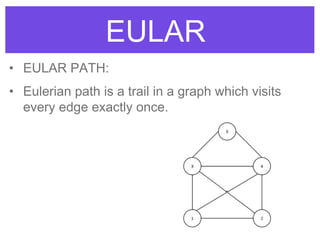
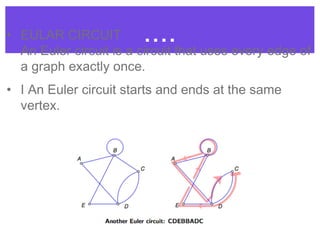
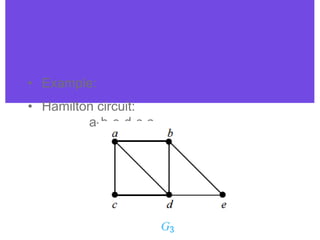
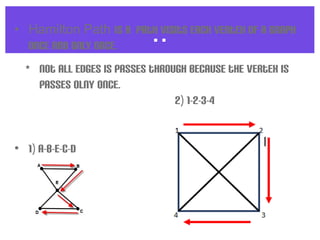
An Euler circuit is a trail that starts and ends at the same vertex and uses every edge in a graph exactly once. An Euler path starts and ends at different vertices and uses every edge once but may not visit every vertex. To determine if a graph contains an Euler circuit or path, one checks if every vertex has an even degree; if so, it contains an Euler circuit. For an Euler path, exactly two vertices may have an odd degree. Algorithms for finding these trails include picking a starting vertex and traversing edges, darkening used edges until all are traversed. A Hamilton circuit is similar but visits every vertex exactly once, returning to the starting point. A Hamilton path visits each vertex once without returning to the starting point