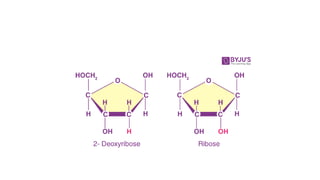
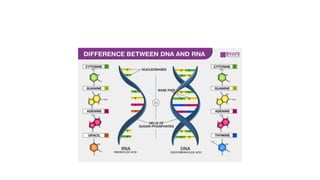
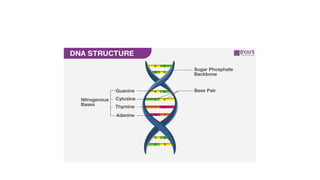
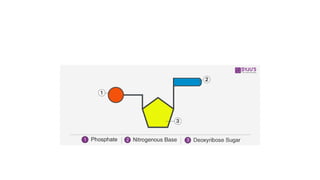
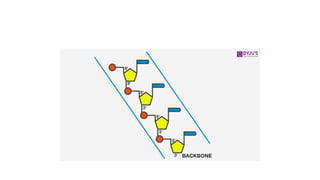
DNA is a nucleic acid that carries genetic instructions in all living organisms. It is composed of nucleotides with a sugar (deoxyribose), phosphate groups, and nitrogenous bases (adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine). DNA has a double helix structure with the bases on each strand bonded to their complement on the other strand. This structure was discovered by Watson and Crick based on experimental evidence. DNA is found in the nucleus of cells and carries the genetic code that is passed from parents to offspring.