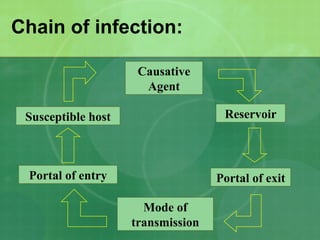
The document discusses diseases, their causes and types. It defines disease as an abnormal condition that impairs the body's normal functioning and can cause discomfort, dysfunction, distress and death. It categorizes diseases as communicable/contagious which can pass from person to person, and non-communicable which result from genetics or lifestyle. It also discusses the chain of infection and lists common communicable diseases like cold, influenza, pneumonia, chickenpox and measles.