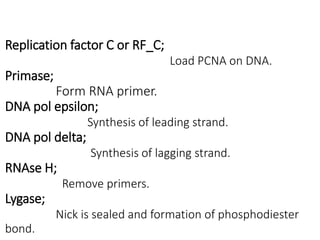
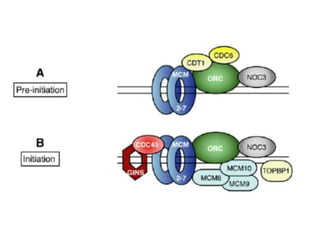
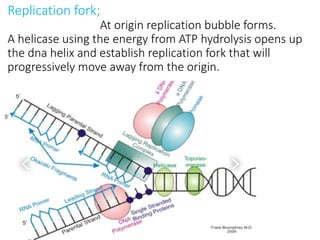
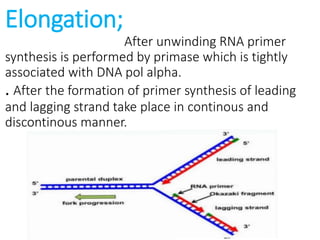
DNA replication in eukaryotes occurs in the nucleus and proceeds in the 5' to 3' direction. It involves several enzymes including helicase, which opens the DNA helix, and DNA polymerase epsilon and delta, which synthesize the leading and lagging strands respectively. Replication occurs through initiation, elongation, and termination steps. At the origin of replication, a pre-replication complex forms and the replication fork bubbles outwards. RNA primers are laid down and DNA synthesis occurs continuously on the leading strand but discontinuously on the lagging strand. The primers are later removed and the gaps filled in.