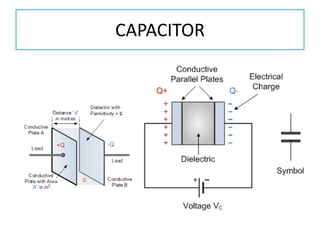
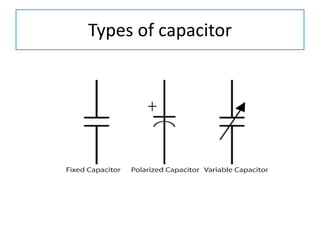
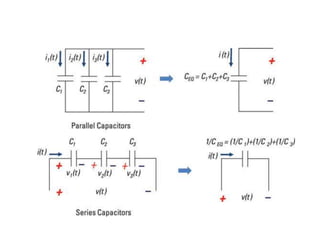
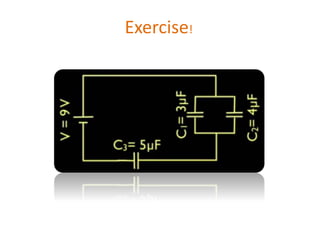
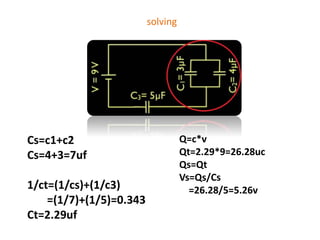
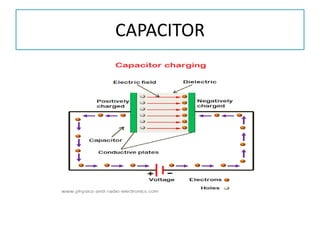
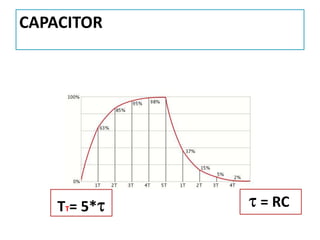
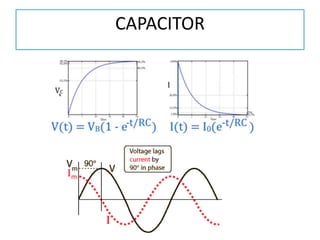
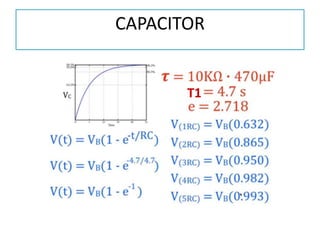
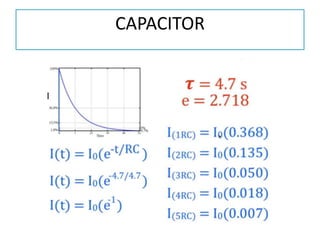
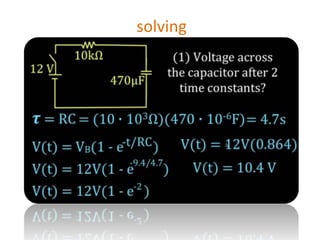
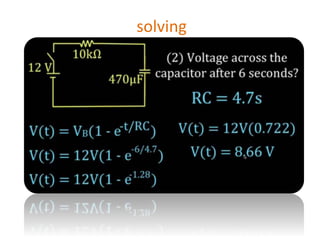
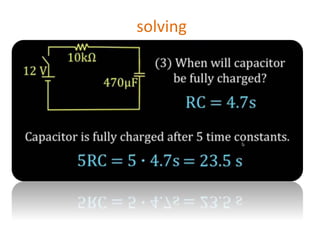
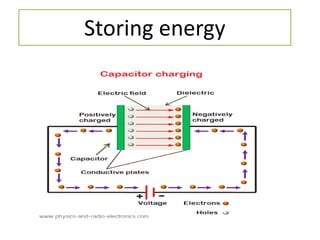
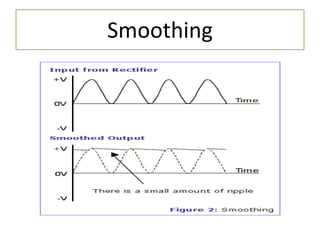
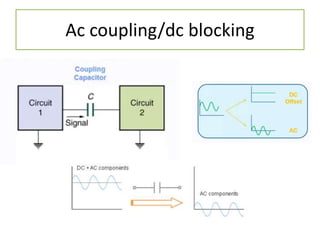
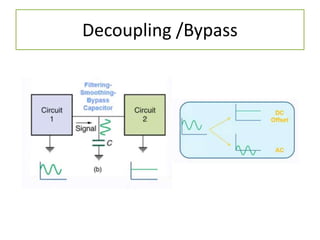
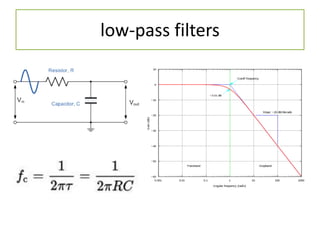
