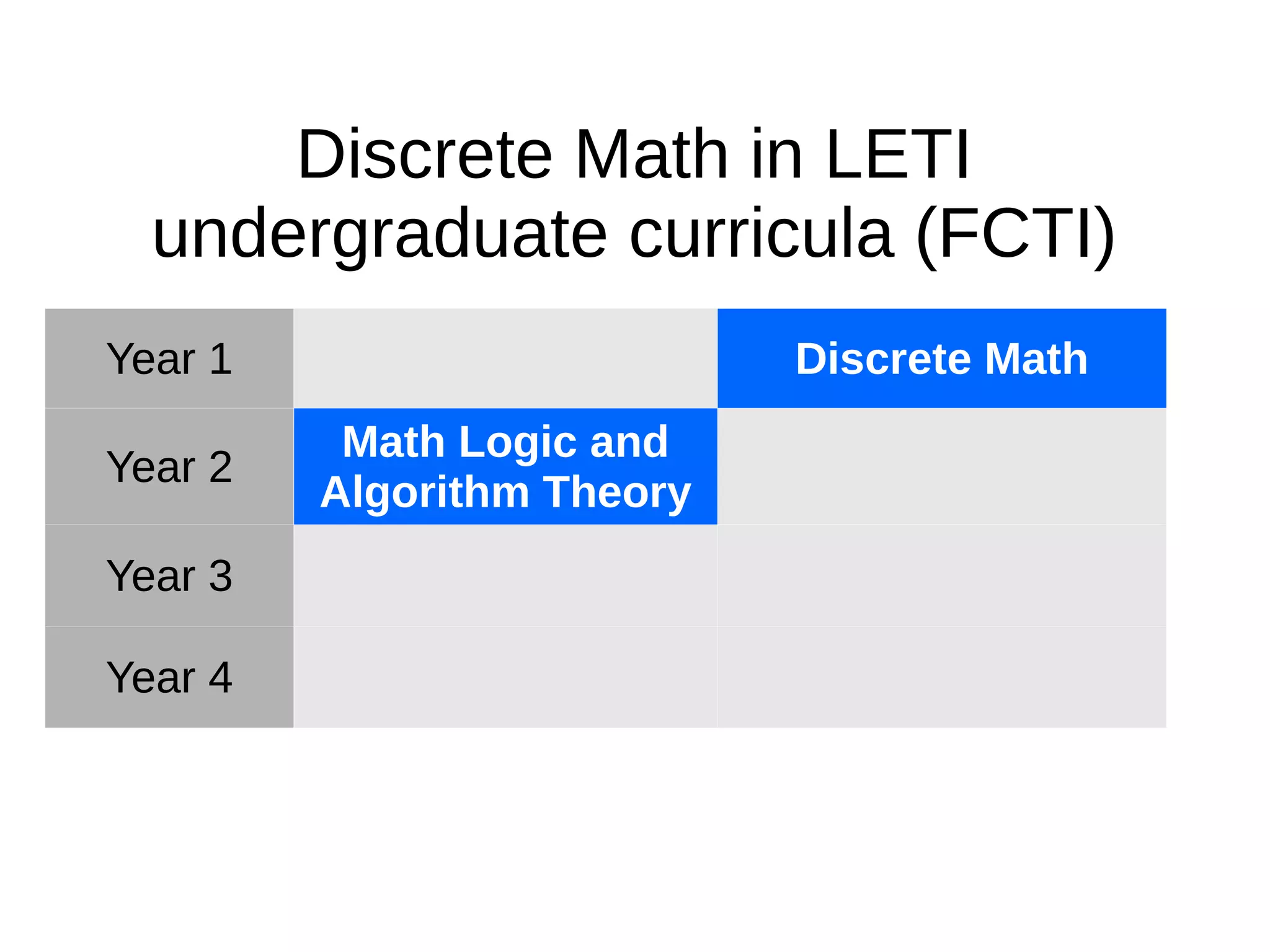
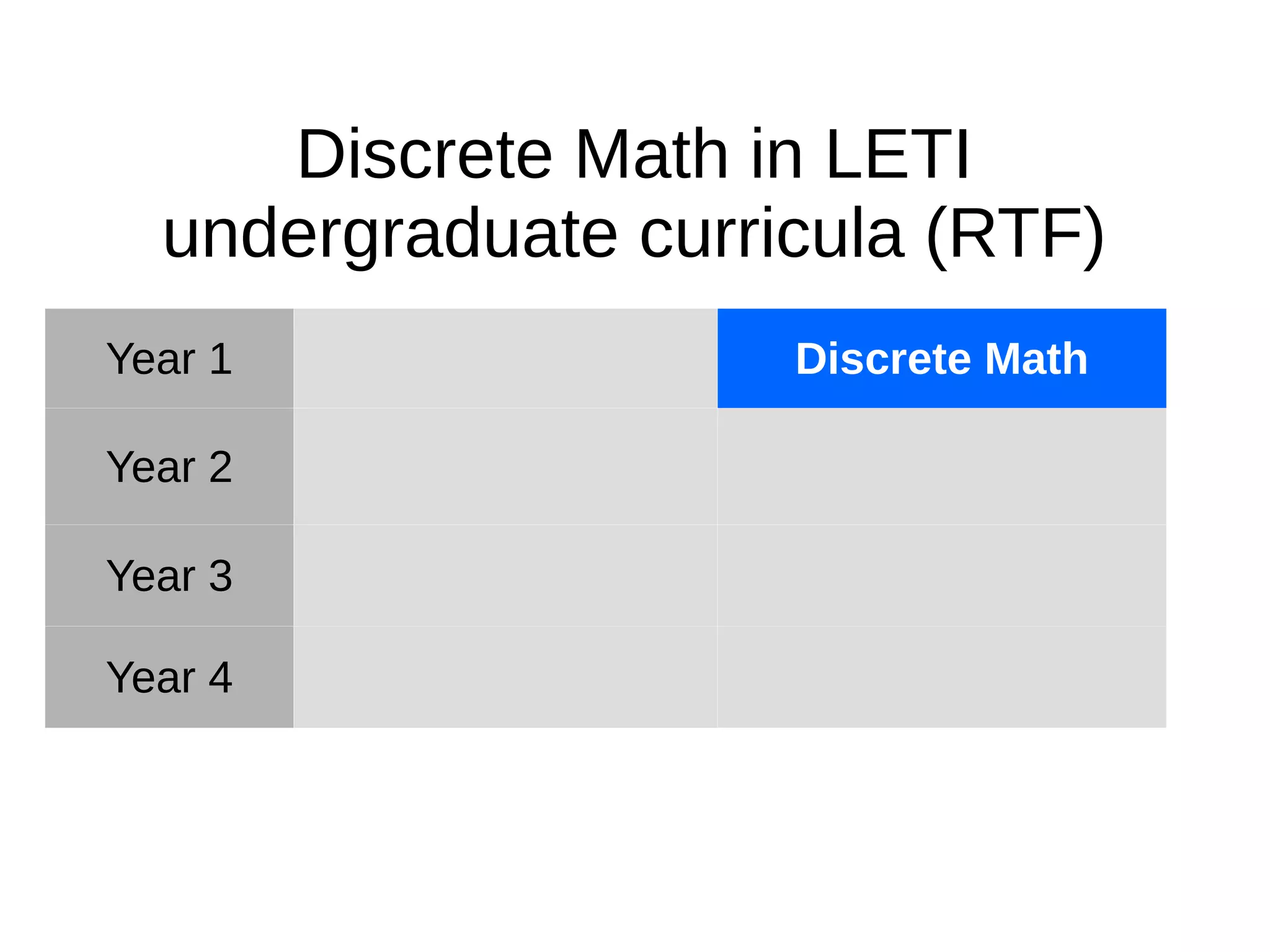
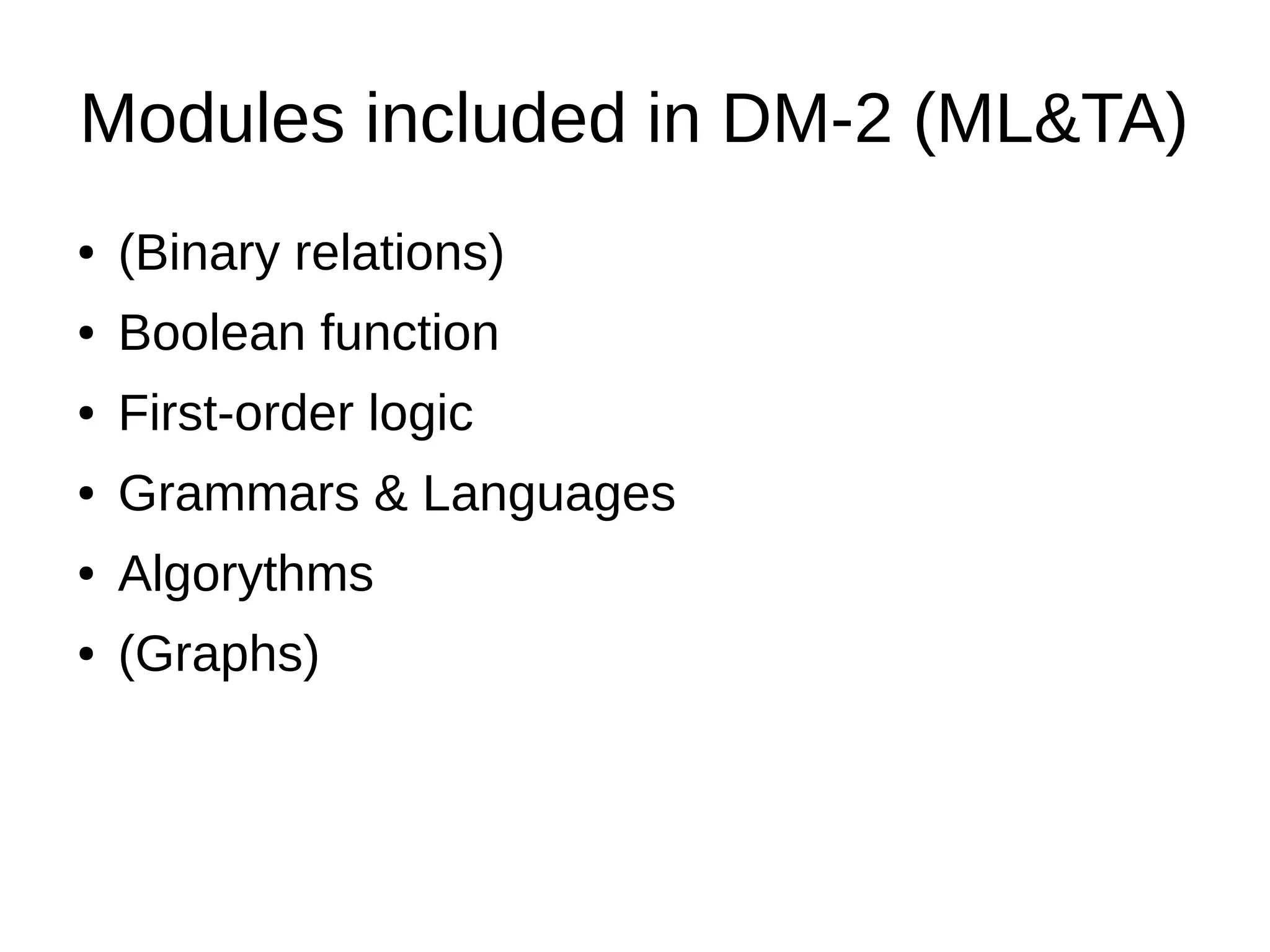
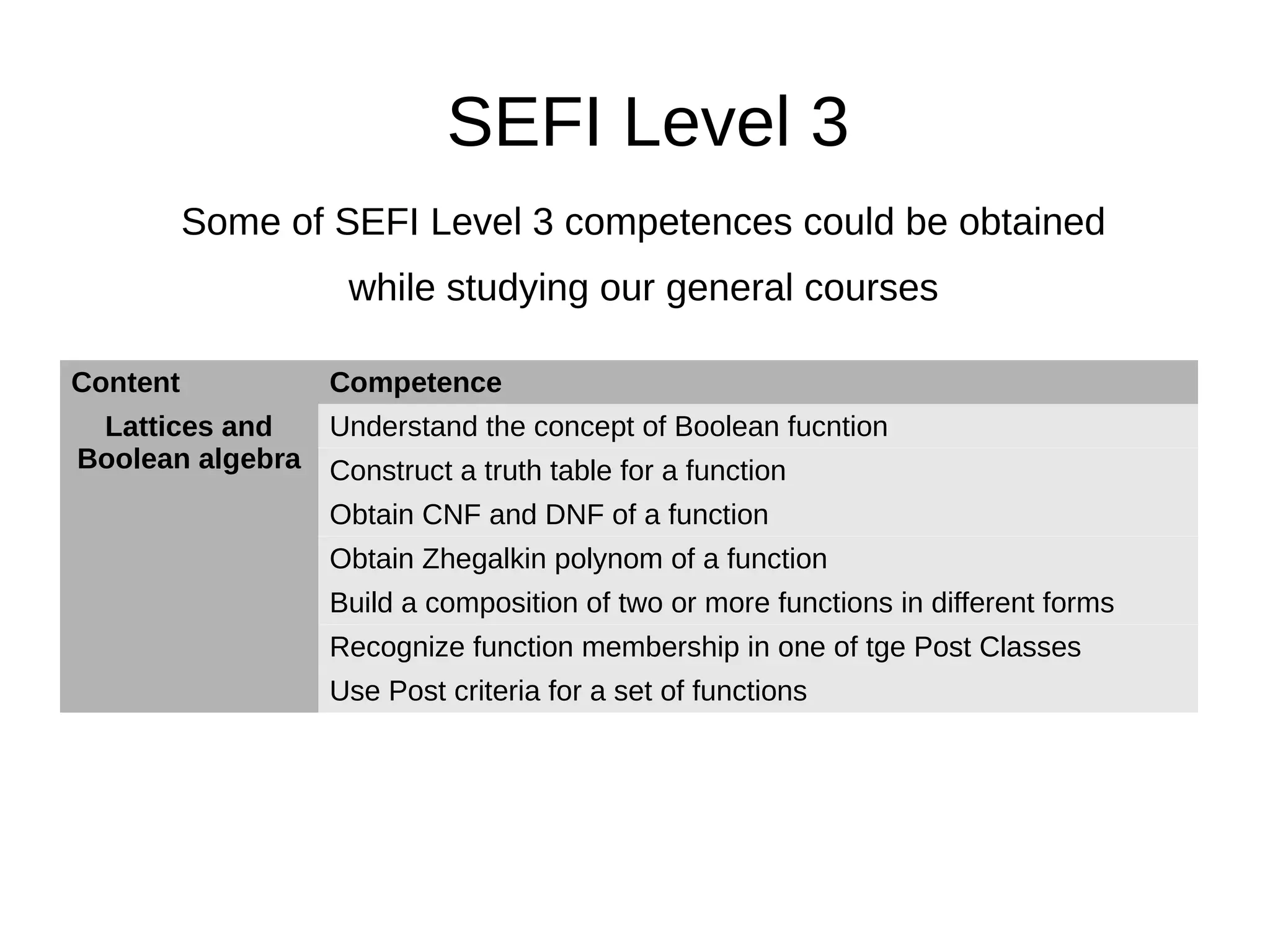
