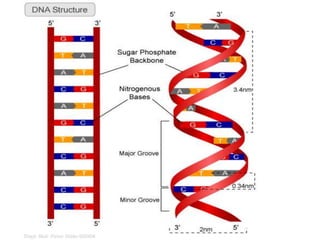
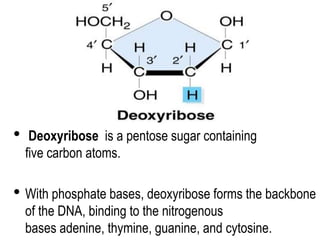
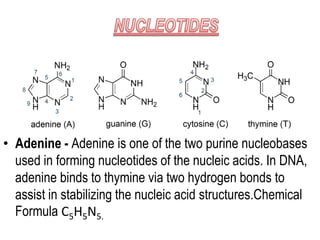
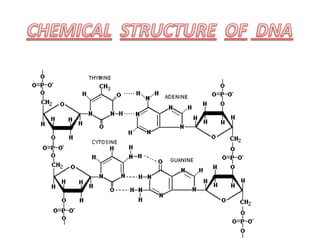
DNA is a complex molecule found inside cells that contains all the genetic instructions needed to build an organism. It takes the form of a double helix, with two strands coiled around each other. Each strand is made up of repeating nucleotide bases adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine that bond together in specific patterns between the strands. This nucleotide sequence encodes the unique traits of each organism. DNA is tightly packed into chromosomes inside the cell nucleus to allow many DNA molecules to fit in each cell.