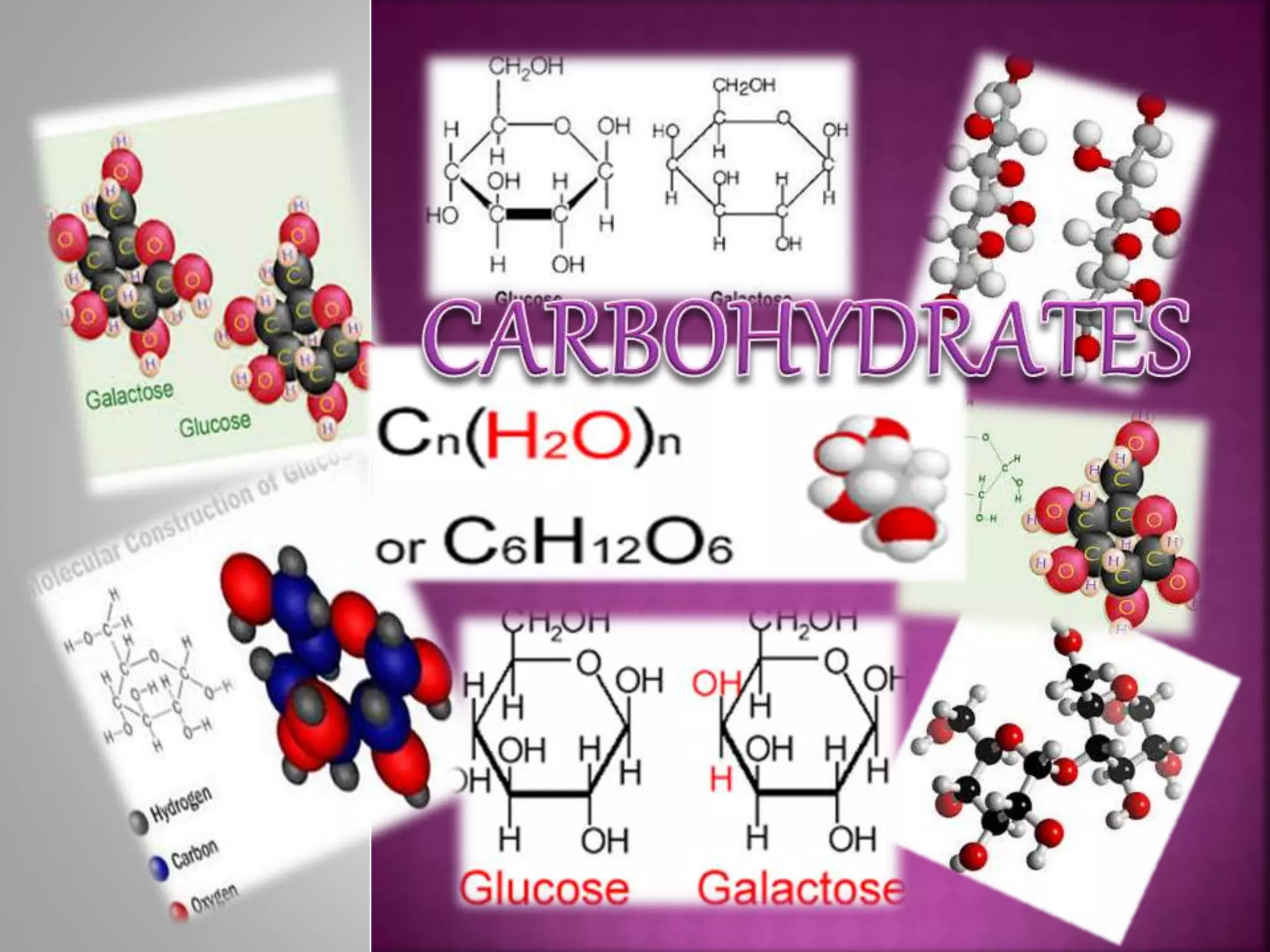
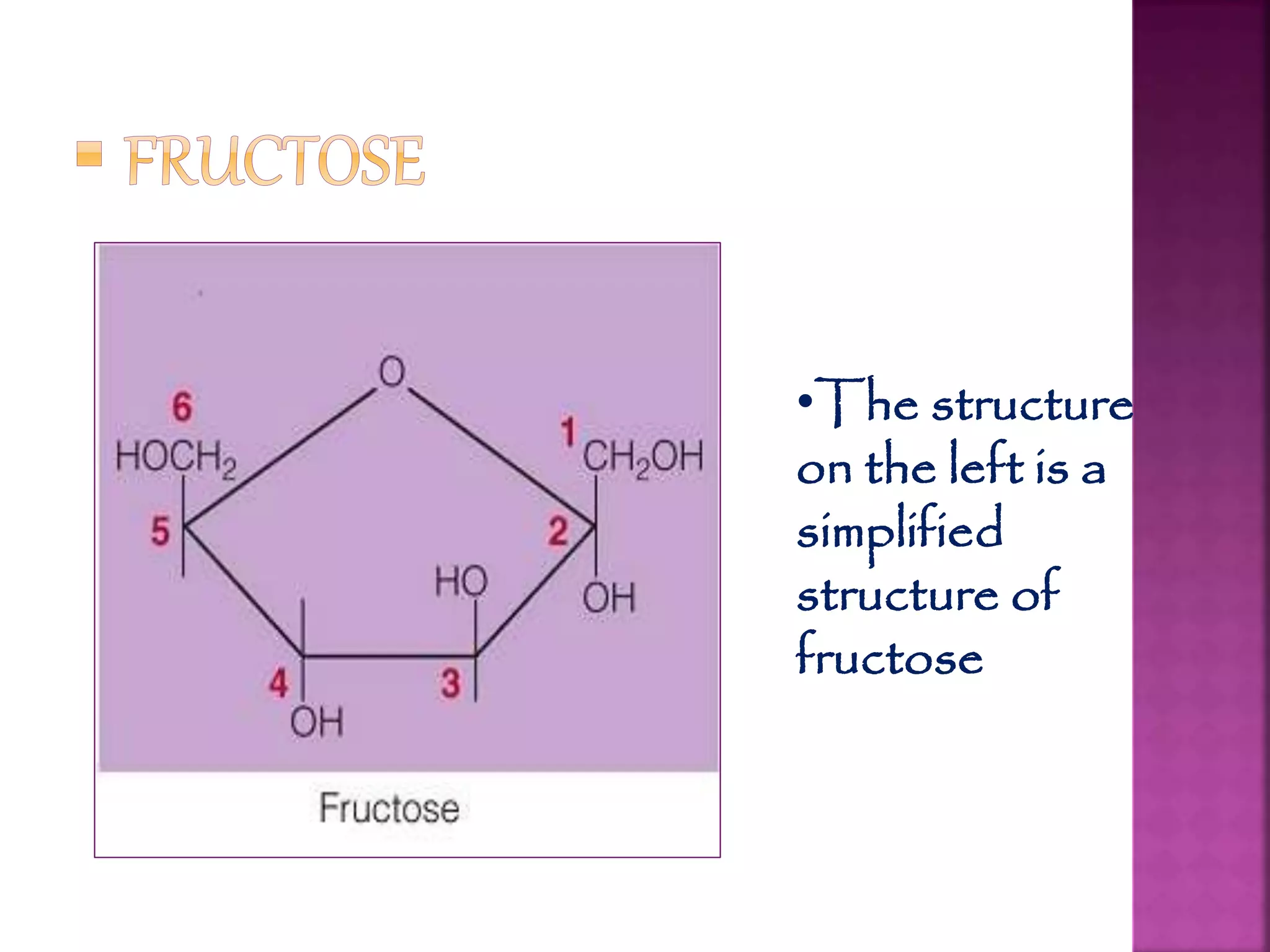
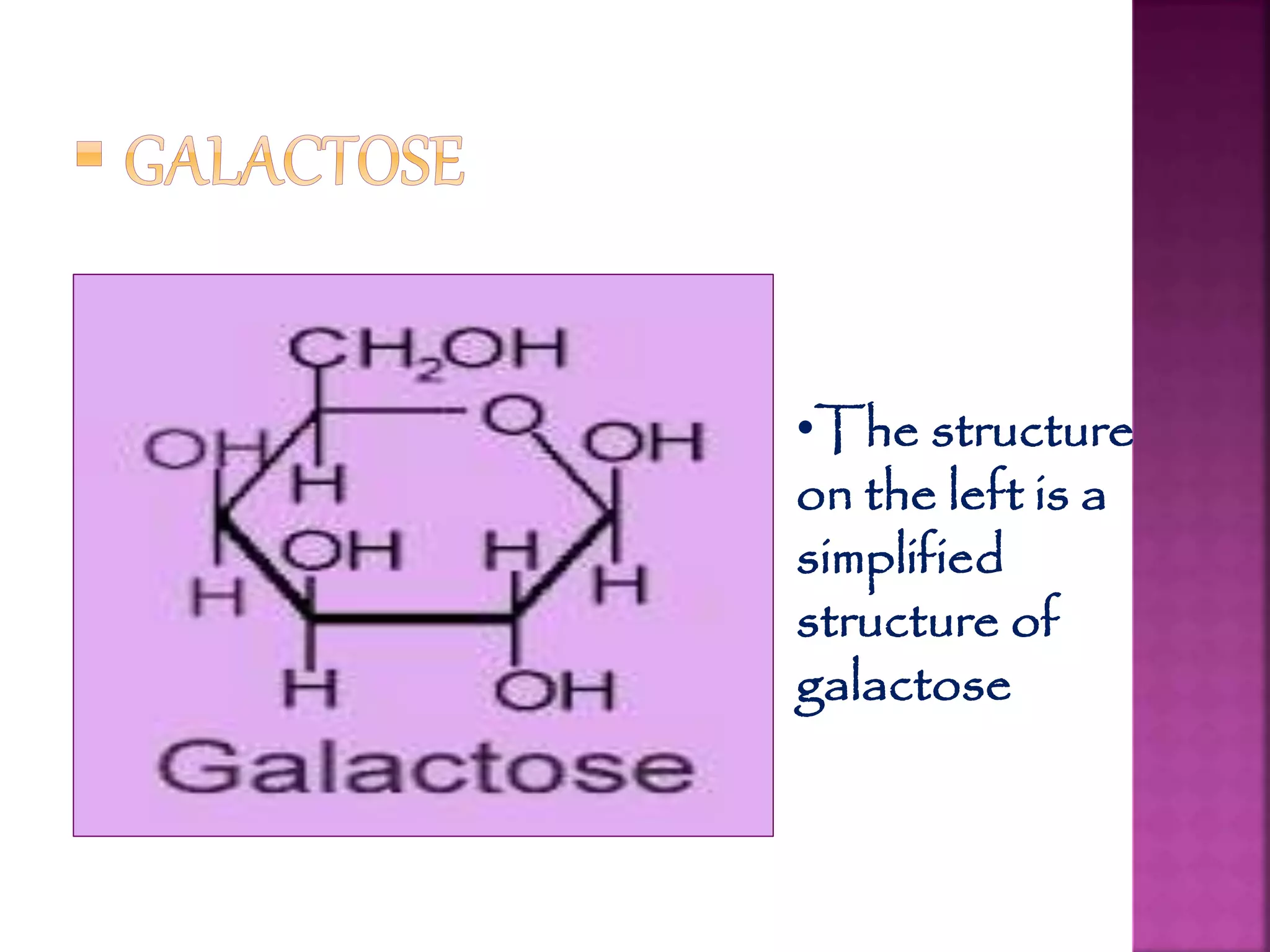