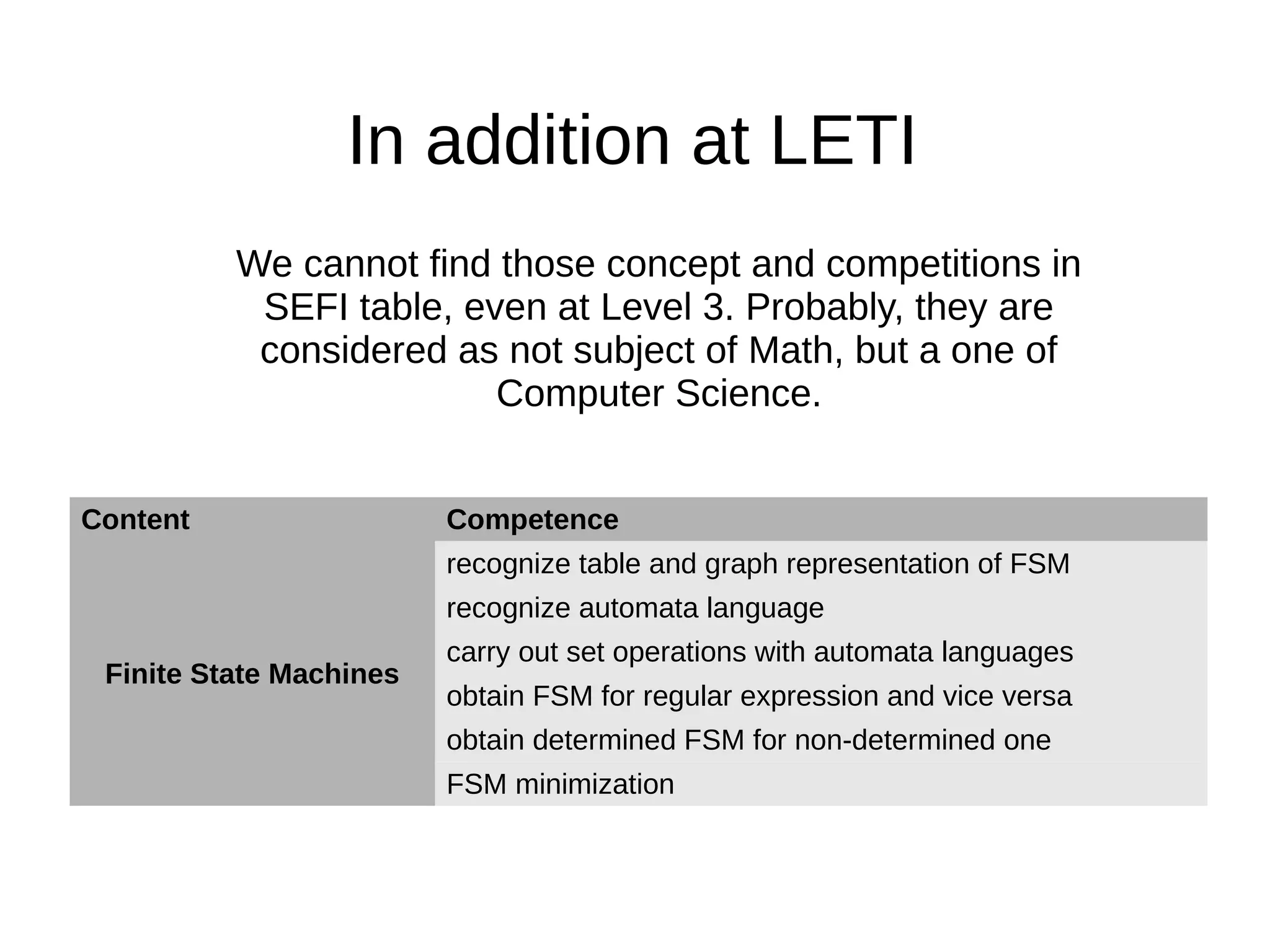
The document discusses the discrete mathematics curriculum at Saint-Petersburg Electrotechnical University. It provides an overview of which discrete math topics are covered in each year of study for different degree programs. It also compares course parameters like credits and hours between the university and TUT. Key modules covered in the second year Math Logic and Algorithm Theory course are outlined. Competencies addressed in the curriculum are mapped to SEFI levels, with additional competencies covered uniquely at the university. Suggested modifications to improve the curriculum structure are presented.