Embed presentation
Downloaded 63 times
![Diode – Basic
Applications
Yong Heui Cho @ Mokwon University
Some of slides are referred to:
[1] A. S. Sedra & K. C. Smith, Microelectronic Circuits.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-151016032015-lva1-app6892/75/Diode-Basic-Applications-1-2048.jpg)

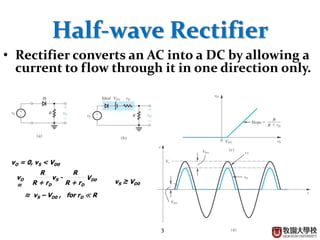
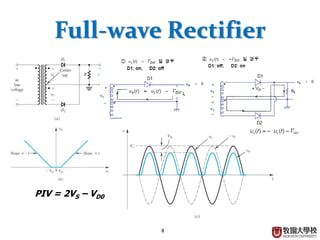
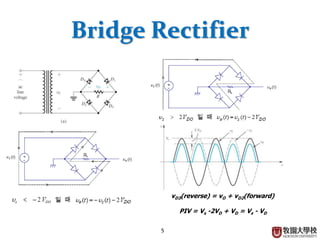
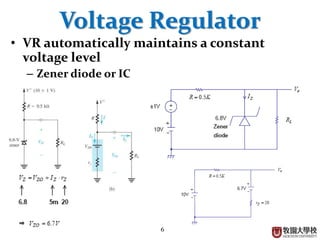
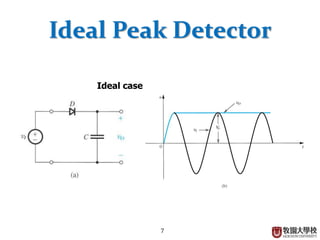
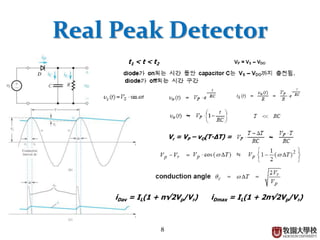
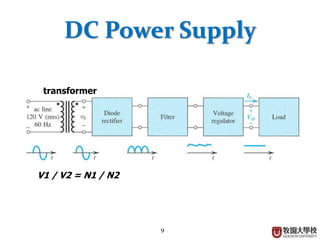
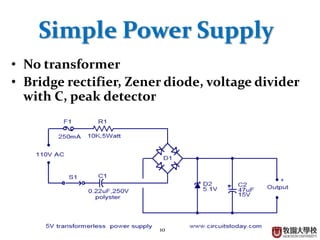
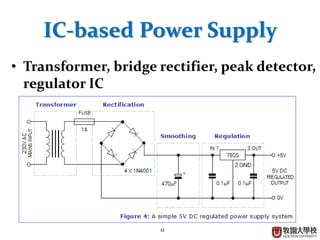

Diodes have several basic applications including half-wave rectification, full-wave rectification, and voltage regulation. A half-wave rectifier uses a diode to allow current to flow through it in only one direction, converting an alternating current into a pulsing direct current. A full-wave rectifier uses a bridge rectifier configuration to allow current to flow through on both halves of the alternating current cycle. Voltage regulators, which can use Zener diodes or integrated circuits, automatically maintain a constant voltage level.
![Diode – Basic
Applications
Yong Heui Cho @ Mokwon University
Some of slides are referred to:
[1] A. S. Sedra & K. C. Smith, Microelectronic Circuits.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-151016032015-lva1-app6892/75/Diode-Basic-Applications-1-2048.jpg)









