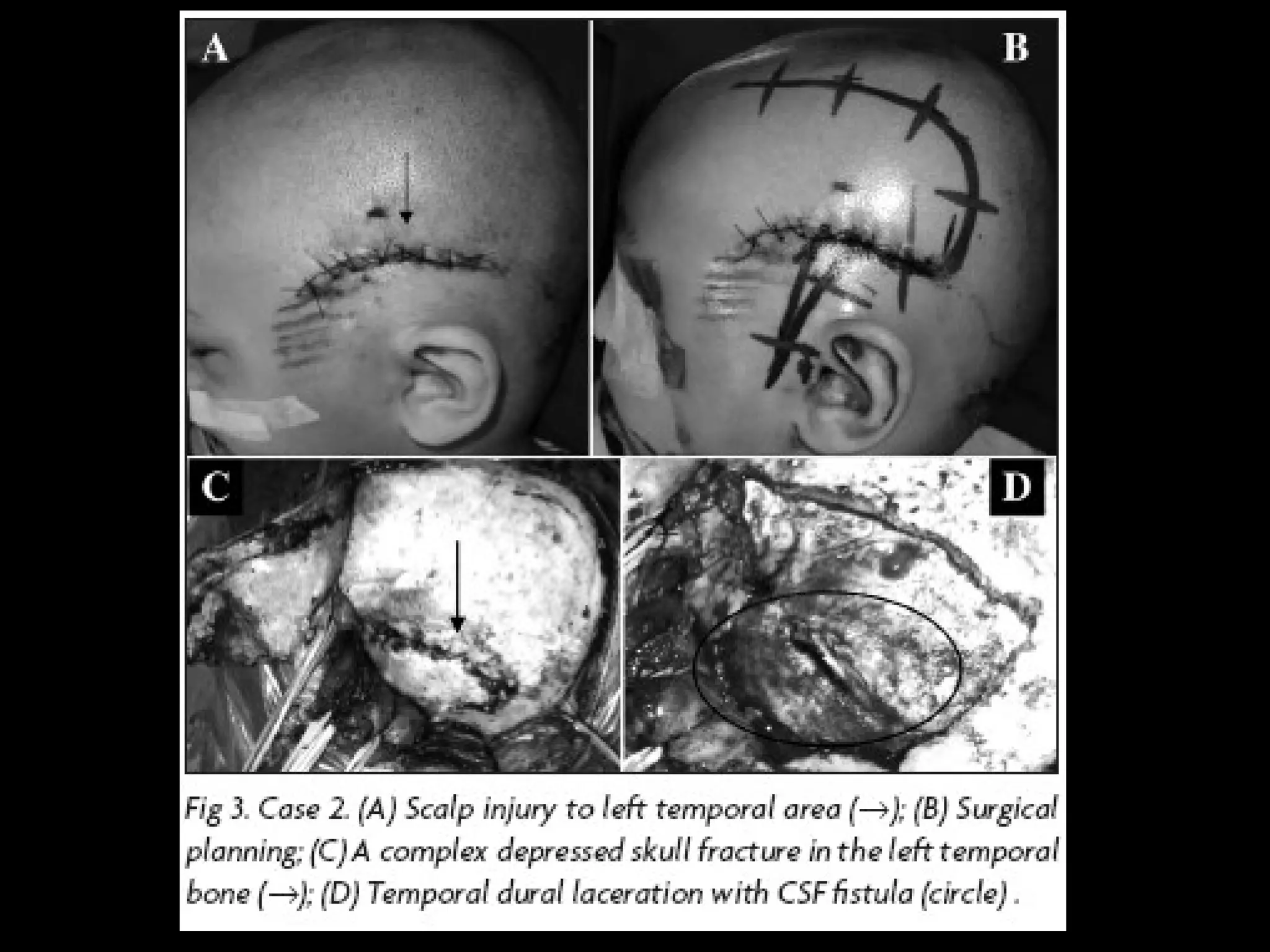
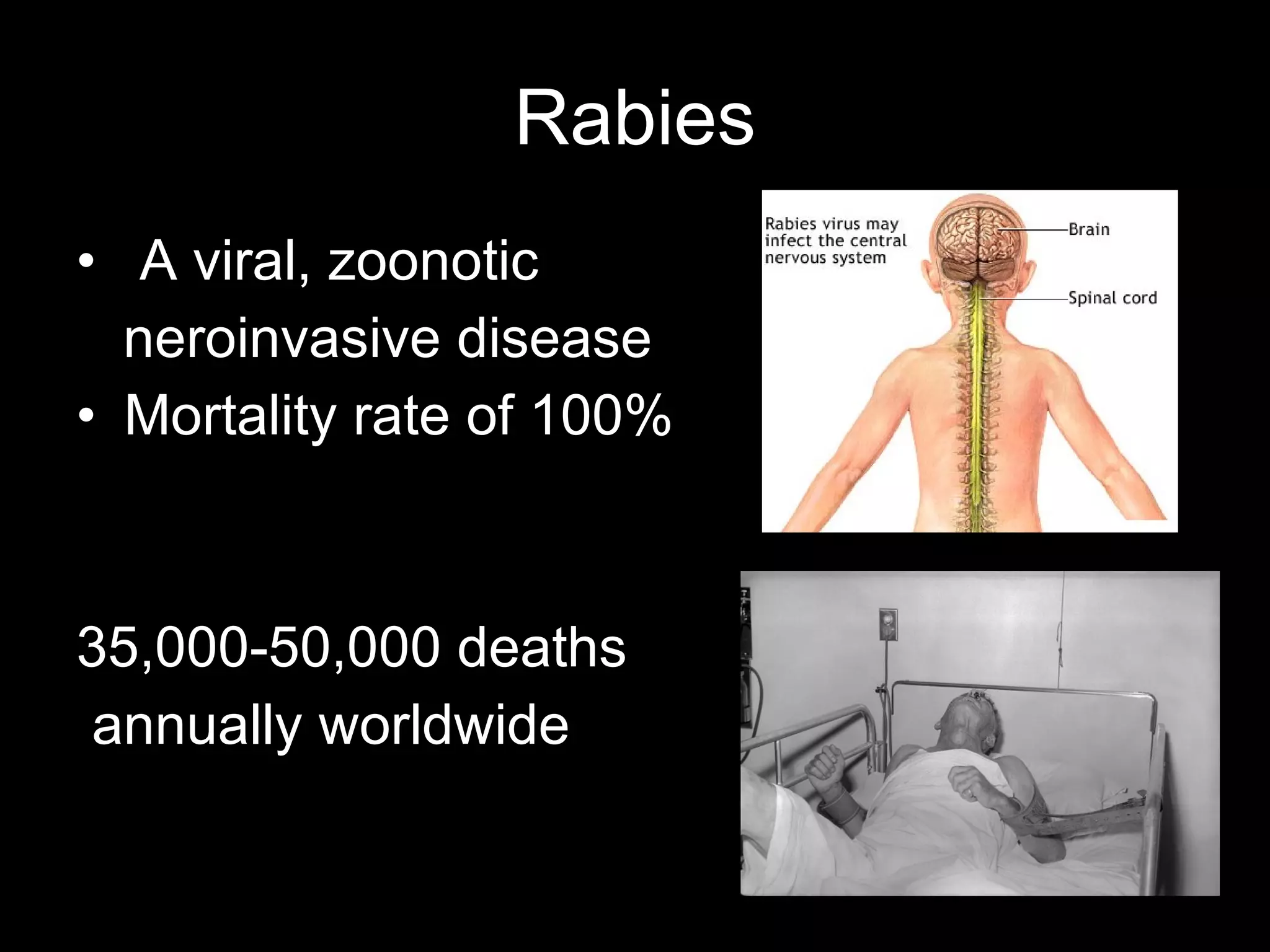
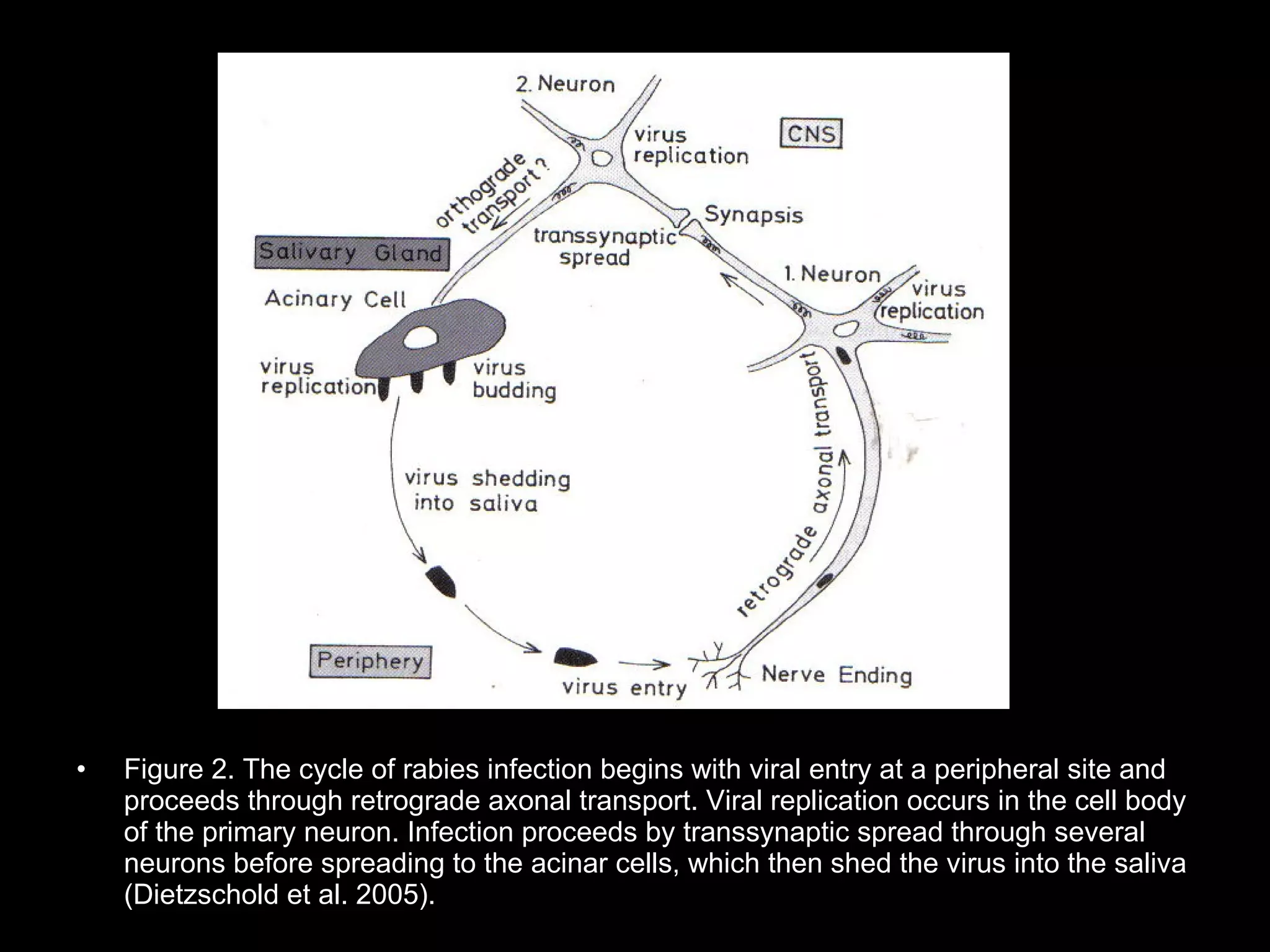
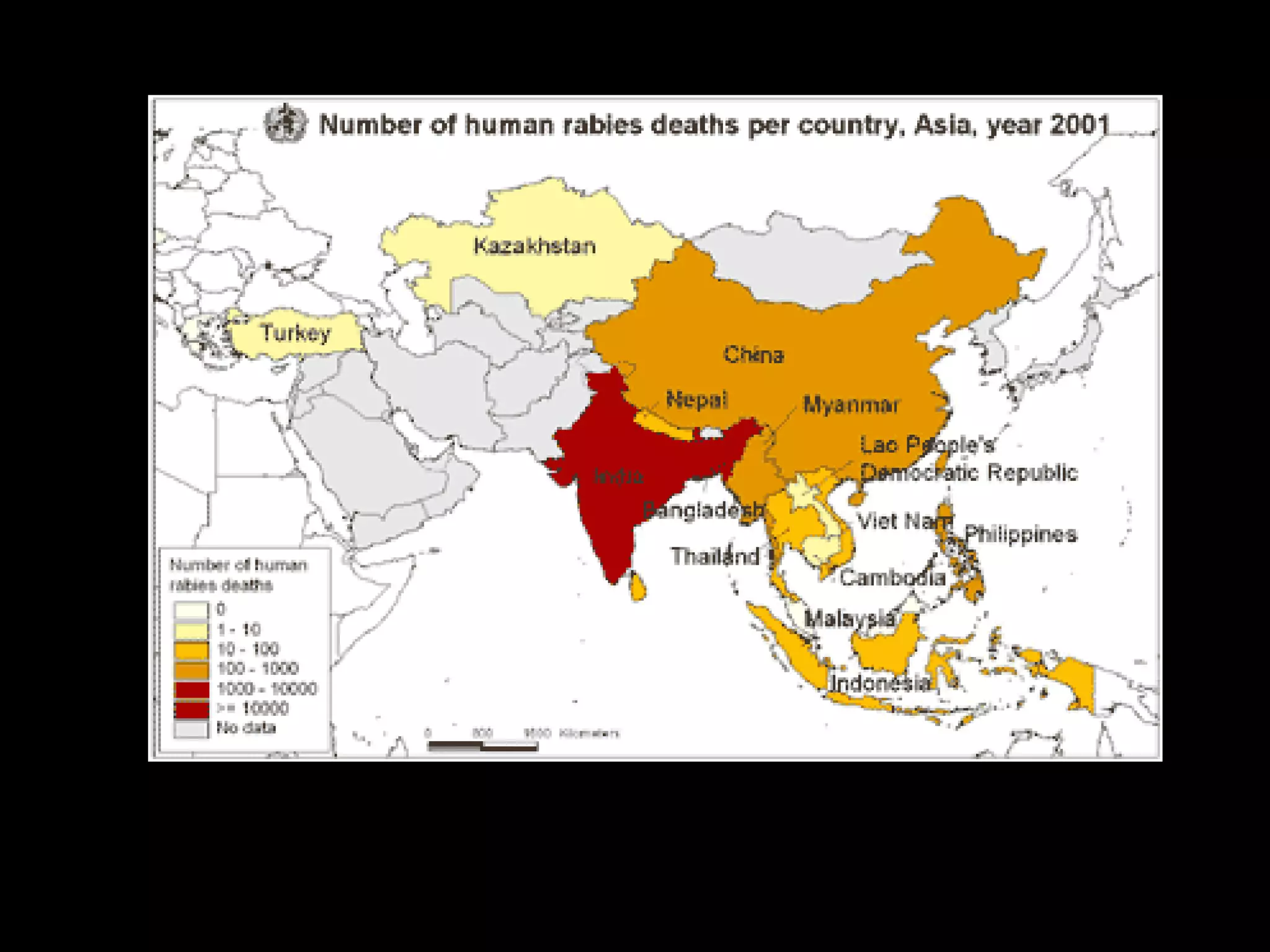