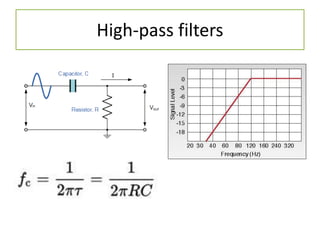
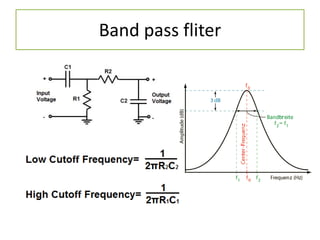
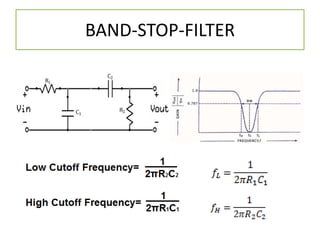
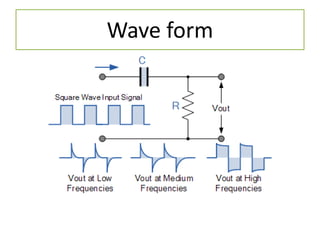
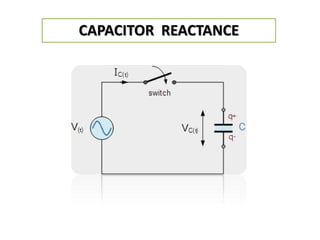
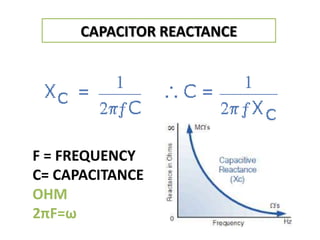
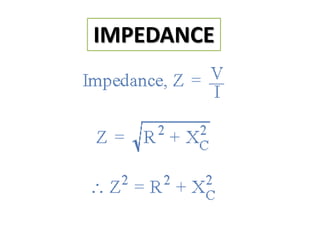
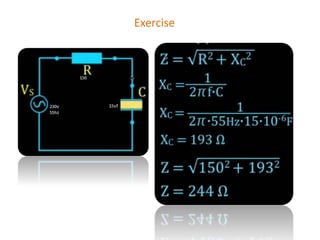
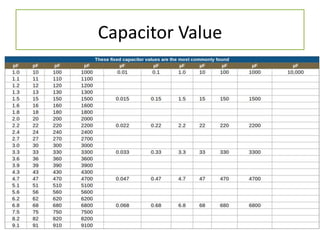
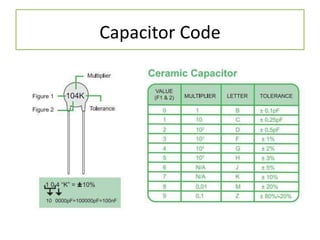
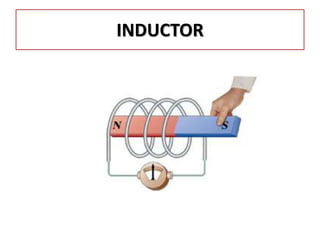
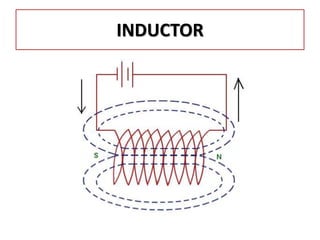
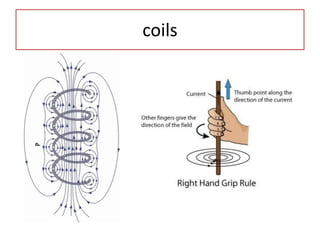
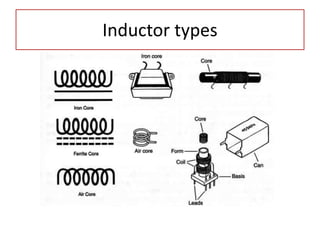
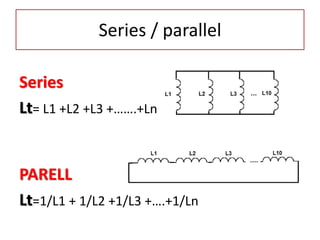
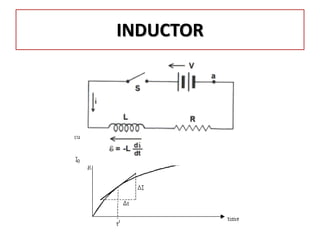
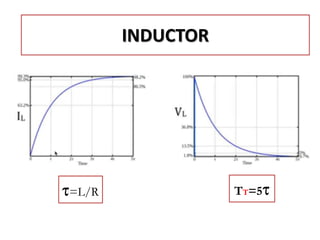
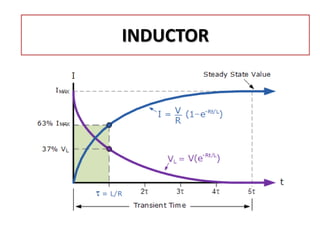
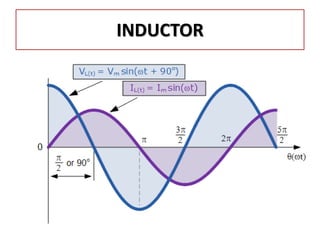
