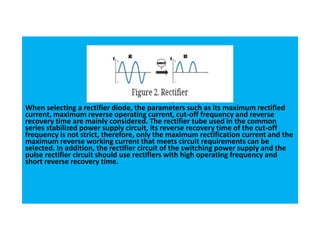
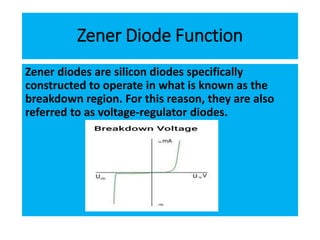
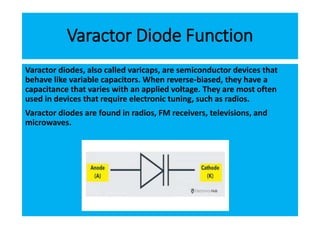
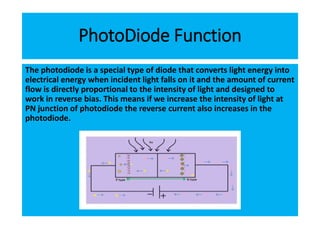
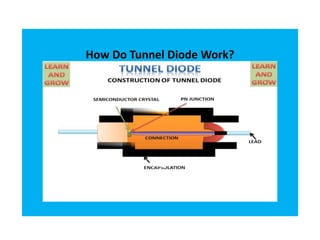
The document discusses different types of diodes and their functions and applications. It describes rectifier diodes, which can rectify AC power into DC power using their unidirectional conductivity. Zener diodes are constructed to operate in the breakdown region and are used as voltage regulators. Varactor diodes have a capacitance that varies with voltage and are used in devices requiring electronic tuning. Light emitting diodes emit light when forward biased and are used as indicator lights and in displays. Photodiodes convert light into electrical current and are used in light sensors.