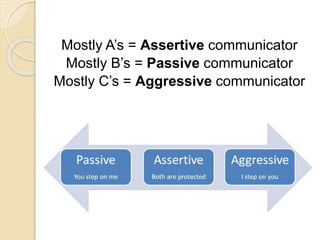
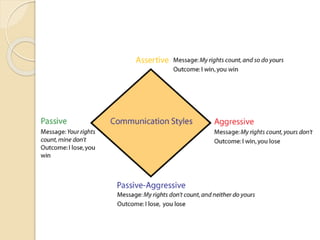
This document discusses communication skills, including different types of communication, listening skills, and nonverbal communication. It addresses passive, aggressive, assertive, and passive-aggressive styles of communication. It emphasizes the importance of assertive communication using "I-messages", active listening, and reflective listening. The document also discusses how most communication is nonverbal and covers body language and electronic communication.