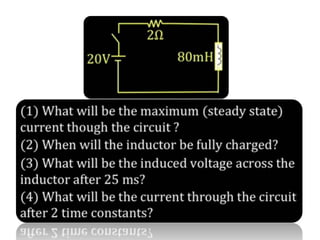
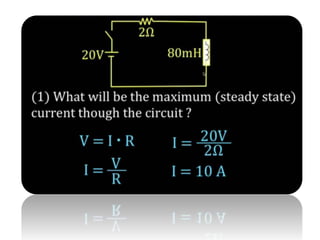
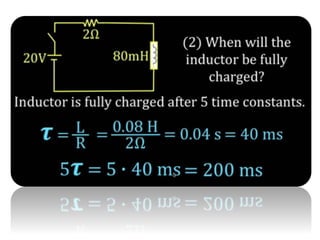
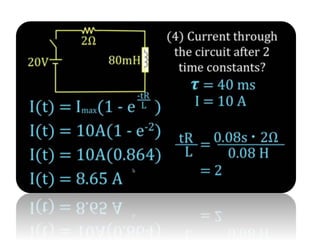
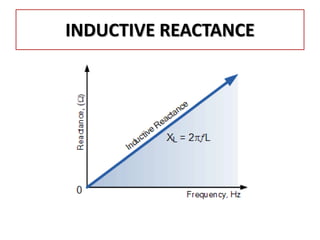
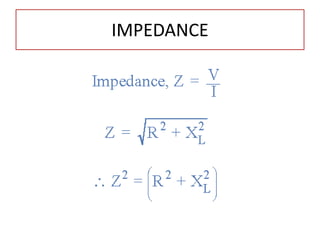
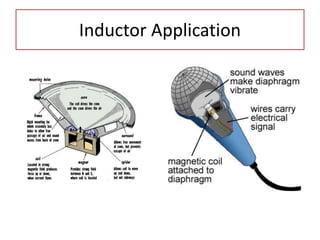
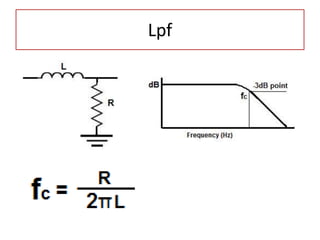
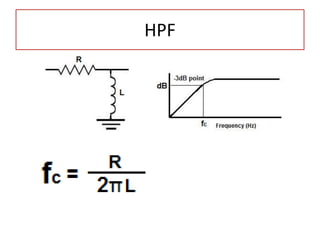
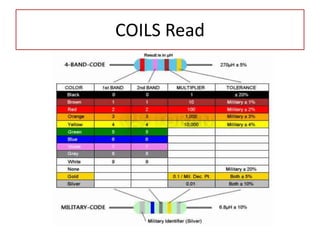
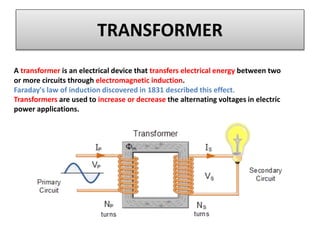
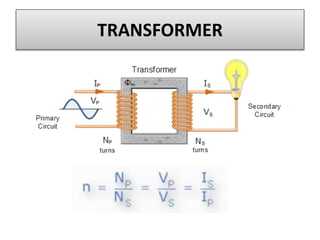
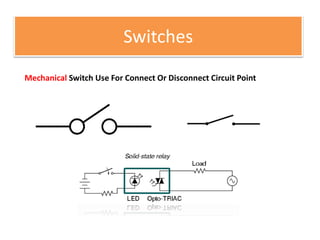
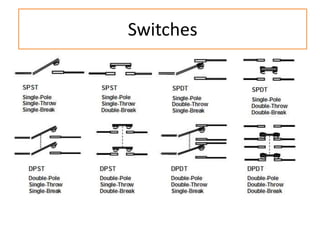
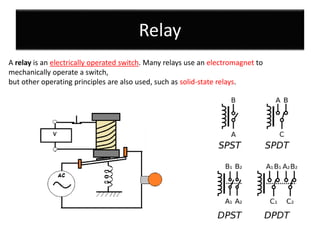
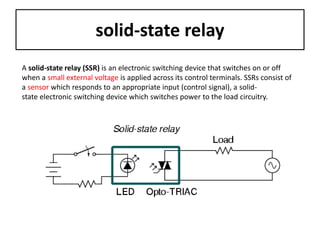
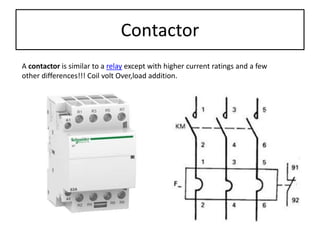
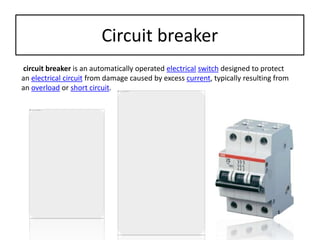
