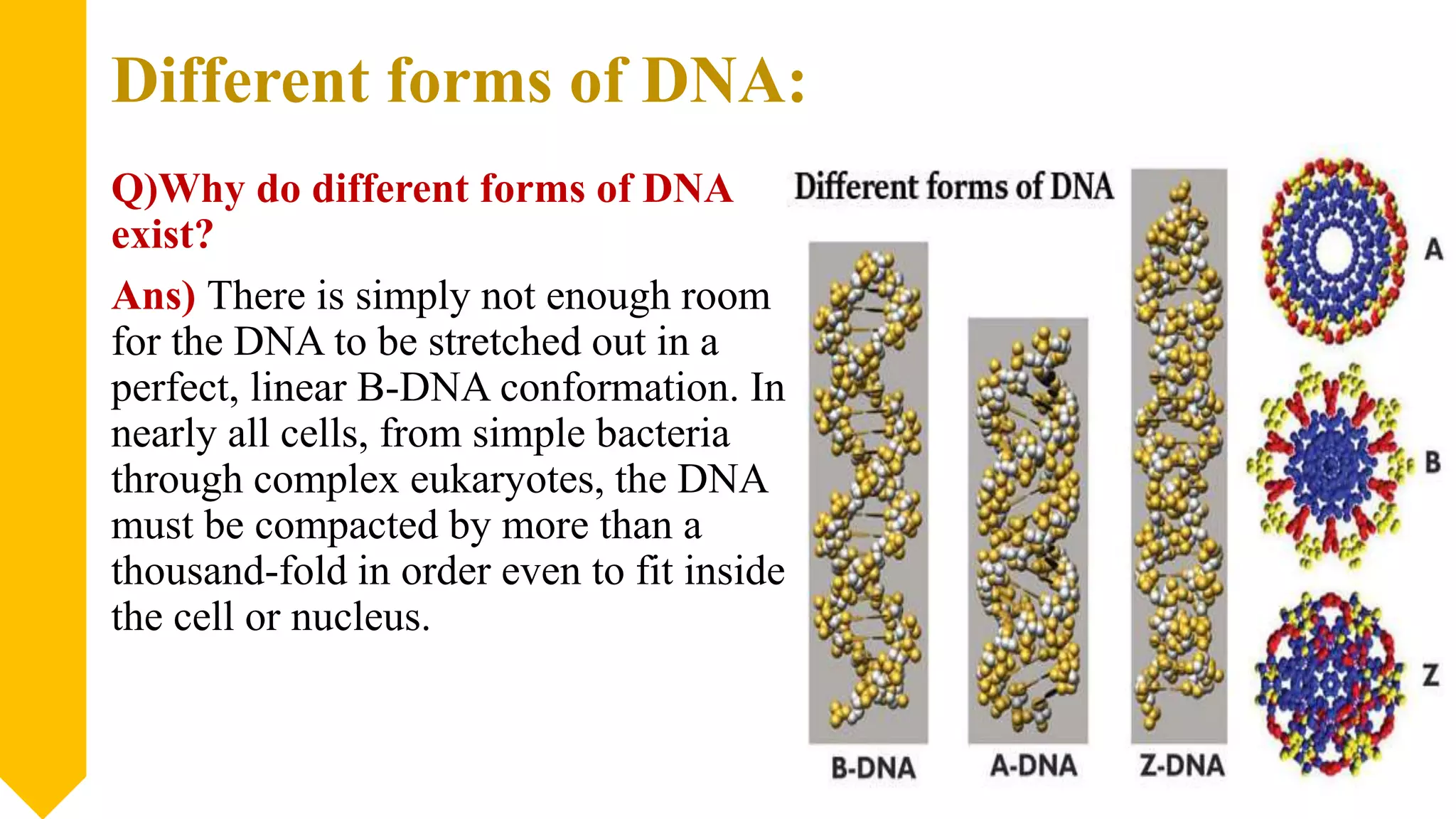
There are three main forms of DNA structure: A-DNA, B-DNA, and Z-DNA. B-DNA is the most common form found under physiological conditions, having a right-handed double helix with 10.5 base pairs per turn. A-DNA forms under dehydrating conditions and has a wider helix with 11 base pairs per turn. Z-DNA is a left-handed helix that forms with alternating purine-pyrimidine sequences, containing 12 base pairs per turn in a narrow, zig-zag structure. While B-DNA is most prevalent, the structure can vary depending on sequence and environmental conditions.