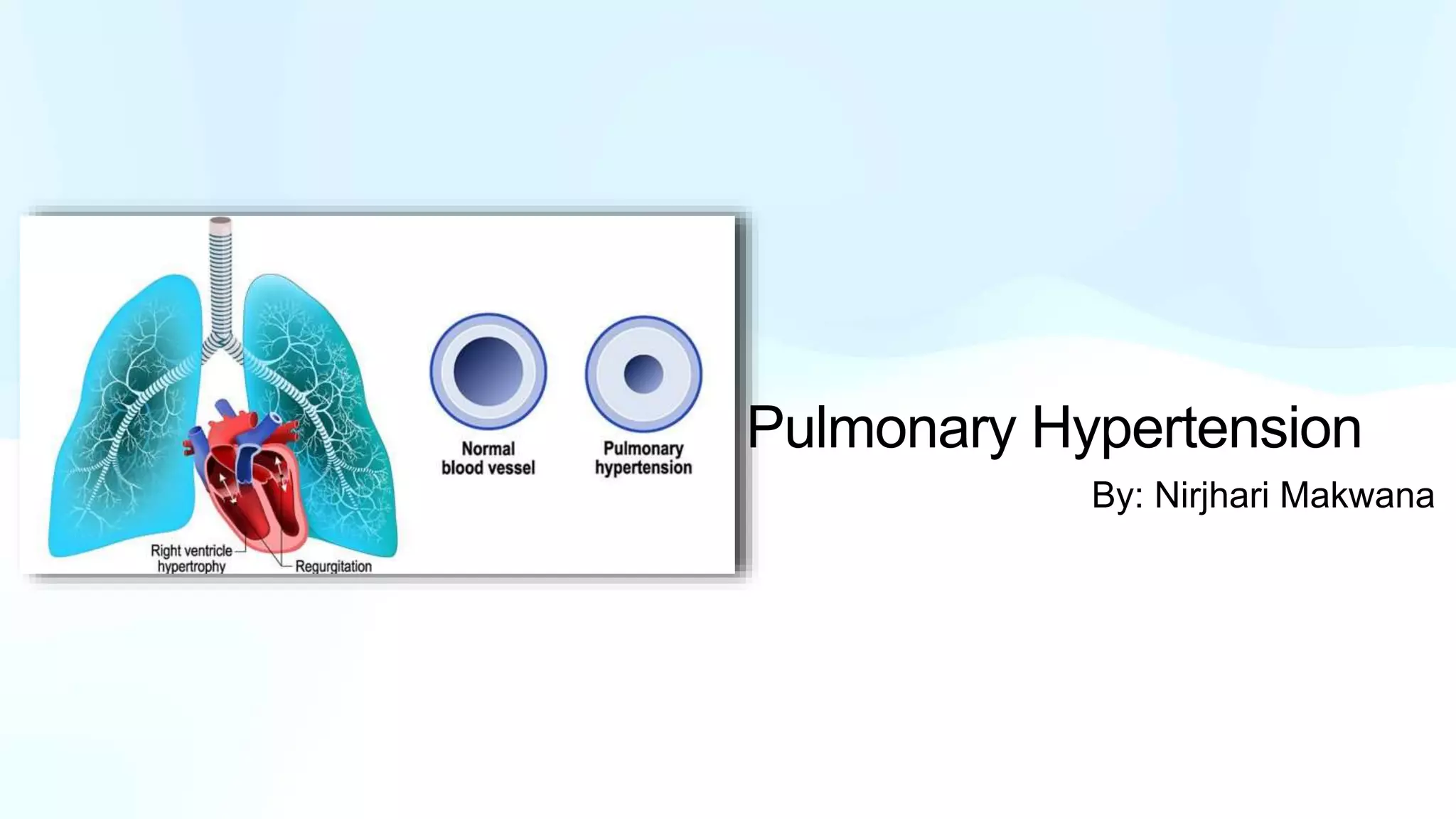
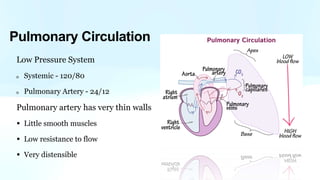
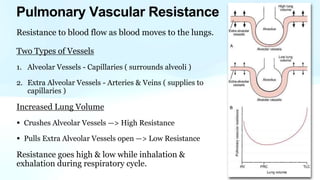
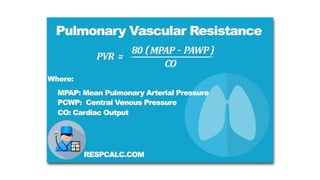
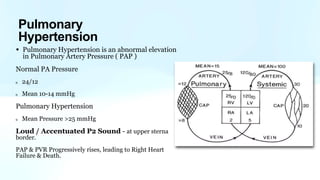
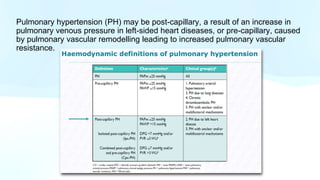
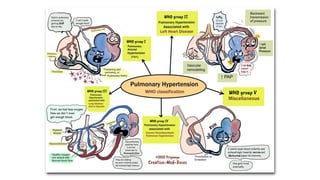
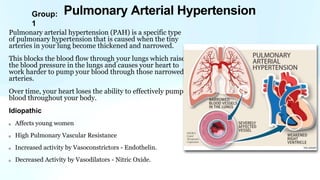
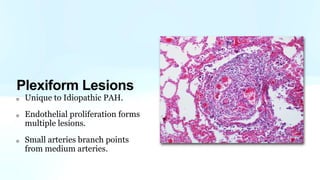
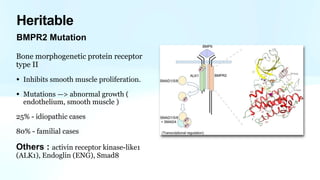
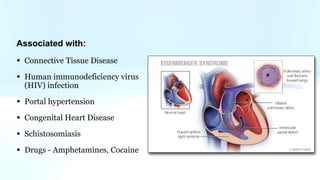
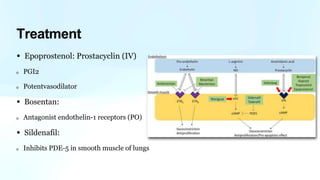
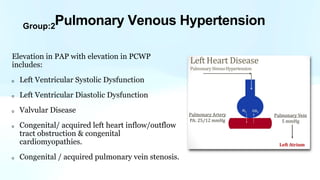
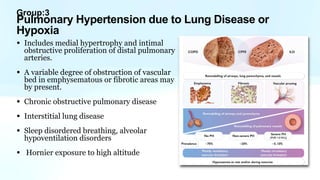
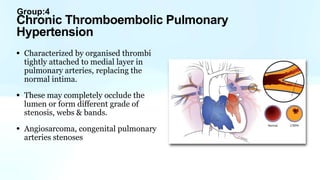
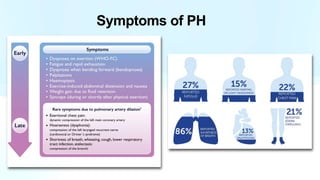
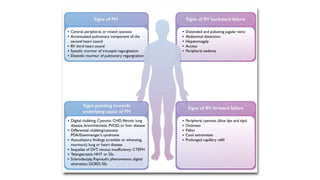
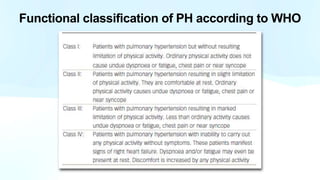
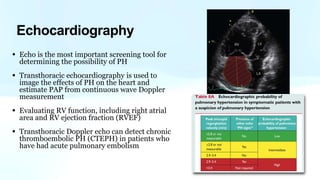
Pulmonary hypertension is abnormal elevation of pulmonary artery pressure that can be caused by several factors. It occurs when the arteries in the lungs become narrowed, blocking blood flow and overworking the heart. There are five groups of pulmonary hypertension distinguished by their causes, which include left heart disease, lung diseases that cause hypoxia, chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension, rare diseases with unclear causes, and pulmonary arterial hypertension. The latter involves thickening of pulmonary arteries and is the most severe form, sometimes caused by genetic mutations. Symptoms include shortness of breath and right heart failure over time if left untreated.