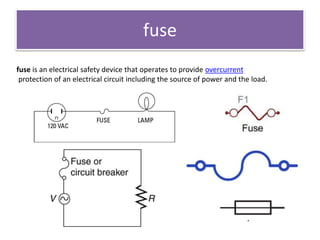
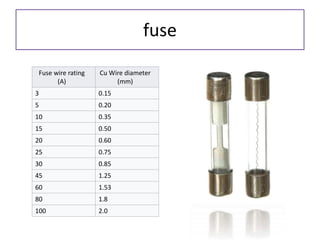
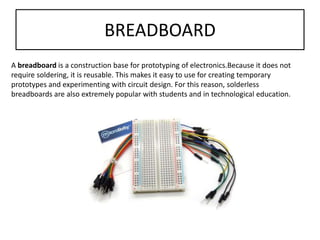
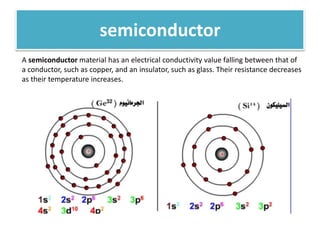
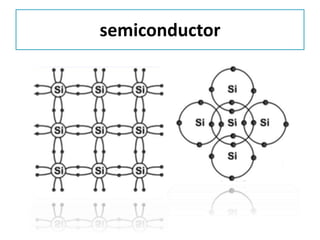
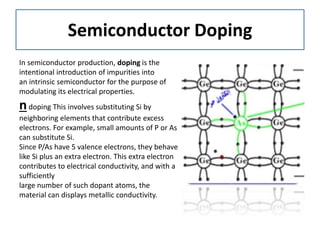
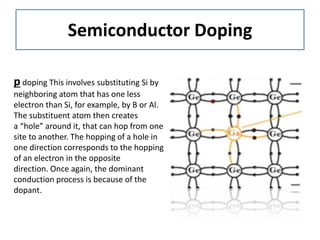
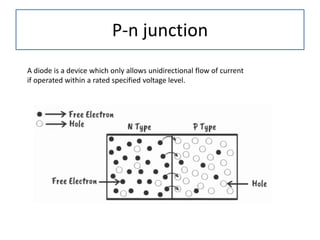
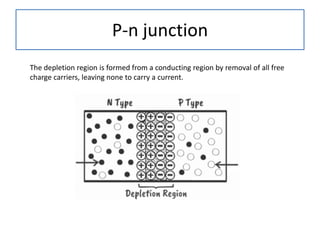
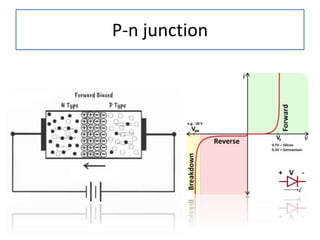
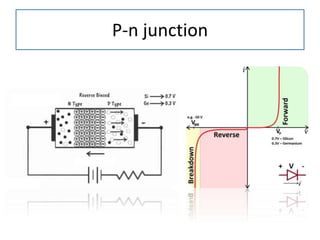
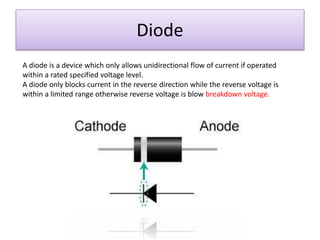
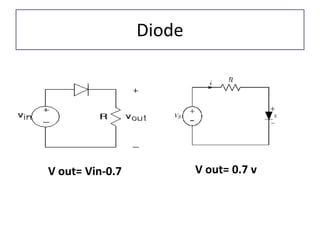
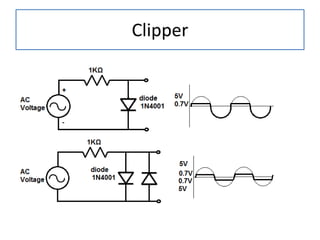
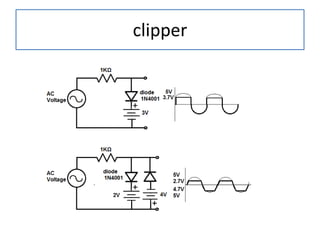
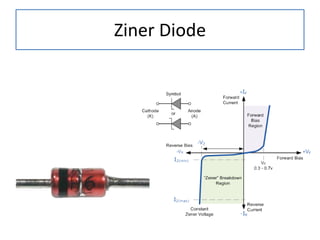
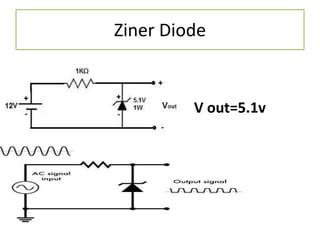
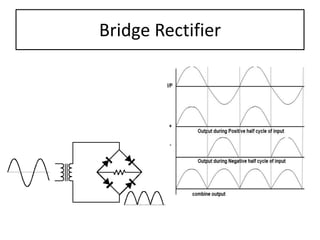
