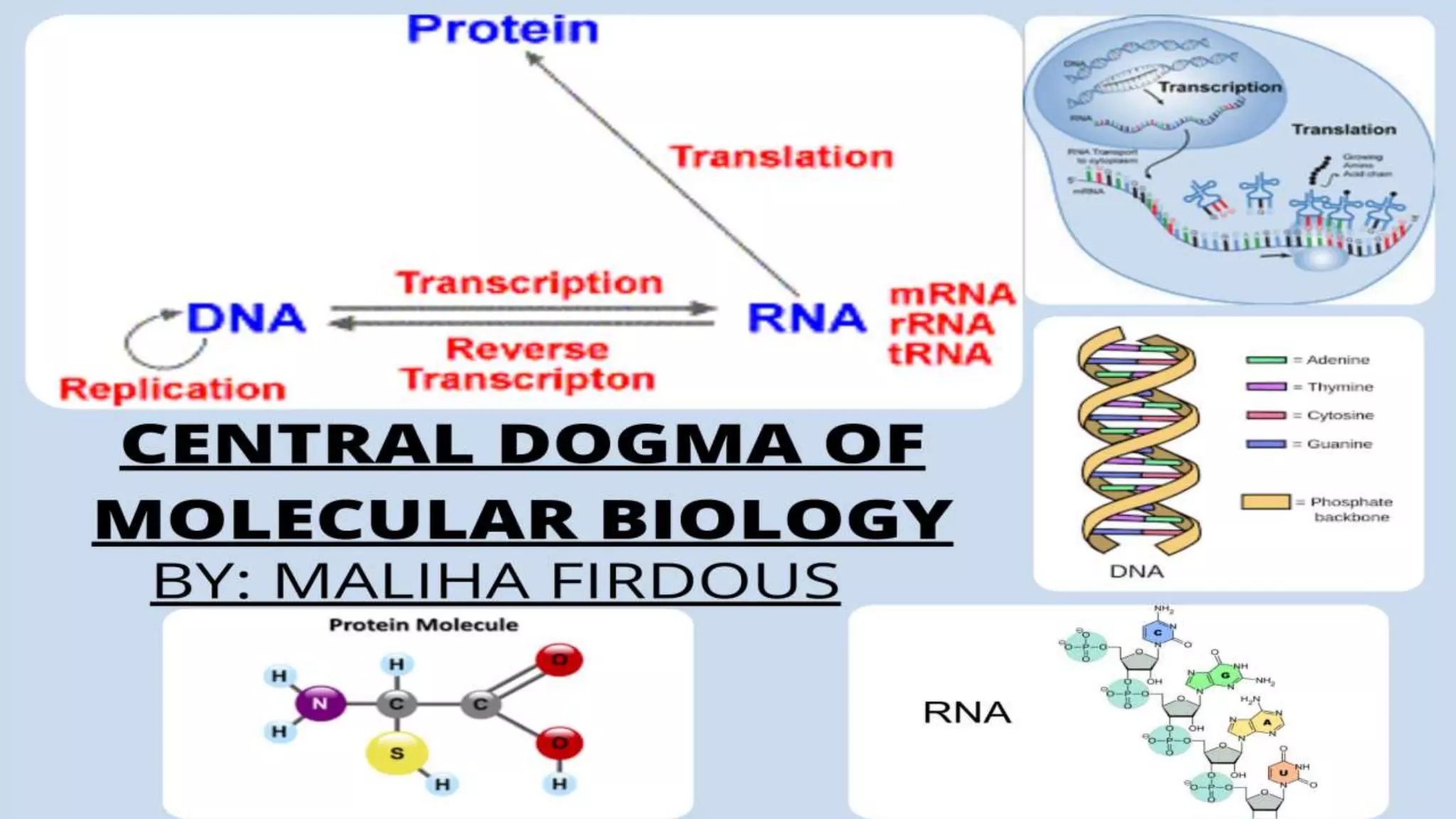
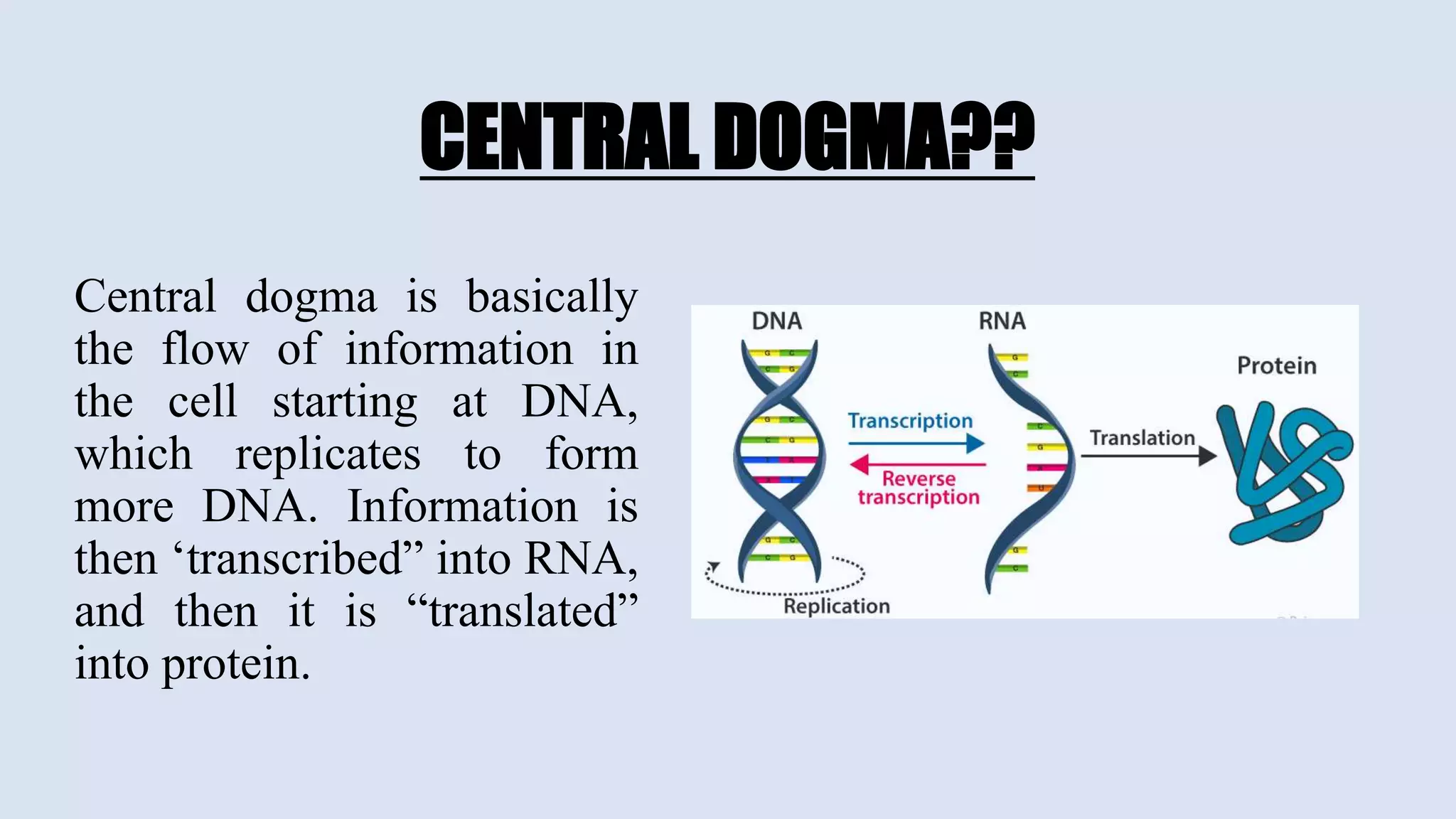
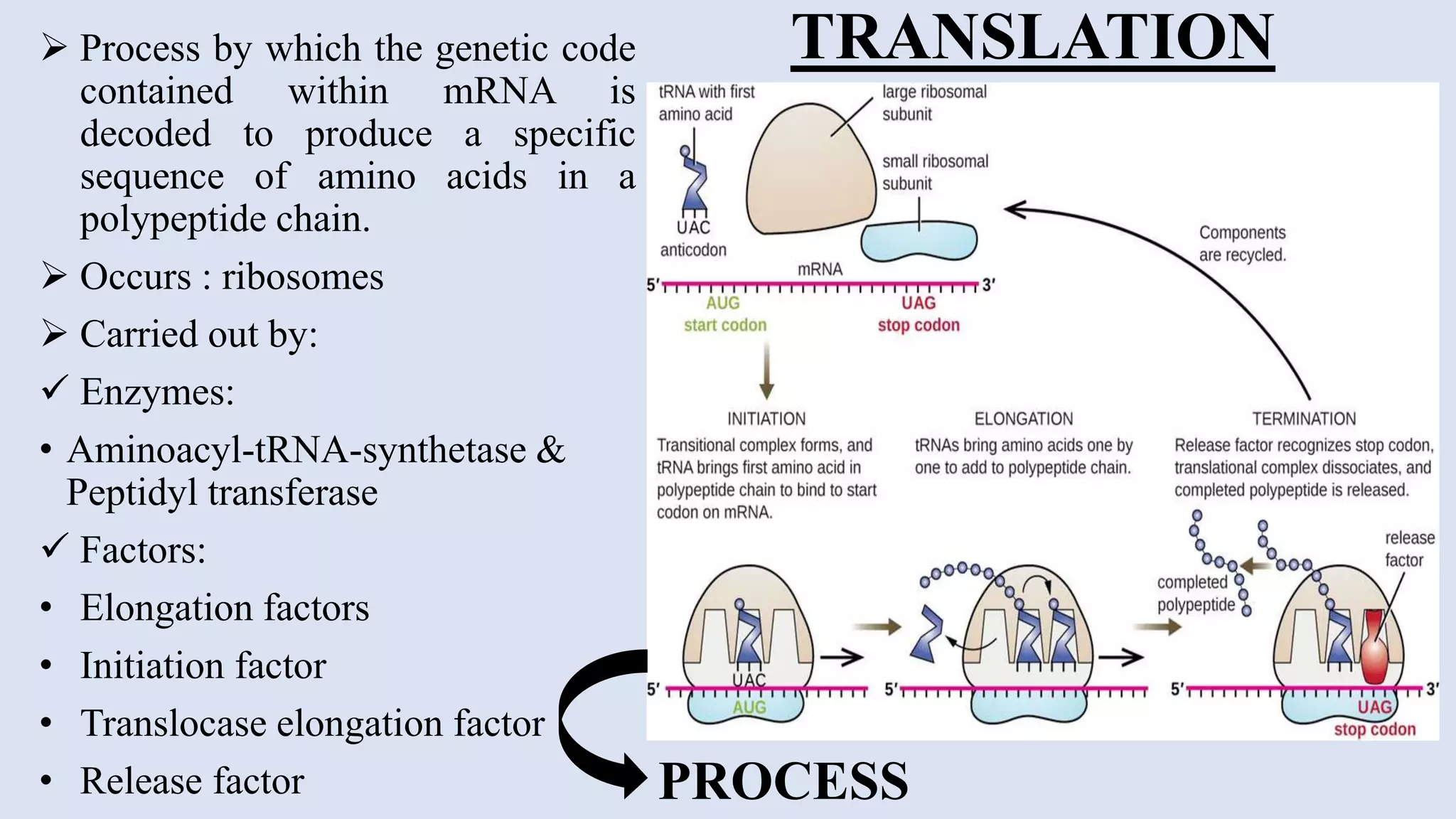