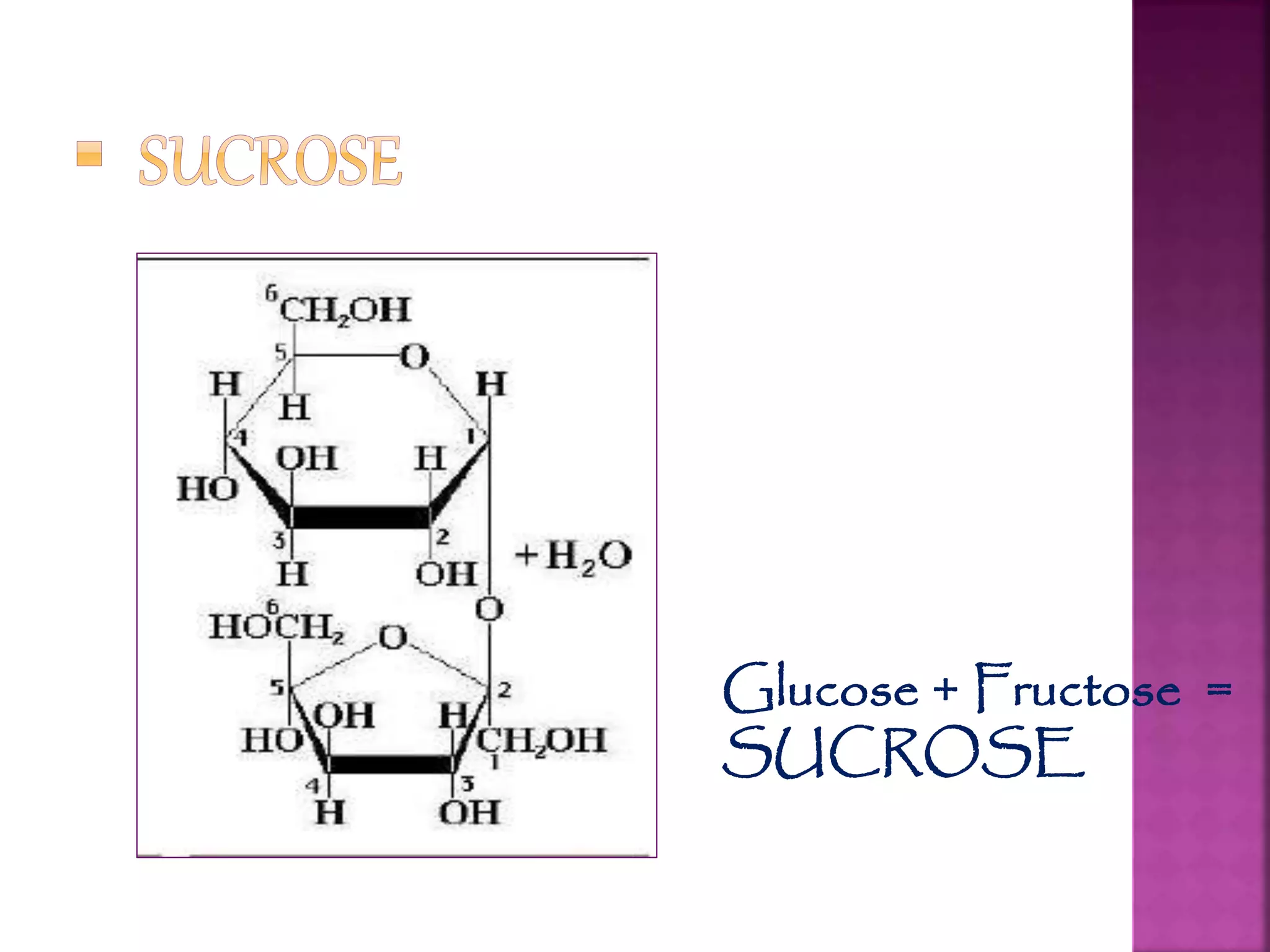
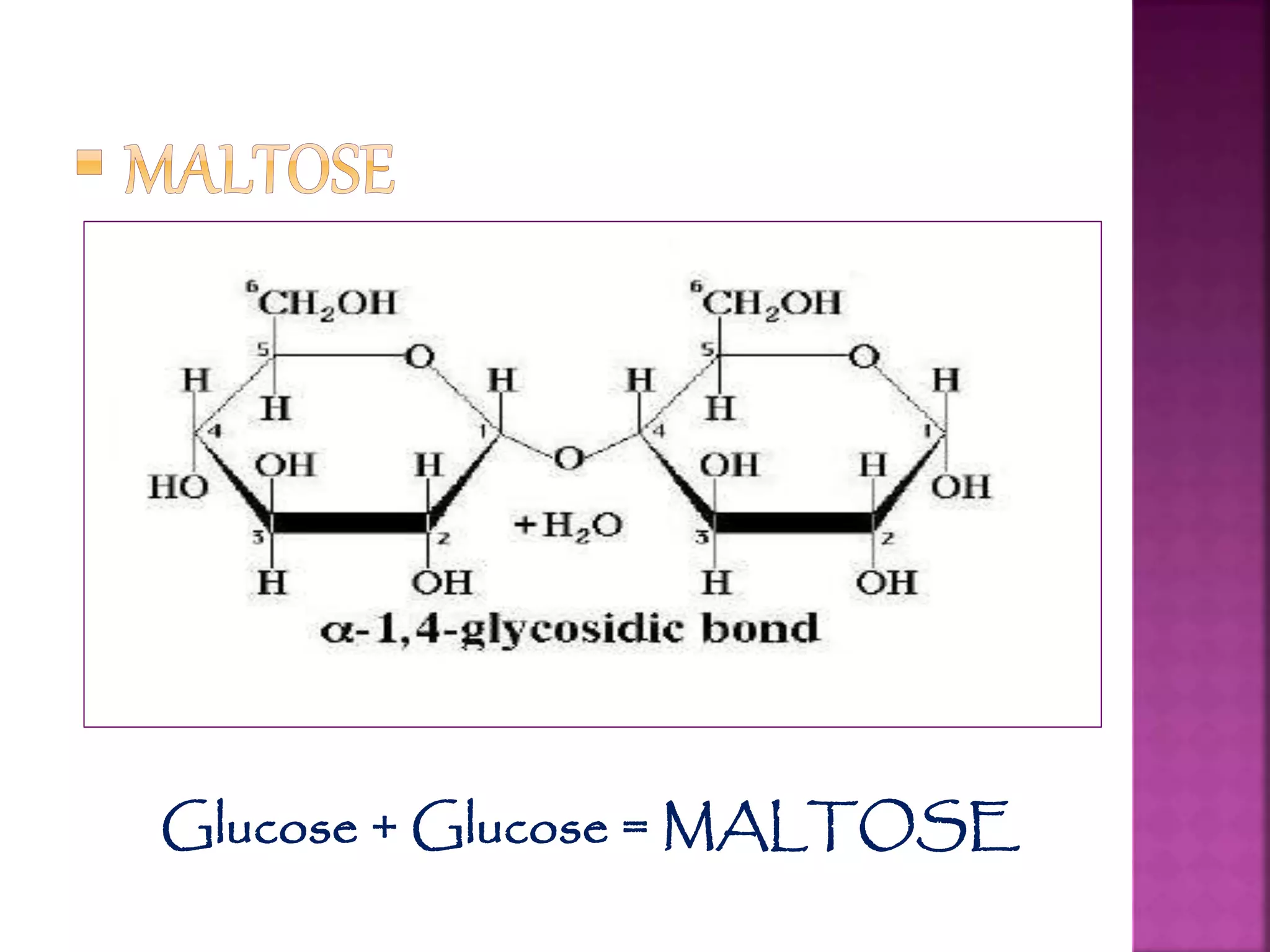
Carbohydrates are the most abundant compounds on earth and are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They exist as monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Glucose, fructose, and galactose are common monosaccharides that serve as energy sources. Disaccharides like sucrose, lactose, and maltose are formed by joining two monosaccharides. Polysaccharides including starch, glycogen, and cellulose consist of long chains of monosaccharides and serve structural and storage functions.