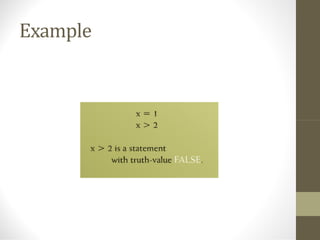
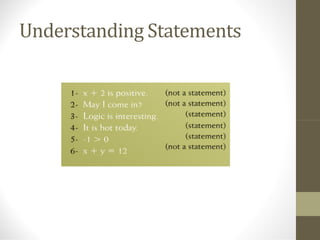
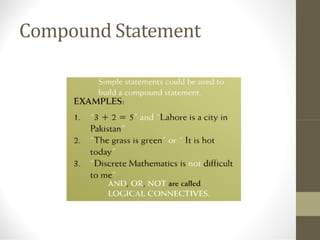
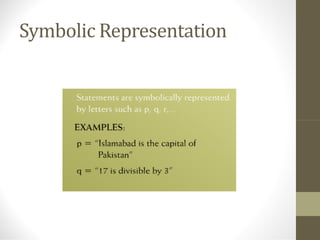
This document provides an overview of the topics covered in a discrete structures course, including logic, sets, relations, functions, sequences, recurrence relations, combinatorics, probability, and graphs. It defines discrete mathematics as the study of mathematical structures that have distinct, separated values rather than varying continuously. Some examples given are problems involving a fixed number of islands/bridges or connecting a set number of cities with telephone lines. Logic is introduced as the study of valid vs. invalid arguments, and basic logical concepts like statements, truth values, compound statements, logical connectives, negation, and truth tables are outlined.