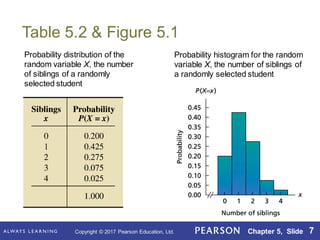
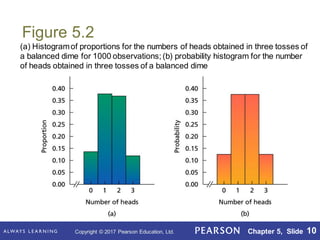
This document summarizes key concepts from Chapter 5 of a statistics textbook, including discrete random variables and their probability distributions. Section 5.1 defines discrete random variables as variables that can take on countable values and introduces probability distributions and histograms to show the probabilities of different outcomes. Section 5.2 provides examples of defining random variables and constructing probability distributions. Section 5.3 covers the binomial distribution for experiments with two possible outcomes. Section 5.4 introduces the Poisson distribution for modeling rare events.