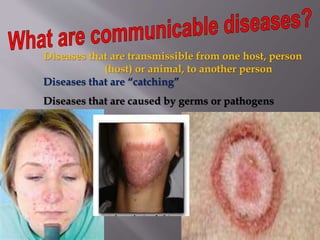
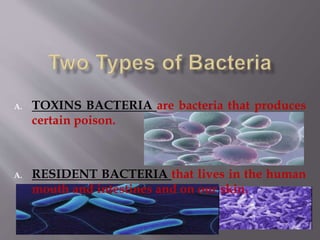
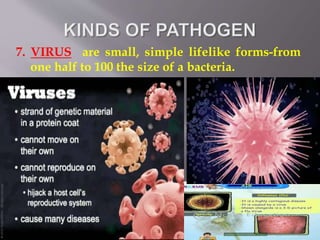
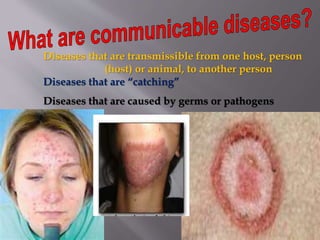
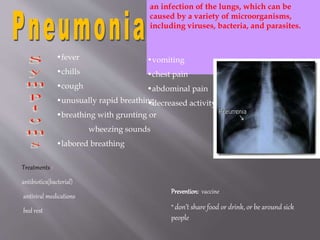
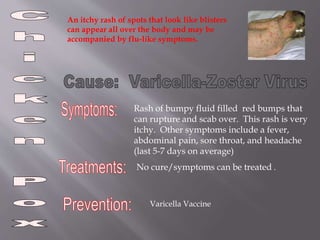
Diseases can be communicable or non-communicable. Communicable diseases spread between individuals through various means like direct contact, vectors/reservoirs, airborne transmission, contaminated food/water, or indirect contact. They are caused by pathogens like viruses, bacteria, parasites, protozoa, and fungi. Factors like environment, culture, and behavior affect disease transmission. Common communicable diseases include the cold, flu, hepatitis B, pneumonia, mononucleosis, chickenpox, and their symptoms, treatments, and means of prevention are discussed.