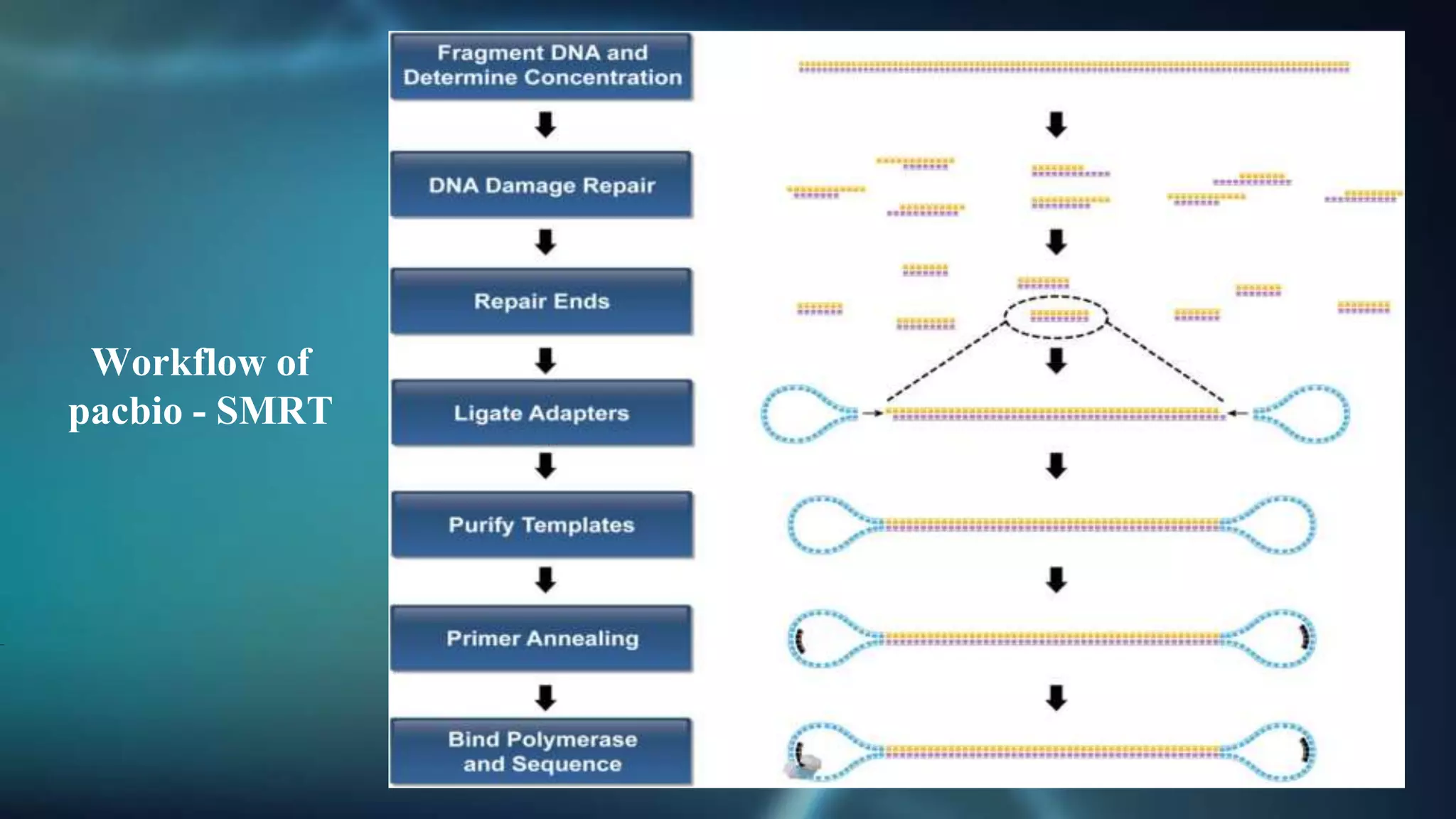
The document discusses third-generation sequencing technologies, including Ion Torrent, PacBio, and Oxford Nanopore, which enable direct sequencing of single DNA molecules without fragmentation or amplification. Advantages include longer read lengths, real-time sequencing capabilities, and improved detection of DNA modifications, while limitations consist of higher error rates and varying throughput efficiencies. Each method has specific applications in genomics and transcriptomics but faces challenges regarding sequencing accuracy and data output compared to second-generation techniques.