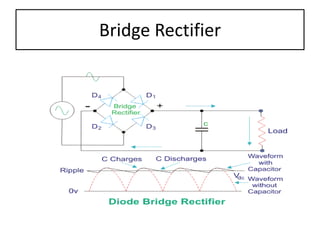
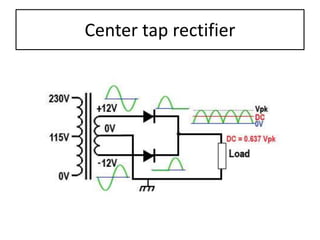
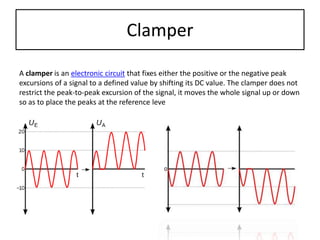
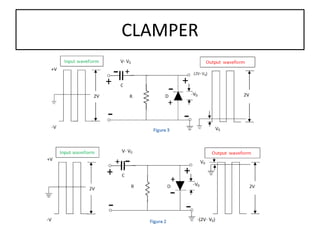
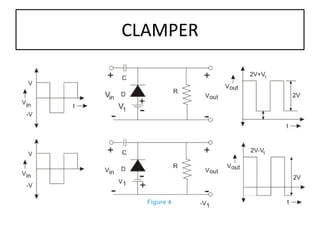
The document discusses different types of capacitors and their applications including energy storage, smoothing, filtering, and coupling. It also covers capacitor calculations, testing, and component identification. The document then discusses inductors and their applications in filtering and other circuits. It covers transformers, switches, relays, contactors, circuit breakers, fuses, breadboards, semiconductors, and PN junctions. Finally, it discusses different types of diodes and their applications in rectification and clipping circuits.