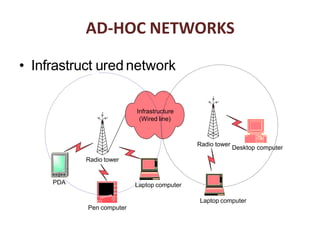
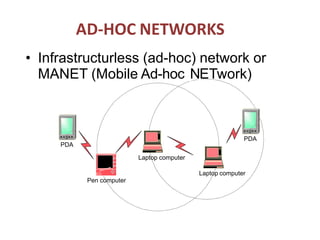
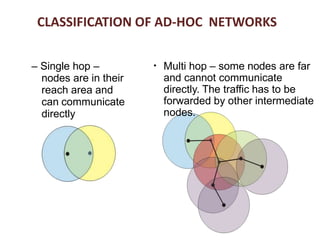
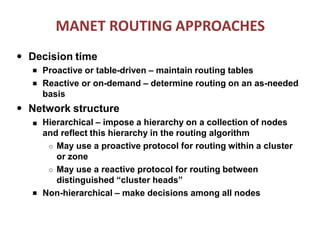
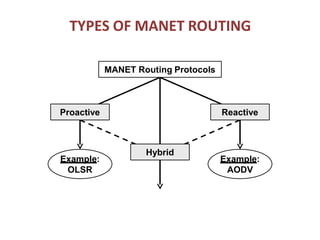
The document discusses routing in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks (MANETs), focusing on the processes and challenges involved in selecting paths for data packets among mobile devices. It differentiates between infrastructured and ad-hoc networks and highlights the characteristics and applications of MANETs, including their spontaneous setup and benefits in scenarios lacking fixed infrastructure. Routing methods and protocols, such as source routing, hop-by-hop routing, and various MANET routing protocols with their respective advantages and challenges, are also described.