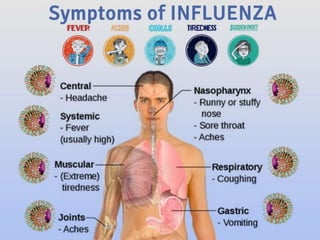
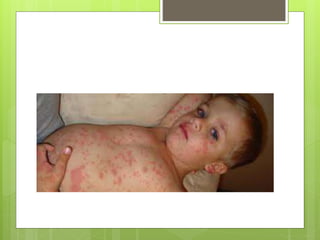
This document discusses communicable diseases, which are diseases that can be spread from one person to another. It provides examples of common communicable diseases like the flu, HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, measles, hepatitis, and polio. For each disease, it discusses how the disease is transmitted or spread from person to person, typical symptoms, those most at risk, methods of prevention, and other key details. Overall, the document aims to educate about common communicable diseases, how they are contracted and spread between individuals, and important prevention strategies.