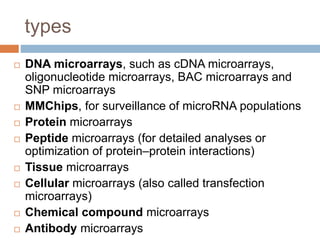
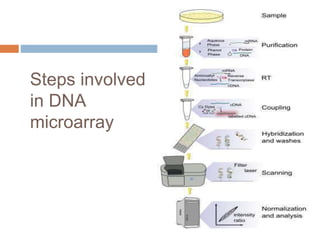
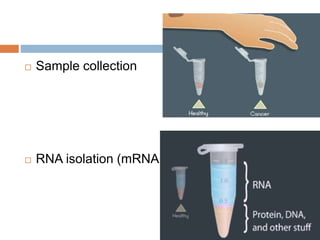
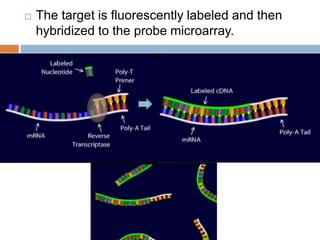
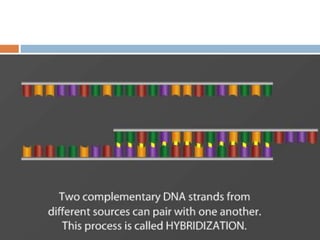
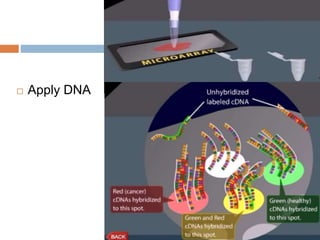
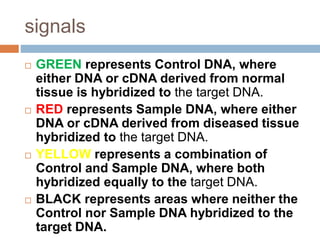
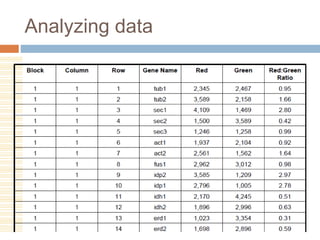
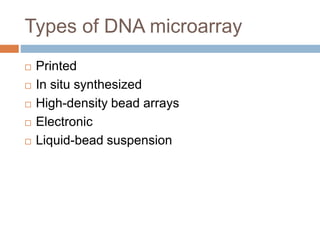
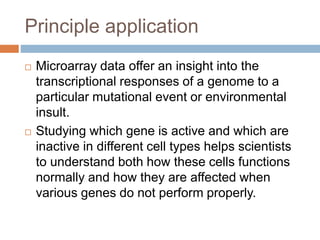
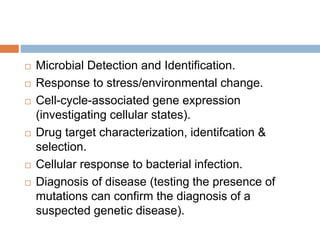
DNA microarrays are solid supports with organized grids of DNA probes that represent single genes. They use hybridization of fluorescent targets to probes to measure gene expression. Key steps involve sample collection, RNA isolation, fluorescent target labeling, hybridization to the array, washing, and scanning to analyze gene expression levels. Microarrays can be used for applications like gene expression profiling, disease diagnosis, and response to environmental changes. However, they have drawbacks like decreased specificity of probes and challenges with RNA quality and quantity from samples.