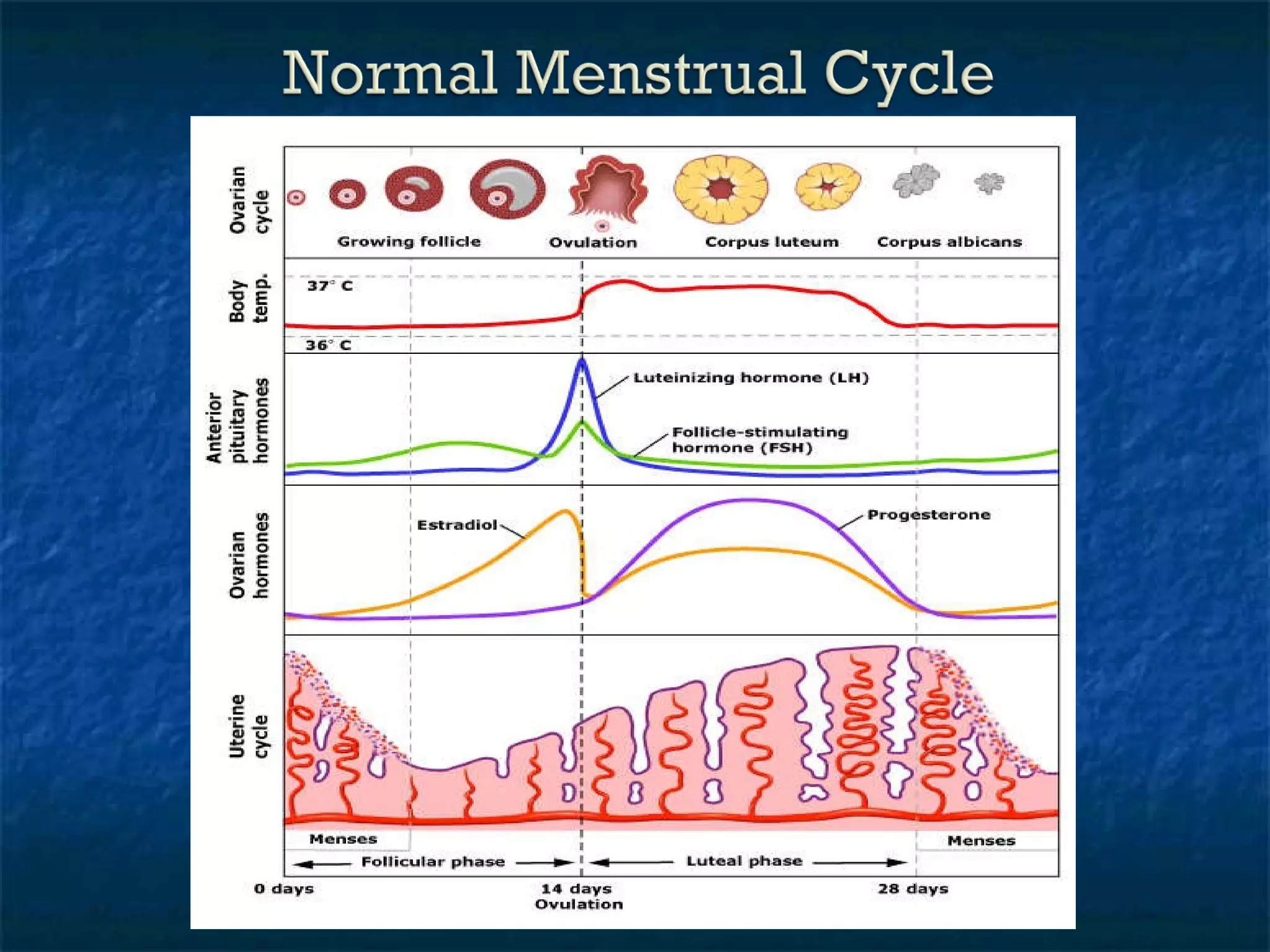
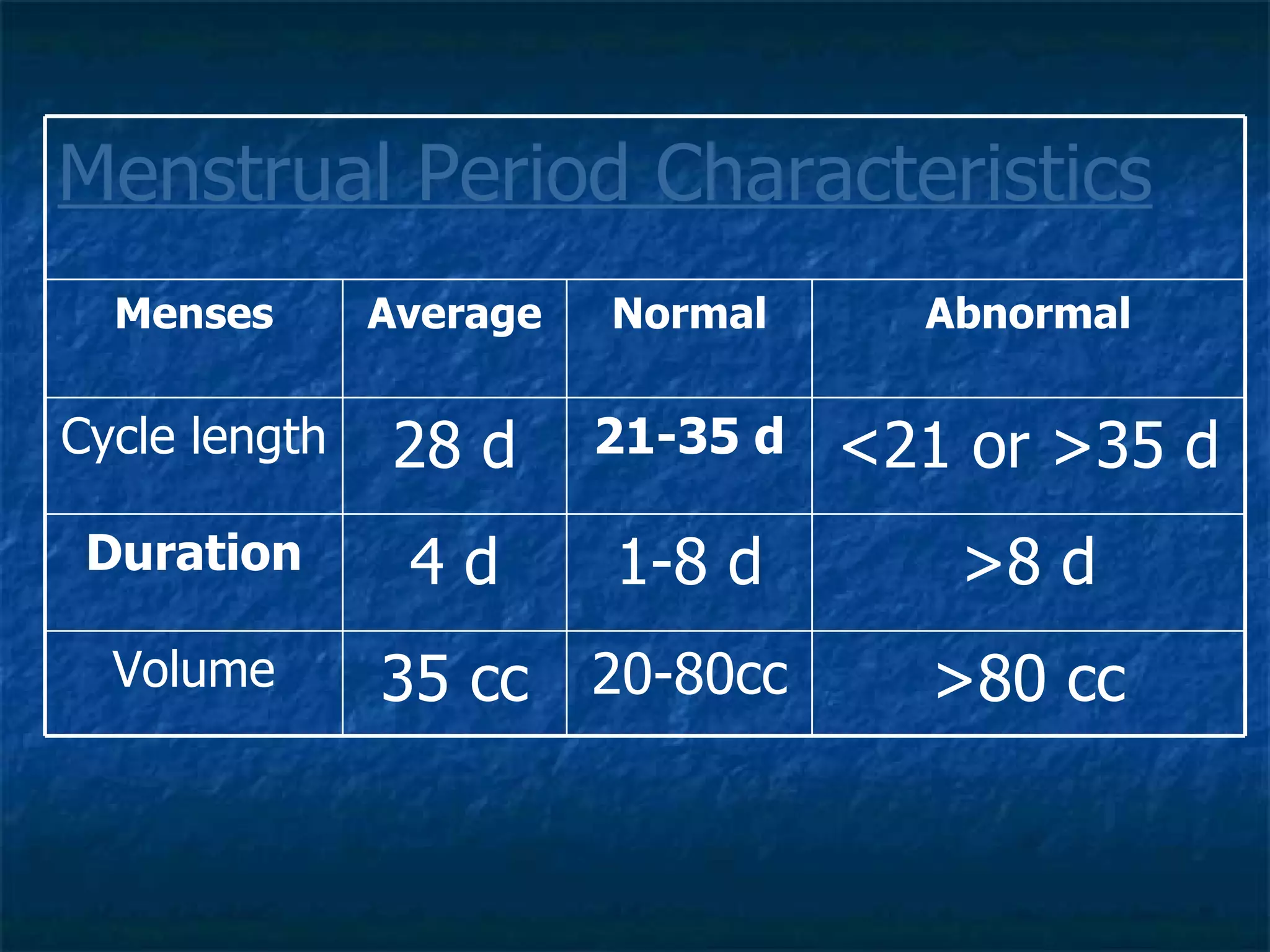
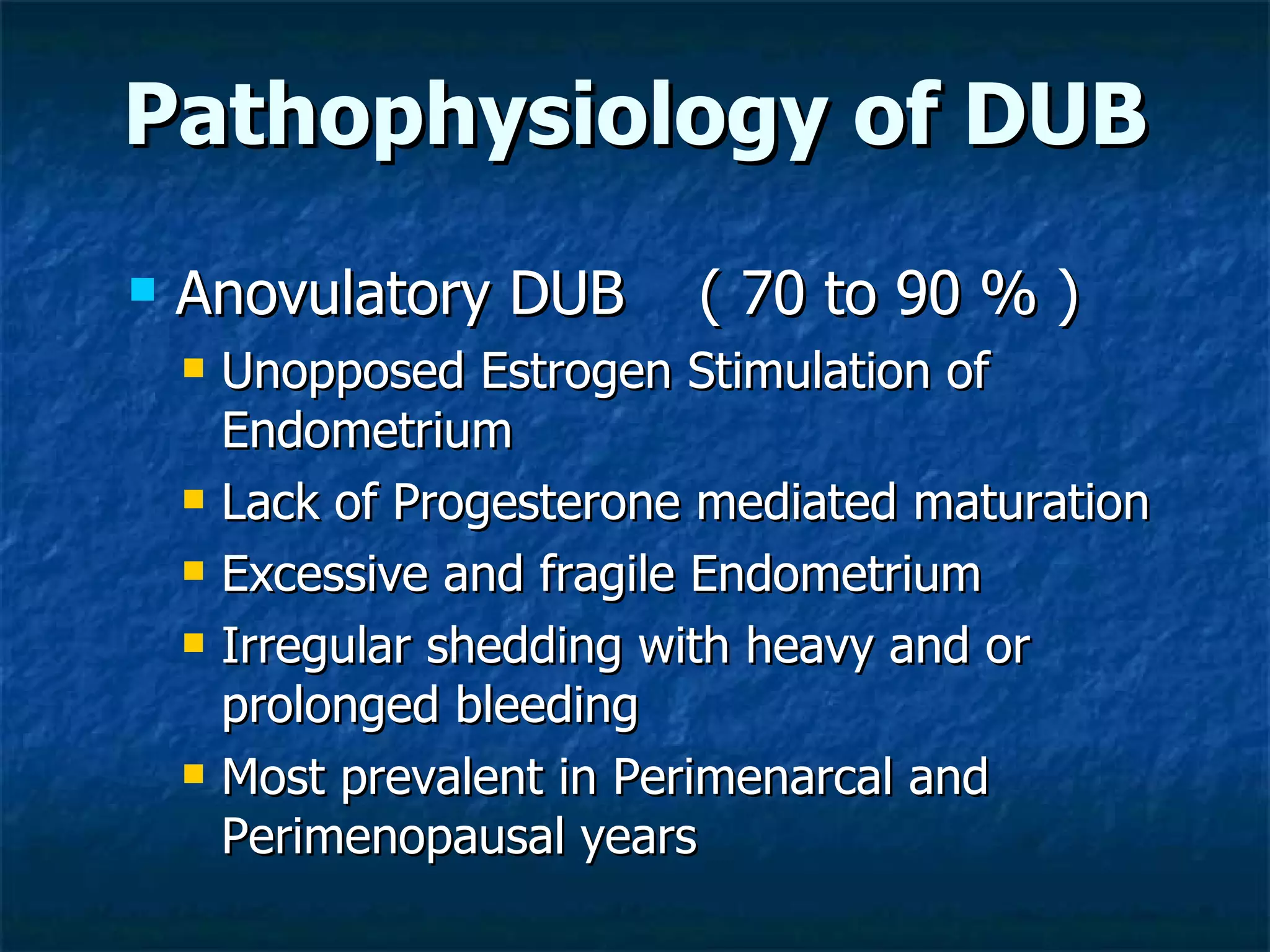
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB) is a common cause of abnormal uterine bleeding outside of pregnancy, and is caused by functional abnormalities of the hypothalamic-pituitary axis. DUB accounts for the large majority of abnormal uterine bleeding cases. Evaluation involves obtaining a detailed history, physical exam, and endometrial sampling. Treatment options include medical management with various hormonal regimens or surgical options like endometrial ablation or hysterectomy.