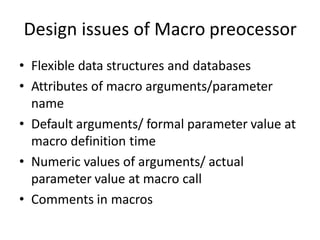
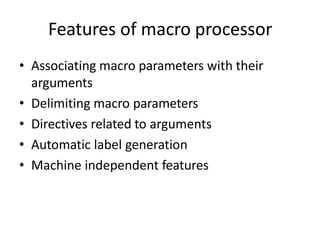
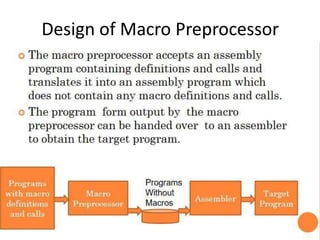
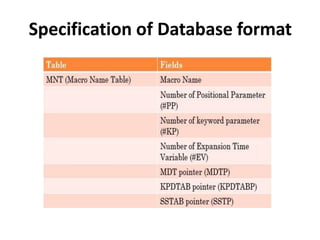
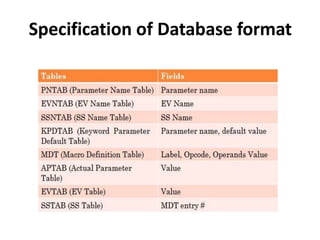
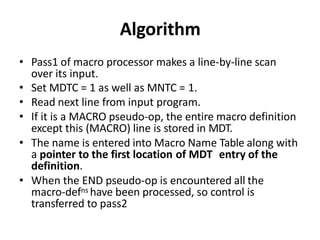
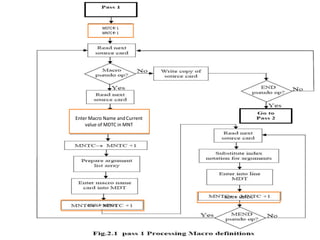
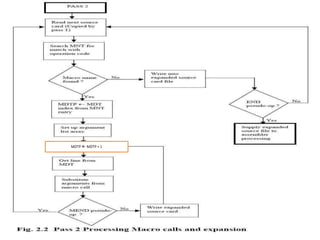
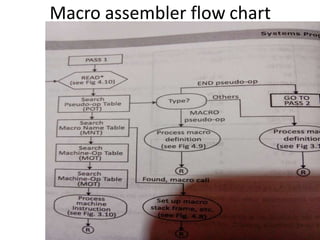
The document discusses the design of a two-pass macro preprocessor. In pass one, macro definitions are identified and stored in a macro definition table along with their parameters. A macro name table is also created. In pass two, macro calls are identified and replaced by retrieving the corresponding macro definition and substituting actual parameters for formal parameters using an argument list array. Databases like the macro definition table, macro name table, and argument list array are used to store and retrieve macro information to enable expansion of macro calls. The algorithm scans the input sequentially in each pass to process macro definitions and calls.