Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX





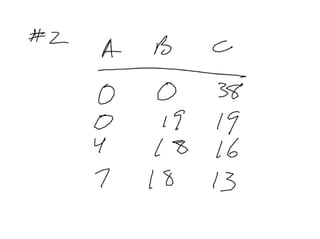








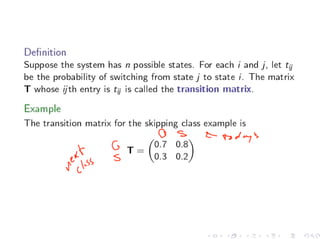
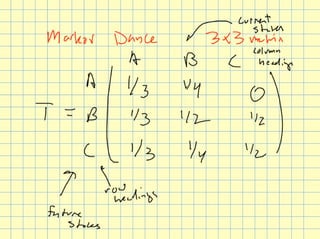

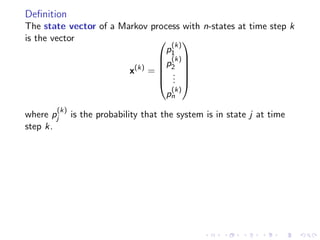
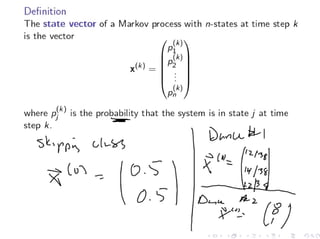
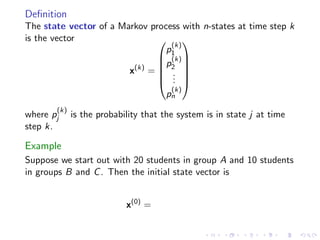
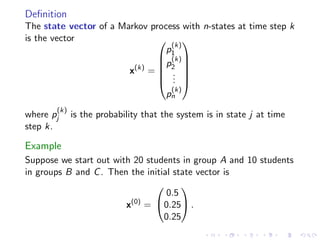







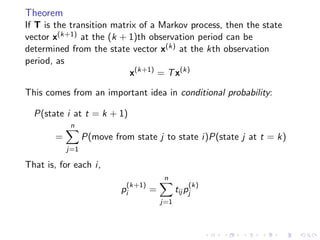
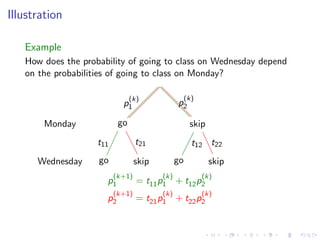













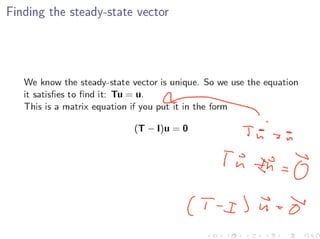

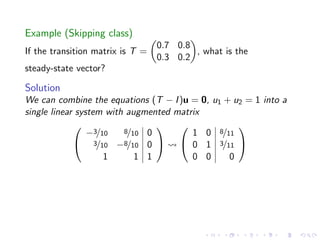
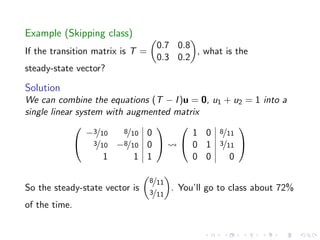

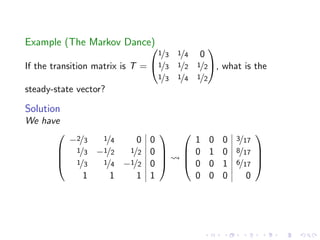

The document discusses Markov chains and their application to modeling transitions between states over time. It defines Markov chains as processes where the probability of the next state depends only on the current state. Transition matrices are used to represent the probabilities of moving between states. The powers of a transition matrix converge to a steady state as time increases, with all columns being identical, representing the long-term probabilities of being in each state. Finding the steady state vector involves solving the equation Tu=u. An example of modeling class attendance as a Markov chain is presented.

















































