Embed presentation
Downloaded 124 times
![BJT – Operational
Principle
Yong Heui Cho @ Mokwon University
Some of slides are referred to:
[1] A. S. Sedra & K. C. Smith, Microelectronic Circuits.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8-151026120133-lva1-app6891/75/BJT-Operational-Principle-1-2048.jpg)


![7
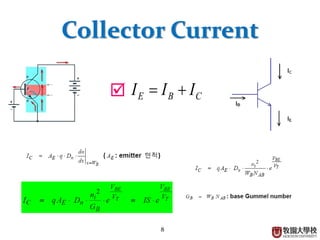
Base Current
For short emitter
LP
IB2 = Qn/τb
1
1 1
Qn = AE·q·1/2·np(0)·W = (AE·q·W·ni
2/2NA)evBE/VT
IB = IB1 + IB2 = IC/β
Dp
Dn
NA
ND
WB
Lp
W2
2Dnτb
β = +[ ]
-1
: common emitter current gain
CBE III ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8-151026120133-lva1-app6891/85/BJT-Operational-Principle-7-320.jpg)
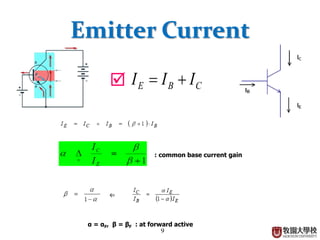

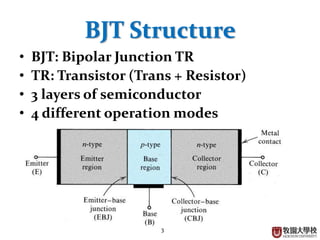
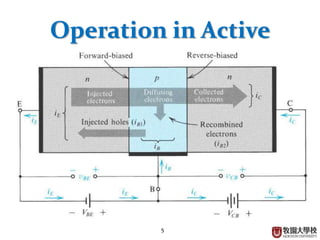
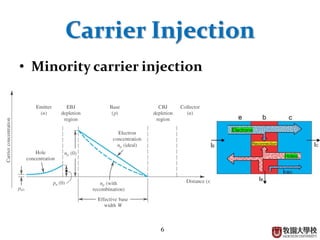
This document summarizes the operational principle of a bipolar junction transistor (BJT). It describes the basic BJT structure as having 3 layers of semiconductor material and lists the 4 main operation modes. It then explains active mode operation in more detail, discussing how minority carrier injection at the base leads to collector and emitter currents that are proportional to the base current, with current gain factors alpha and beta.
![BJT – Operational
Principle
Yong Heui Cho @ Mokwon University
Some of slides are referred to:
[1] A. S. Sedra & K. C. Smith, Microelectronic Circuits.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8-151026120133-lva1-app6891/75/BJT-Operational-Principle-1-2048.jpg)





![7
Base Current
For short emitter
LP
IB2 = Qn/τb
1
1 1
Qn = AE·q·1/2·np(0)·W = (AE·q·W·ni
2/2NA)evBE/VT
IB = IB1 + IB2 = IC/β
Dp
Dn
NA
ND
WB
Lp
W2
2Dnτb
β = +[ ]
-1
: common emitter current gain
CBE III ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8-151026120133-lva1-app6891/85/BJT-Operational-Principle-7-320.jpg)