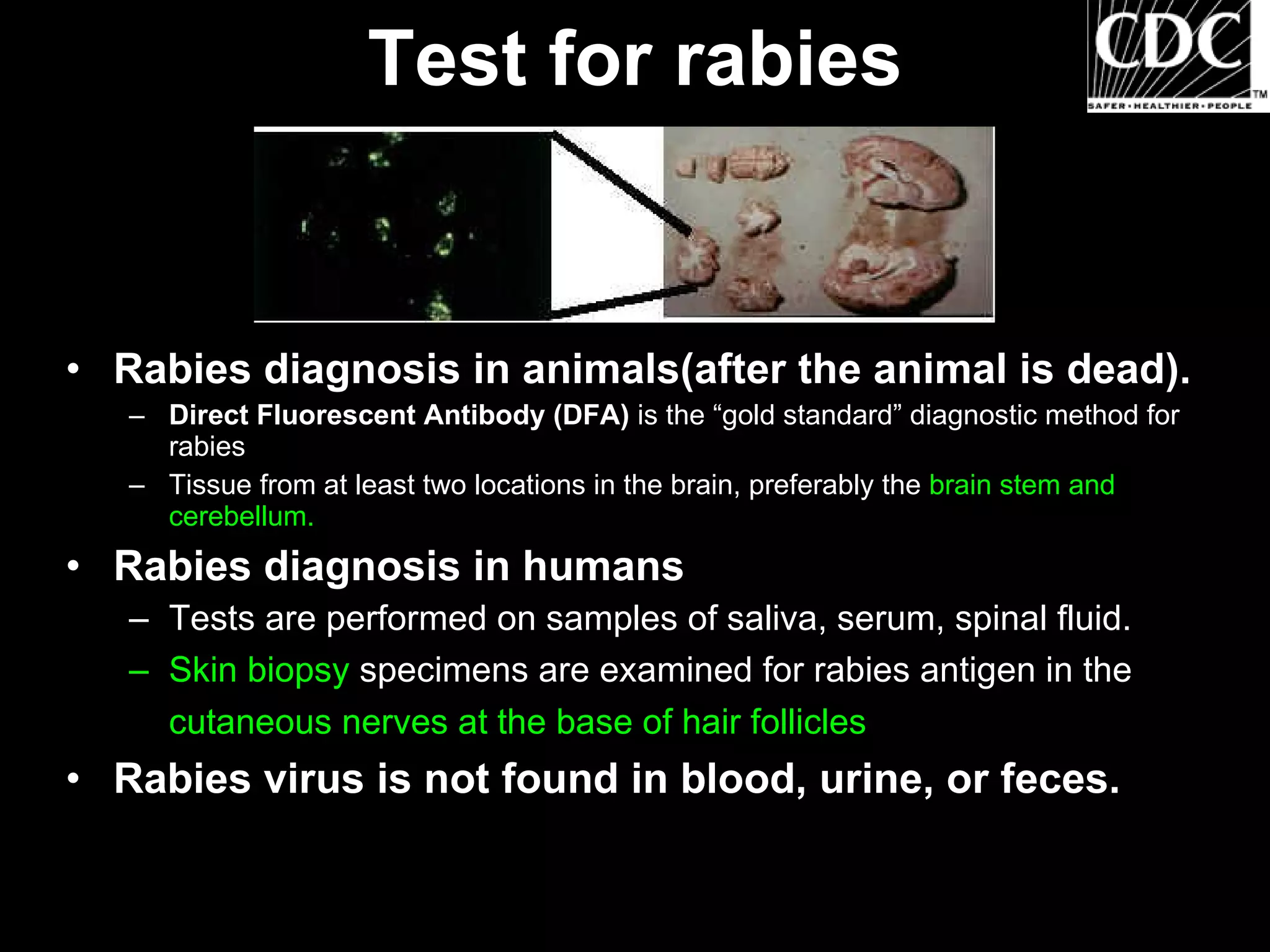
Dog bites can cause serious wounds and infections. Large dog breeds are more likely to bite the head and neck, causing deep tissue damage. Children aged 5-14 are most commonly bitten. Bites may be provoked by antagonizing or hurting an animal, or unprovoked by approaching young animals, food, or territorial animals. Wounds require cleaning, suturing if appropriate, antibiotics, and tetanus prophylaxis. For exposures, rabies post-exposure prophylaxis including vaccine and possibly immune globulin is administered based on category of exposure. The rabies virus causes encephalitis with a nearly 100% fatality rate if left untreated.