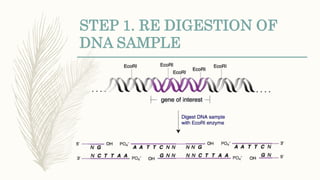
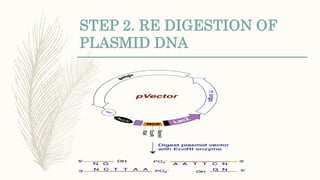
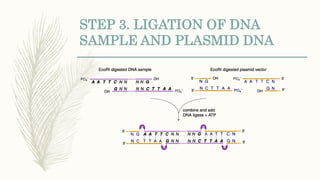
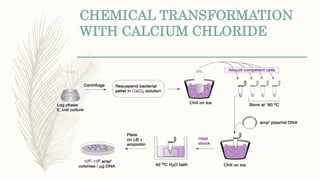
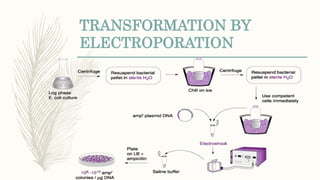
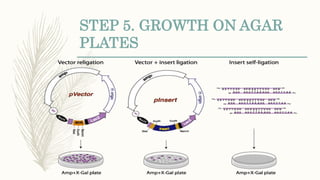
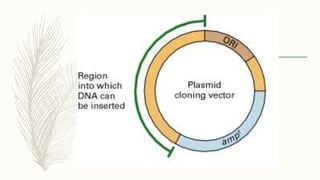
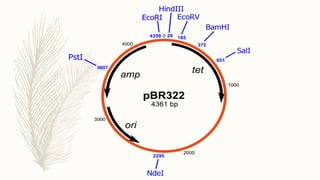
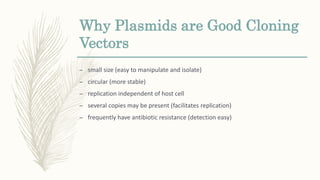
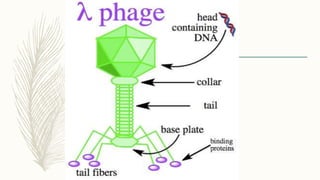
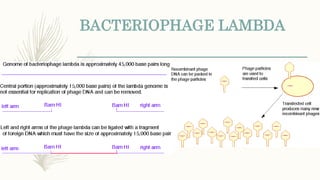
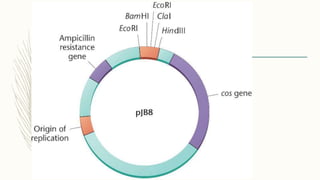
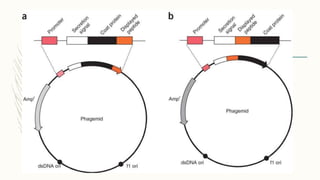
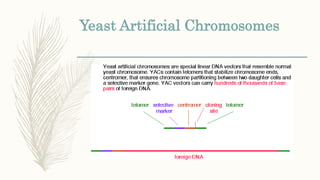
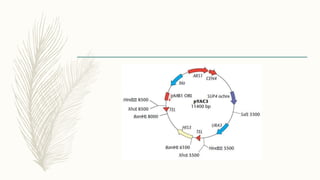
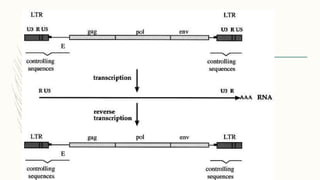
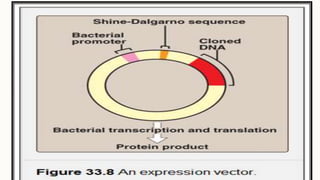
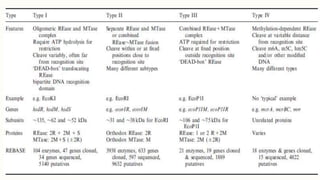
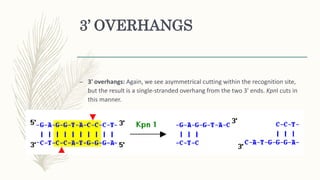
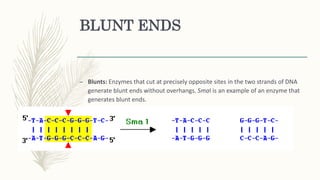
DNA cloning is a technique for reproducing DNA fragments through cell-based methods or polymerase chain reaction (PCR), requiring a vector to carry the DNA into host cells. The process includes cutting the gene of interest, ligating it into a plasmid, and transforming bacterial cells to amplify the DNA, which is selected using antibiotic resistance. Cloning vectors have specific properties to facilitate DNA transport and selection, with various types suited for different cloning experiments, including plasmids, cosmids, and retroviral vectors.