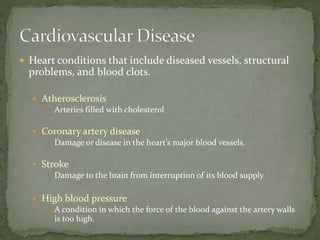
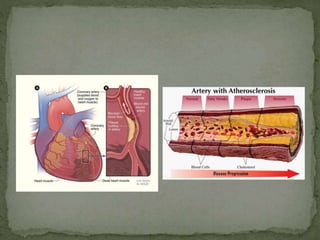
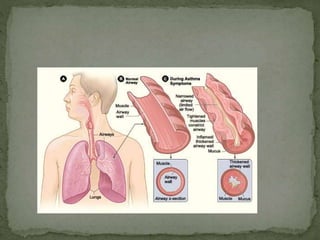
This document discusses non-communicable diseases (NCDs), also known as chronic diseases, which are long-lasting conditions that are not passed from person to person. The four main types of NCDs are cardiovascular diseases, cancers, chronic respiratory diseases, and diabetes. NCDs cause over 36 million deaths annually worldwide and share common risk factors like tobacco use, physical inactivity, unhealthy diets, and alcohol use. Preventing and managing NCDs involves lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol. Early detection of cancers through screening can also improve health outcomes.