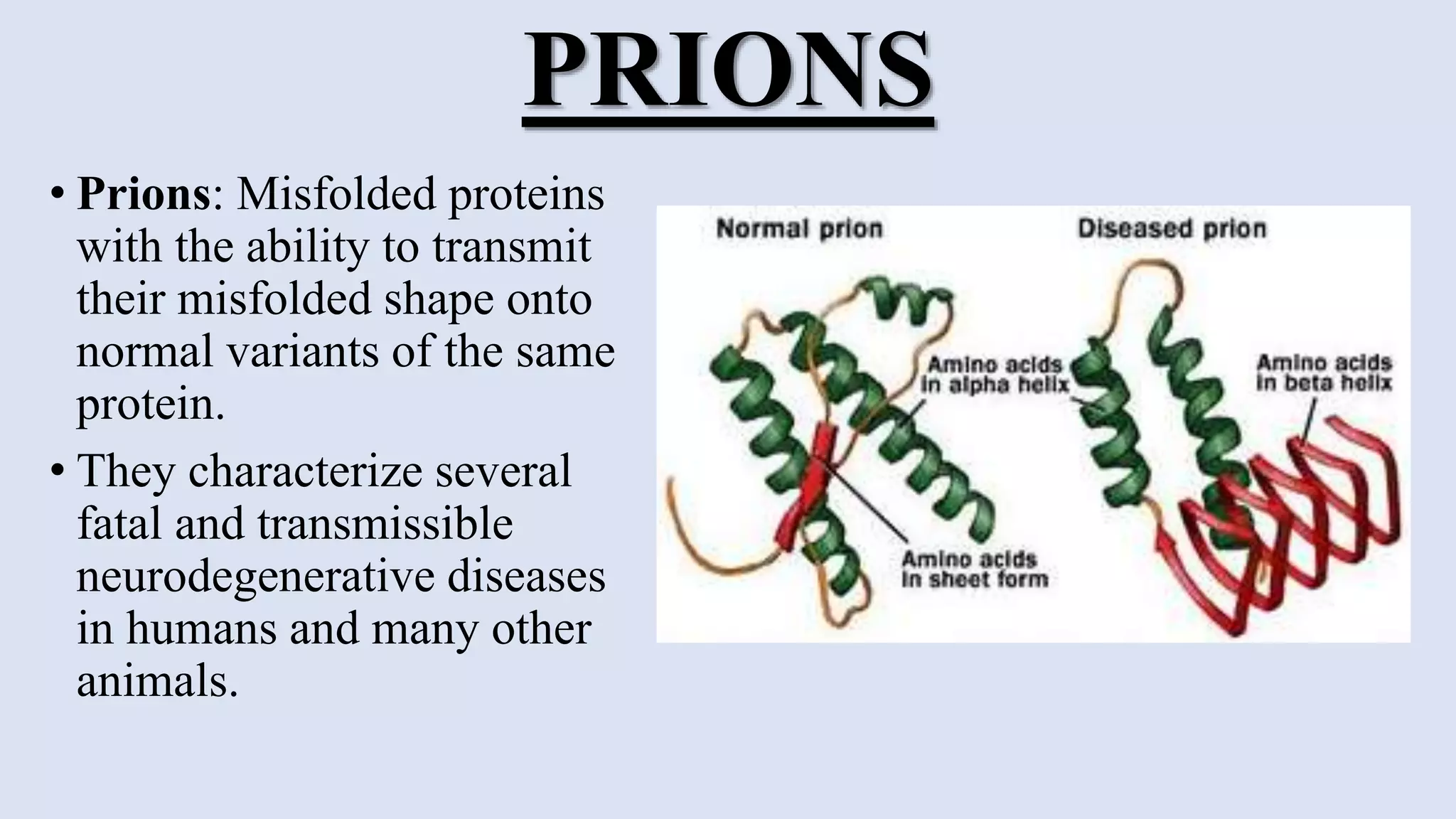
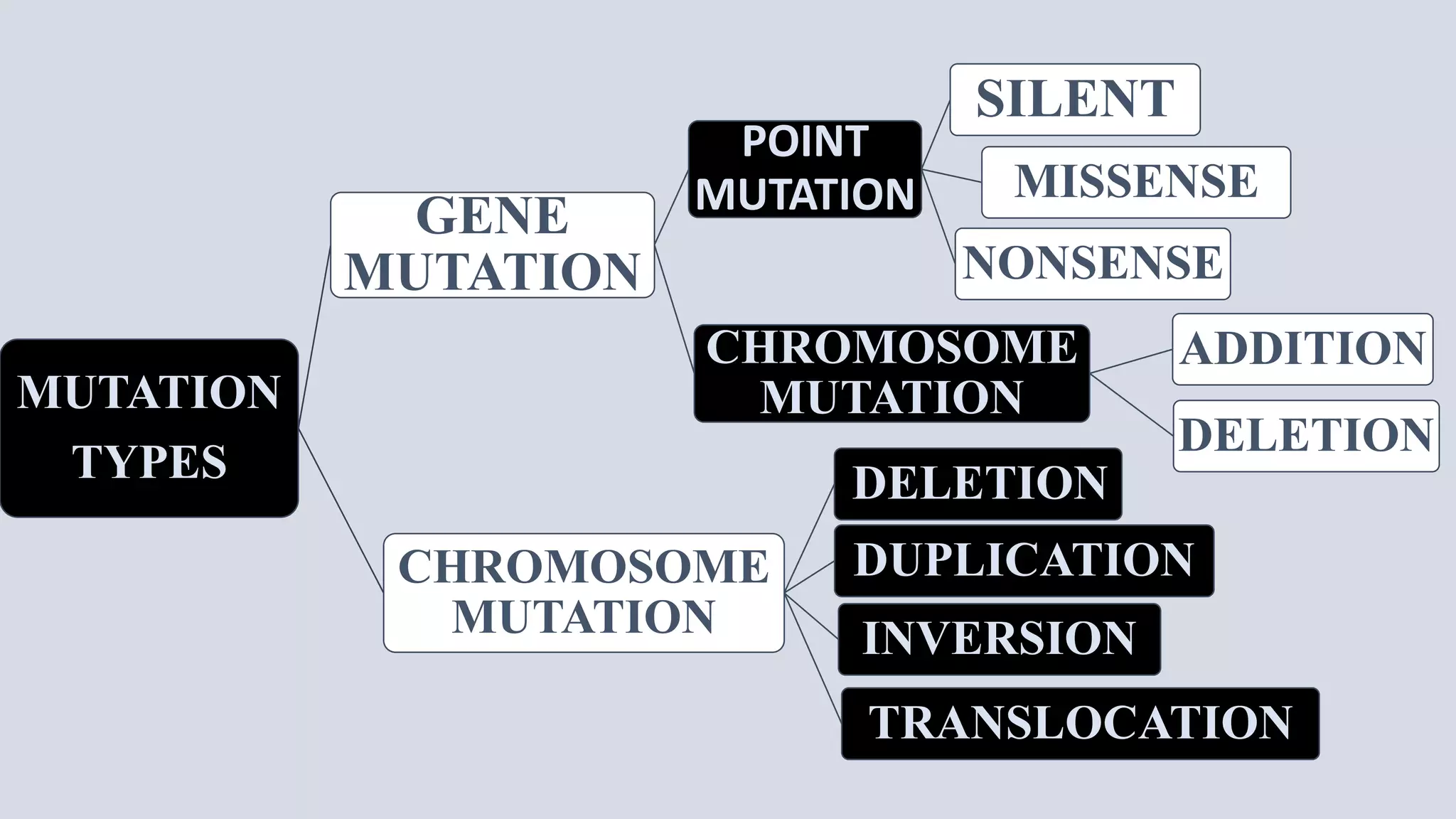
The central dogma of molecular biology describes the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA and then to proteins, a process that involves DNA replication, transcription, and translation. Exceptions to this dogma include reverse transcription and prions, which challenge the traditional understanding of genetic information flow. Mutations can also occur in the nucleotide sequence of DNA, affecting gene expression and protein function.