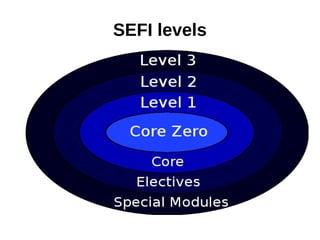
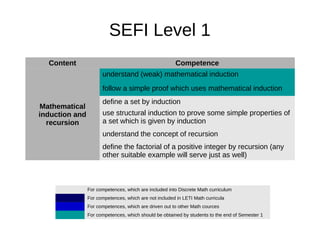
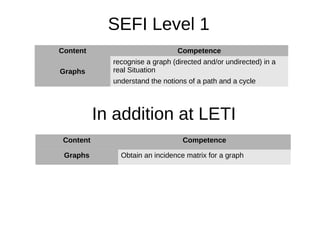
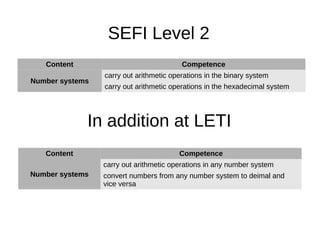
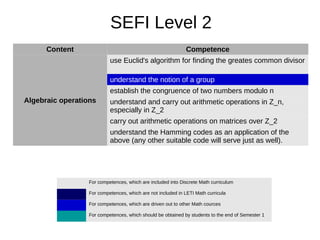
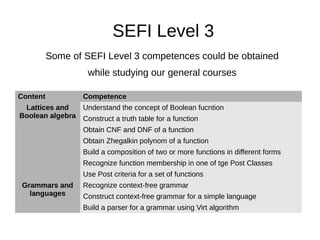
1. The document outlines discrete mathematics competencies covered at different levels in the undergraduate curriculum at Saint-Petersburg Electrotechnical University.
2. Many competencies are covered in the discrete mathematics course in the first year, while others are covered in courses like mathematical logic and algorithm theory in later years.
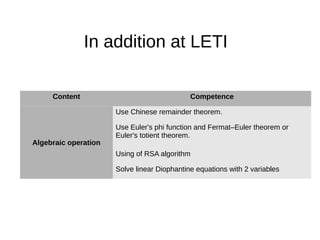
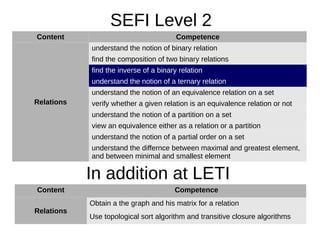
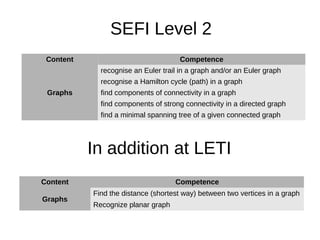
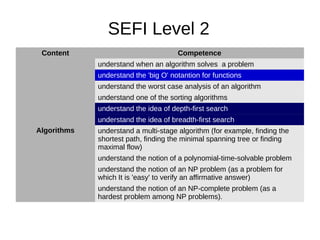
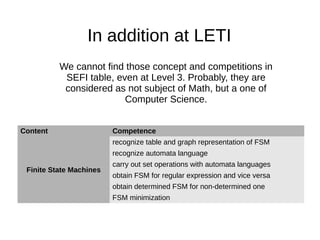
3. LETI aims to develop additional competencies beyond the SEFI levels, such as skills in mathematical logic, graphs, algorithms, and finite state machines.



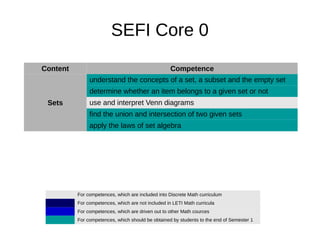
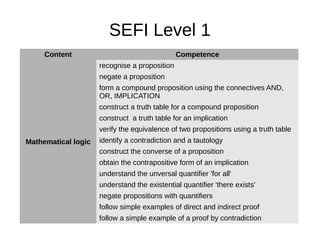

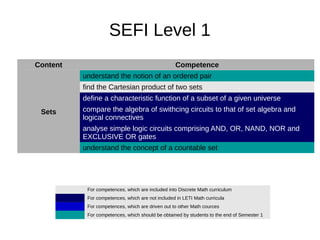




![Content Competence
Algebra of polynoms
carry out arithmetic operations with polynomials in Z[x], R[x]
and alos modulo n
factorize simple polynomials (including factirzation module n)
find GCD using Euclid algorithm for polynomials
find rational root of a integer polynomial
using Lagrange interpolation formula
In addition at LETI
This competences are necessary to students who will later work
with polynomial codes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dmleti-160609131400/85/Discrete-Mathematics-23-320.jpg)